Tubular furnaces are exceptionally versatile, capable of performing a wide range of thermal processes essential for materials science and industrial manufacturing. These furnaces can execute critical heat treatments such as annealing, hardening, quenching, tempering, and sintering. Their unique design also enables specialized applications including material purification, coating, drying, and accelerated aging tests.
The true value of a tubular furnace lies in its ability to create a highly controlled and isolated environment. Its sealed tube design allows for precise management of both temperature and atmosphere (including vacuum or inert gas), making it the ideal instrument for processes that are sensitive to thermal uniformity and oxidation.
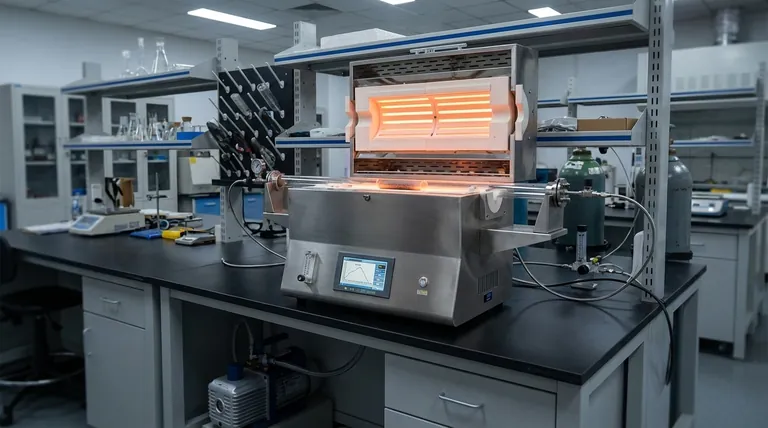

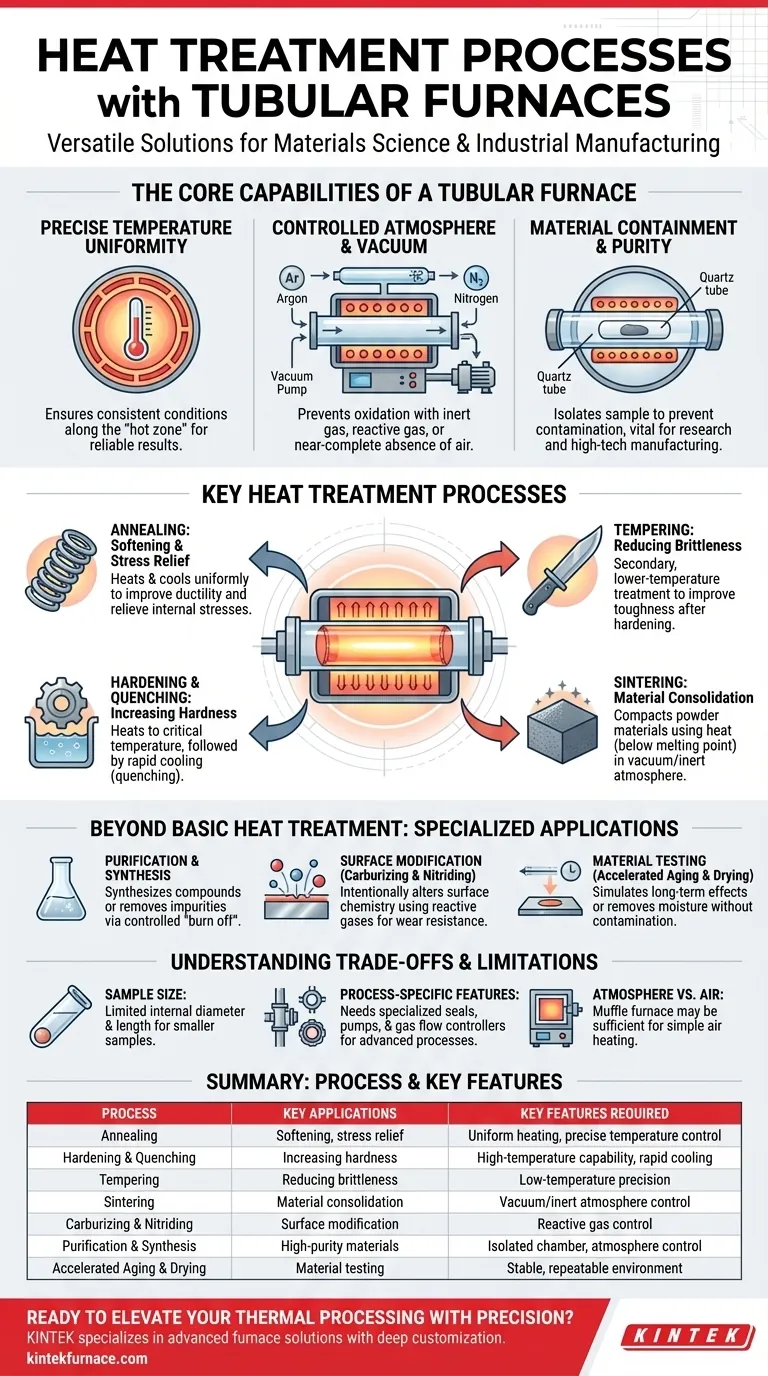
The Core Capabilities of a Tubular Furnace
The effectiveness of a tubular furnace for various heat treatments stems from three fundamental design features. Understanding these features is key to leveraging its full potential.
