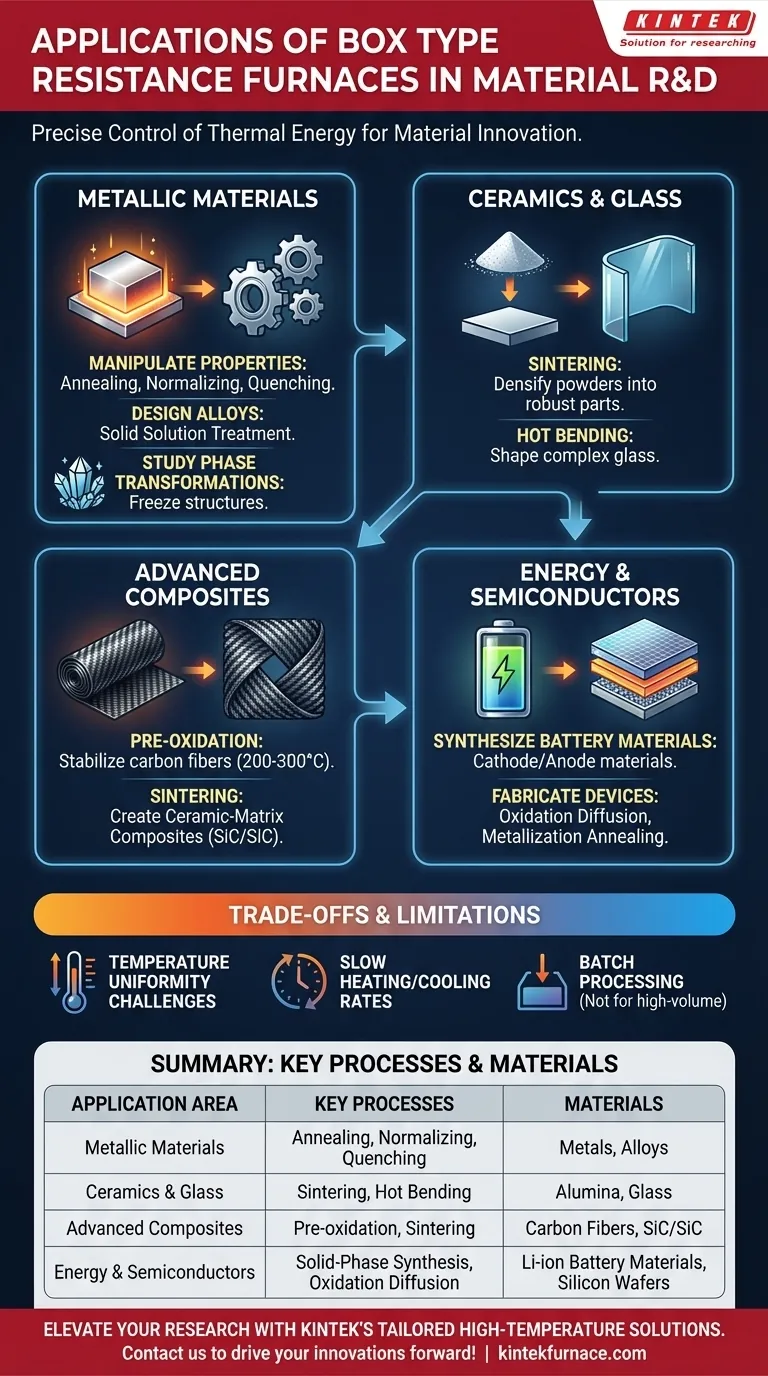
In material research and development, box type resistance furnaces are indispensable tools used for a wide range of thermal processes. Their primary applications include the precise heat treatment of metals to alter their mechanical properties, the sintering and shaping of ceramics and glasses, the synthesis of advanced materials for new energy technologies, and the fabrication of composite and semiconductor components.
The true value of a box resistance furnace lies not just in its ability to generate heat, but in its capacity for precise, repeatable control over temperature. This control is the fundamental mechanism that allows researchers to intentionally manipulate the microstructure of a material to achieve desired properties and functions.

The Principle: Controlled Thermal Energy
A box type resistance furnace operates on a simple yet powerful principle: converting electrical energy into thermal energy. This process is highly controllable, allowing for the precise execution of specific temperature profiles—heating, holding (soaking), and cooling—which are critical for material transformation.
The Role of Temperature and Time
At its core, materials science is about managing a material's internal structure. By controlling the temperature and the duration a material is held at that temperature, a researcher can dictate everything from crystal size and phase composition to internal stress and density.
