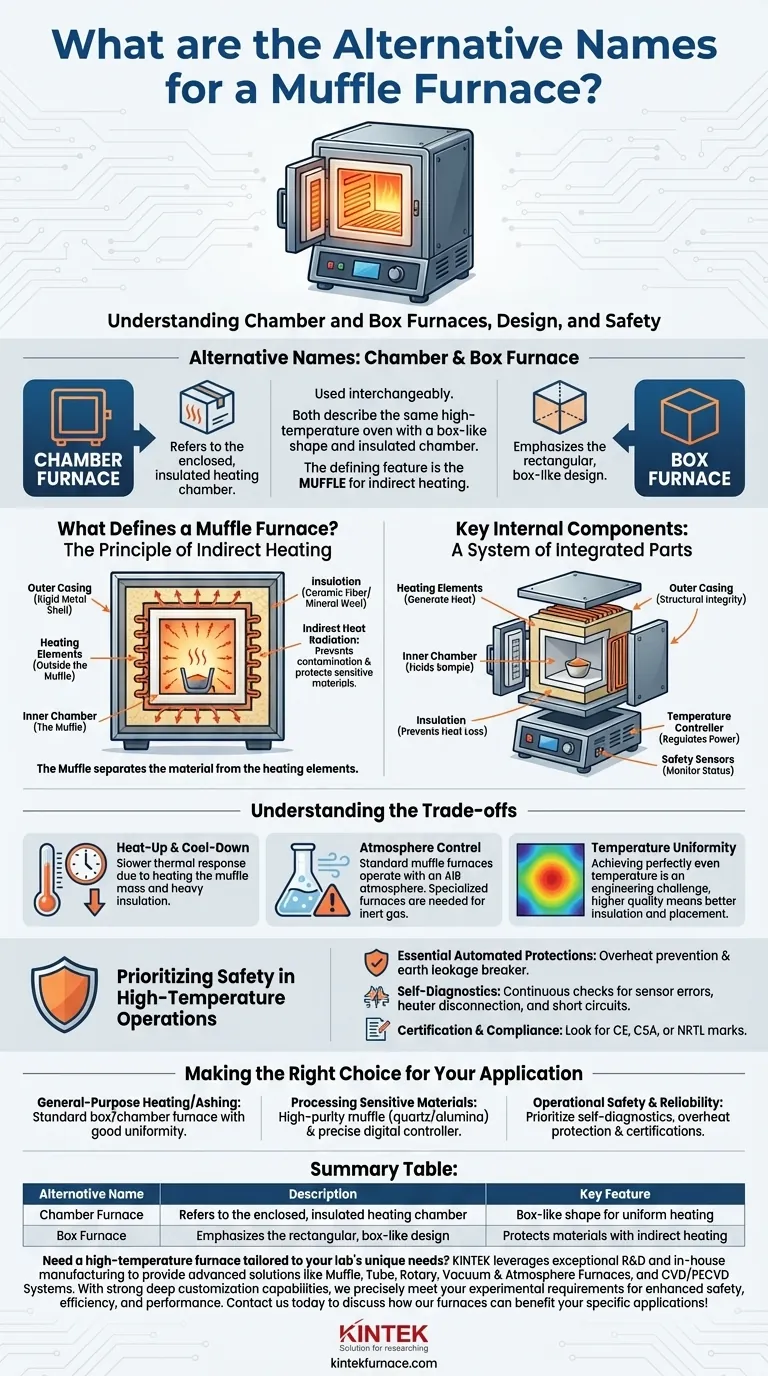
In technical terms, a muffle furnace is most commonly known as a chamber furnace or a box furnace. These names are used interchangeably and refer to the same type of high-temperature oven, distinguished by its enclosed, box-like shape and insulated heating chamber.
While the names "chamber furnace" and "box furnace" are correct, the truly defining feature is the "muffle" itself—an inner chamber that protects the heated material from the heating elements. Understanding this principle of indirect heating and the critical safety features is far more important than the name on the equipment.

What Defines a Muffle Furnace?
The name "muffle furnace" comes from its core design principle. The term "muffle" refers to the practice of wrapping something to deaden sound or, in this case, to separate and shield it.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The "muffle" is the furnace's inner chamber, typically made of a high-temperature refractory material like ceramic, alumina, or quartz.
This chamber contains the material being heated and separates it from the actual heating elements. This separation is the key design feature.
How It Works: Indirect Heating
The heating elements (coils of resistance wire, silicon carbide, etc.) are arranged around the outside of the muffle.
The elements heat the muffle, which then radiates heat evenly into the chamber. This indirect heating prevents contamination from the elements and protects sensitive materials from direct, harsh radiation.
Key Internal Components
A muffle furnace is a system of integrated parts working together. The primary components you will always find are:
- Heating Elements: Made of high-resistance materials like Kanthal, nichrome, or silicon carbide that generate heat when electricity passes through them.
- Inner Chamber (The Muffle): A refractory box that holds the sample and ensures uniform heat distribution.
- Insulation: High-density ceramic fiber or mineral wool packed between the inner chamber and outer casing to prevent heat loss and ensure efficiency.
- Outer Casing: A rigid metal shell, often stainless steel, that provides structural integrity and protects the internal components.
- Temperature Controller: A digital or analog system that regulates power to the heating elements to achieve and maintain a set temperature.
- Safety Sensors: Thermocouples and other sensors that monitor temperature and system status.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the muffle furnace design comes with inherent characteristics you must consider for your specific application.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Times
Because the furnace must first heat the mass of the muffle, which then heats the sample, thermal response times can be slower than in direct-heating ovens. The heavy insulation also retains heat, leading to longer cool-down periods.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. The muffle separates the sample from element byproducts but does not inherently control the gas environment. For processes requiring an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon), you need a specialized furnace with gas-purging capabilities.
Temperature Uniformity
Achieving perfectly even temperature throughout the chamber is a significant engineering challenge. Higher-quality furnaces use superior insulation and strategic placement of heating elements to maximize uniformity, but this often comes at a higher cost.
Prioritizing Safety in High-Temperature Operations
Operating equipment at extreme temperatures demands a non-negotiable focus on safety. Modern furnaces should include several layers of automated protection.
Essential Automated Protections
Look for furnaces equipped with automatic overheat prevention, which cuts power if the temperature exceeds a set limit, and an earth leakage breaker to prevent electrical shocks.
The Importance of Self-Diagnostics
A critical feature of any reliable furnace is a robust self-diagnostic system. This function continuously checks for internal failures before they become catastrophic.
Key checks should include sensor errors, heater disconnection, and short circuits in the power relays (SSR or Triac). This ensures the furnace fails safely if a component malfunctions.
Certification and Compliance
Look for official certifications like CE, CSA, or NRTL. These marks indicate that a third-party organization has tested and verified that the furnace meets established safety and performance standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right furnace means matching the equipment's capabilities to your scientific or industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating or ashing: A standard box or chamber furnace with good temperature uniformity and foundational safety features will be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: Prioritize a furnace with a high-purity muffle material (like quartz or alumina) and a precise digital temperature controller.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and reliability: Make self-diagnostics, overheat protection, and third-party safety certifications (CE, CSA, NRTL) your most important selection criteria.
By looking beyond the name and focusing on the core design, components, and safety systems, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific technical needs.
Summary Table:
| Alternative Name | Description | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Furnace | Refers to the enclosed, insulated heating chamber | Box-like shape for uniform heating |
| Box Furnace | Emphasizes the rectangular, box-like design | Protects materials with indirect heating |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your experimental requirements for enhanced safety, efficiency, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