Precise Temperature Uniformity
A tubular furnace uses heating elements that encircle a cylindrical chamber. This geometry promotes exceptionally uniform heat distribution along the length of the "hot zone," ensuring the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions.
This uniformity is critical for processes where even minor temperature deviations can negatively impact material properties.
Controlled Atmosphere and Vacuum
The most significant advantage of a tube furnace is its ability to contain a specific atmosphere. The sample is placed inside a sealed tube, which can then be purged of air and filled with an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) or a reactive gas.
This capability is essential for preventing oxidation of sensitive materials. Furthermore, many models can be connected to vacuum pumps to perform processes that require a near-complete absence of air.
Material Containment and Purity
By processing materials inside a dedicated tube (often made of quartz, alumina, or ceramic), you isolate the sample from the furnace's heating elements and insulation. This prevents contamination and ensures the purity of the final product, which is vital for research and high-tech manufacturing.
Key Heat Treatment Processes Explained
These core capabilities directly enable a variety of common and specialized heat treatment processes.
Softening and Stress Relief (Annealing)
Annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature and holding it there before a controlled cooling process. This softens the material, improves its ductility, and relieves internal stresses. The uniform heating of a tube furnace ensures consistent results across the entire workpiece.
Increasing Hardness (Hardening & Quenching)
Hardening is achieved by heating a metal (like steel) above a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly, a process known as quenching. A tube furnace provides the precise initial heating phase. Some specialized models are designed to allow for rapid removal or have integrated cooling systems to facilitate the quench.
Reducing Brittleness (Tempering)
After a metal is hardened, it is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment that reduces this brittleness and improves toughness. The precise temperature control of a tube furnace is crucial for achieving the desired balance of hardness and toughness.
Material Consolidation (Sintering)
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from a powder by applying heat below its melting point. It is widely used in ceramics and powder metallurgy. Performing this in a tube furnace with a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere prevents oxidation, resulting in high-density components with minimal porosity.
Beyond Basic Heat Treatment: Specialized Applications
The controlled environment of a tube furnace opens the door to many other advanced thermal processes.
Purification and Synthesis
The furnace's isolated chamber is ideal for synthesizing chemical compounds or purifying materials. Unwanted elements can be "burned off" or evaporated in a controlled manner, leaving behind a higher-purity substance.
Surface Modification (Carburizing & Nitriding)
By introducing reactive gases into the tube, you can intentionally alter the surface chemistry of a material. Processes like carburizing (adding carbon) and nitriding (adding nitrogen) are used to create a hard, wear-resistant surface layer on metal parts, and they demand the precise gas control a tube furnace provides.
Material Testing (Accelerated Aging & Drying)
The stable, repeatable environment in a tube furnace is perfect for simulating the effects of long-term heat exposure on a material, a process known as accelerated aging. It is also an effective tool for precisely drying samples by removing all moisture without introducing contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, tubular furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is critical for proper application.
Sample Size and Geometry
The most obvious limitation is the internal diameter and length of the tube. These furnaces are best suited for smaller samples, powders, wafers, or thin cylindrical parts. They are not practical for heat treating large or irregularly shaped components.
Process-Specific Features
Not all tubular furnaces are created equal. A furnace capable of simple annealing in air may lack the seals and ports required for vacuum or reactive gas processes. Quenching, vacuum brazing, and carburizing all require specific furnace models and ancillary equipment like pumps and gas flow controllers.
Atmosphere vs. Air Furnaces
If your process does not require atmosphere control (e.g., simple drying or heating of non-reactive materials), a standard muffle or box furnace may be a more cost-effective choice. The primary reason to choose a tubular furnace is for its superior atmospheric control.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
To select the right process, consider your primary objective and your furnace's specific features.
- If your primary focus is improving bulk material properties (e.g., ductility or hardness): Focus on annealing, hardening, and tempering, ensuring your furnace has the required temperature range and cooling capabilities.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity components or new materials: Sintering, synthesis, and vacuum processing are key, but they absolutely require a furnace with excellent atmosphere or vacuum control.
- If your primary focus is surface modification: You need a furnace specifically equipped for reactive gas processes like carburizing or nitriding, with precise gas flow controllers.
- If your primary focus is simple thermal testing or drying: A basic tube furnace without advanced atmosphere control may be sufficient and more economical.
Understanding these distinct capabilities allows you to transform a tubular furnace from a simple heater into a precision instrument for advanced material processing.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Applications | Key Features Required |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Softening, stress relief | Uniform heating, precise temperature control |
| Hardening & Quenching | Increasing hardness | High-temperature capability, rapid cooling |
| Tempering | Reducing brittleness | Low-temperature precision |
| Sintering | Material consolidation | Vacuum/inert atmosphere control |
| Carburizing & Nitriding | Surface modification | Reactive gas control |
| Purification & Synthesis | High-purity materials | Isolated chamber, atmosphere control |
| Accelerated Aging & Drying | Material testing | Stable, repeatable environment |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—whether for annealing, sintering, or specialized applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