The Importance of Atmosphere
While basic models operate in air, more advanced box furnaces allow for processing under controlled atmospheres (e.g., inert gas like argon or nitrogen). This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, which is crucial for processing sensitive metals and advanced materials.
Core Applications in Metallic Materials
The most traditional and widespread use of box furnaces is in metallurgy. These furnaces provide the controlled environment needed to refine and enhance the properties of metals and alloys.
Manipulating Mechanical Properties
Heat treatment is a cornerstone of metallurgy. Processes like annealing (softening a metal for better workability), normalizing (refining grain structure for uniformity), and quenching (rapidly cooling to increase hardness) all rely on the precise temperature cycles executed in a box furnace.
Designing Advanced Alloys
Creating high-performance alloys, such as nickel-based superalloys for aerospace, requires uniform composition. Solid solution treatment in a box furnace ensures that alloying elements are evenly diffused throughout the base metal, resulting in a homogenous and reliable final product.
Studying Phase Transformations
These furnaces are critical for fundamental research. By heating a sample and holding it at various temperatures, researchers can "freeze" different structural phases to study how a material's crystal structure changes, providing insight into its behavior and potential applications.
Shaping and Densifying Advanced Materials
Beyond metals, box furnaces are essential for creating dense, high-performance ceramic, glass, and composite components from precursor powders or fibers.
Sintering Ceramics and Glass
Sintering is the process of heating a compacted powder (like alumina) to a temperature below its melting point, causing the particles to bond and densify. This turns a fragile "green" part into a hard, robust ceramic. Similarly, these furnaces are used for hot bending glass, such as forming the 3D cover glass for modern smartphones.
Processing Advanced Composites
The creation of materials like carbon fiber reinforced composites involves critical thermal steps. A box furnace is used for the low-temperature pre-oxidation of carbon fibers (200-300°C) to stabilize their structure before the final high-temperature carbonization. They are also used for preparing ceramic-matrix composites, like SiC/SiC, through high-temperature sintering.
Enabling New Energy and Semiconductor Technologies
Box furnaces are playing a vital role in developing the materials that power modern electronics and sustainable energy solutions.
Synthesizing Battery Materials
The performance of lithium-ion batteries depends on their electrode materials. Box furnaces are used for the high-temperature solid-phase synthesis of cathode materials like Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO₂) and Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) ternary materials. They are also used to modify anode materials, such as coating graphite with amorphous carbon to improve performance.
Fabricating Semiconductor Devices
In semiconductor manufacturing, precision is everything. Box furnaces are used for oxidation diffusion, a process where silicon wafers are heated to 800-1200°C to grow a high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO₂) insulating layer. They are also used for metallization annealing to improve the electrical contact between metal layers and the silicon substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, the standard box type resistance furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Temperature Uniformity
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity across the entire chamber can be a challenge. For highly sensitive processes or very large parts, temperature gradients can lead to inconsistent material properties. More advanced models incorporate multiple heating zones to mitigate this.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Standard box furnaces have relatively slow heating and cooling rates due to their thermal mass (insulating bricks). Processes requiring extremely rapid quenching or thermal cycling may demand more specialized equipment, such as rapid thermal processing (RTP) systems.
Process Scalability
Box furnaces are fundamentally batch processing tools. This is ideal for research, development, and small-scale production, but it is less efficient for high-volume manufacturing, where continuous tunnel kilns or conveyor furnaces are often preferred.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of a box furnace should be directly tied to your specific research or development objective.
- If your primary focus is improving metal properties: Use the furnace for precise heat treatment cycles like annealing, quenching, or tempering to control hardness and toughness.
- If your primary focus is developing new ceramics: Leverage the furnace for controlled sintering profiles to achieve maximum density and desired mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is creating battery or catalyst materials: Employ the furnace for high-temperature synthesis and modification to produce materials with specific chemical compositions and structures.
- If your primary focus is fundamental materials science: Use the furnace as a tool to access and study the specific temperature-dependent states and phase transformations of your material.
Ultimately, the box type resistance furnace is a cornerstone of the modern materials lab, providing the essential control over thermal energy needed to design the materials of the future.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Materials Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Materials | Annealing, Normalizing, Quenching | Metals, Alloys |
| Ceramics & Glass | Sintering, Hot Bending | Alumina, Glass |
| Advanced Composites | Pre-oxidation, Sintering | Carbon Fibers, SiC/SiC |
| Energy & Semiconductors | Solid-Phase Synthesis, Oxidation Diffusion | Li-ion Battery Materials, Silicon Wafers |
Ready to elevate your material research with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you're developing alloys, ceramics, or energy materials. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing



















