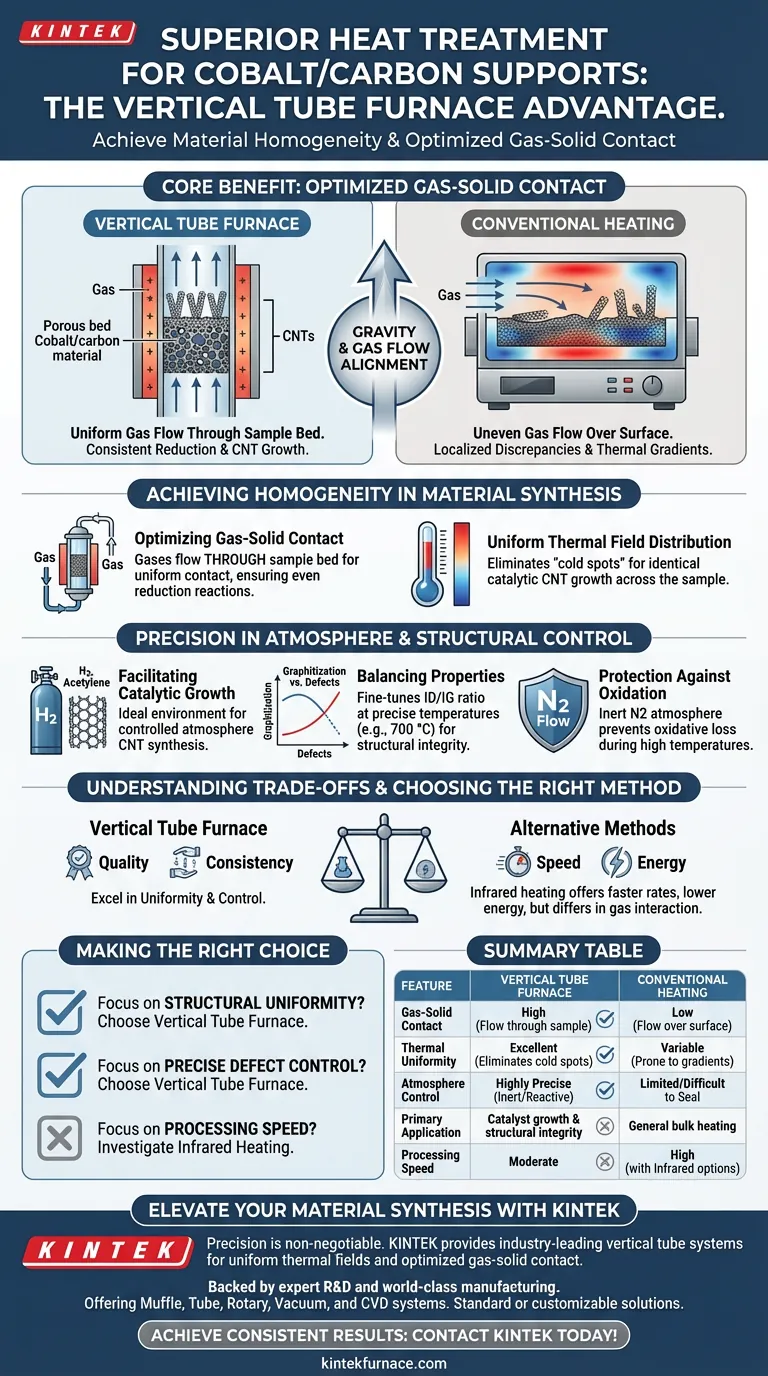
The primary benefit of using a vertical tube furnace for heat-treating cobalt/carbon supports is the achievement of superior material homogeneity through optimized gas-solid contact. Unlike conventional static heating, the vertical configuration ensures that reaction gases—such as hydrogen or acetylene—make uniform contact with the powder or thin film samples, resulting in consistent reduction reactions and uniform carbon nanotube growth across the entire heated zone.
Core Takeaway While conventional heating often struggles with uneven gas distribution and thermal gradients, vertical tube furnaces leverage gravity and gas flow alignment to create a highly uniform thermal and chemical environment. This ensures that the structural integrity and catalytic properties of the resulting carbon supports are consistent throughout the batch.

Achieving Homogeneity in Material Synthesis
Optimizing Gas-Solid Contact
The defining feature of this apparatus is the ability to position the reactor vertically.
In this configuration, reaction gases flow through the sample bed rather than merely passing over it. This facilitates uniform contact between the gas phase and the solid cobalt/carbon supports.
This is critical for ensuring that reduction reactions occur evenly, preventing localized discrepancies in the material.
Uniform Thermal Field Distribution
Vertical tube furnaces are engineered to provide a highly uniform thermal field.
This consistency eliminates "cold spots" that can occur in conventional ovens.
For cobalt/carbon supports, this thermal uniformity ensures that the catalytic growth of carbon nanotubes is identical throughout the sample, rather than varying based on the sample's position within the furnace.
Precision in Atmosphere and Structural Control
Facilitating Catalytic Growth
The vertical setup is particularly effective when working with controlled atmospheres required for carbon nanotube synthesis.
By allowing for the precise introduction of gases like hydrogen or acetylene, the furnace creates the ideal environment for the reduction of cobalt catalysts and the subsequent growth of carbon structures.
Balancing Graphitization and Defects
Beyond simple heating, these furnaces allow for the fine-tuning of material properties through precise temperature regulation.
For example, during pyrolysis at 700 °C, the precise thermal control helps balance graphitization levels against defect formation (the ID/IG ratio).
This ensures the resulting carbon nanotube layer maintains ideal hydrophobicity and structural integrity.
Protection Against Oxidation
The design allows for a strictly controlled inert atmosphere, typically using a nitrogen flow.
This creates a protective environment during high-temperature phases.
It effectively prevents the oxidative loss of carbon nanotubes, which is a common risk in less controlled heating environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Energy Consumption and Speed
While vertical tube furnaces excel in uniformity and control, they may not be the most energy-efficient option for all applications.
Alternative methods, such as laboratory infrared heating, utilize radiation heat transfer to achieve significantly faster heating rates (up to 60 °C/min) and lower energy consumption.
Throughput Limitations
The vertical configuration prioritizes quality and consistency over bulk throughput.
If the goal is rapid processing with extremely short exposure times (e.g., ~2 minutes as seen in infrared PET conversion), a vertical tube furnace may be slower compared to radiation-based methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct heating method for your cobalt/carbon supports, assess your specific priorities:
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Choose the vertical tube furnace to ensure consistent gas-solid contact and identical reaction kinetics across the entire sample.
- If your primary focus is precise defect control: Rely on the vertical tube furnace for its ability to fine-tune the ID/IG ratio and protect against oxidation via controlled atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is processing speed: Investigate infrared heating alternatives, which offer rapid heating rates and lower energy consumption but may differ in gas interaction mechanics.
Ultimately, the vertical tube furnace is the superior choice when the quality, consistency, and structural integrity of the carbon support are the non-negotiable metrics of success.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vertical Tube Furnace | Conventional Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Gas-Solid Contact | High (Flow through sample bed) | Low (Flow over sample surface) |
| Thermal Uniformity | Excellent (Eliminates cold spots) | Variable (Prone to thermal gradients) |
| Atmosphere Control | Highly Precise (Inert/Reactive) | Limited/Difficult to Seal |
| Primary Application | Catalyst growth & structural integrity | General bulk heating |
| Processing Speed | Moderate | High (with Infrared options) |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing cobalt/carbon supports and carbon nanotubes. KINTEK provides industry-leading vertical tube systems engineered to deliver the uniform thermal fields and optimized gas-solid contact your research demands.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you need standard laboratory setups or fully customizable high-temperature furnaces for unique applications, our technical team is ready to support your goals.
Achieve consistent results and superior structural integrity—Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Nicolas Moreau, J.B. Nagy. Physical Methods for the Preparation of Cobalt Nanoparticles for Use in the Synthesis of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. DOI: 10.3390/inorganics13010007
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vertical tube furnace play in oily iron scale simulation? Master Blast Furnace Component Distribution
- What role does a high-purity quartz tube furnace play in graphene growth? Achieve Conformal Optical Resonator Coating
- What is the future potential of fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces? Unlock Efficiency and Growth in Your Industry
- What heat treatment processes can be performed using tubular furnaces? Unlock Precision for Materials Science
- What materials are required for high-temperature operation in tube furnaces? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of pre-treating sapphire substrates in a tube furnace? Optimize Your Epitaxial Growth Foundation
- What specific experimental conditions does a Tube Furnace provide for studying the oxidation of tungsten? 800°C Static Air
- What is the significance of the 700°C tube furnace treatment for T-Nb2O5/RMF? Unlock Peak Pseudocapacitive Performance



















