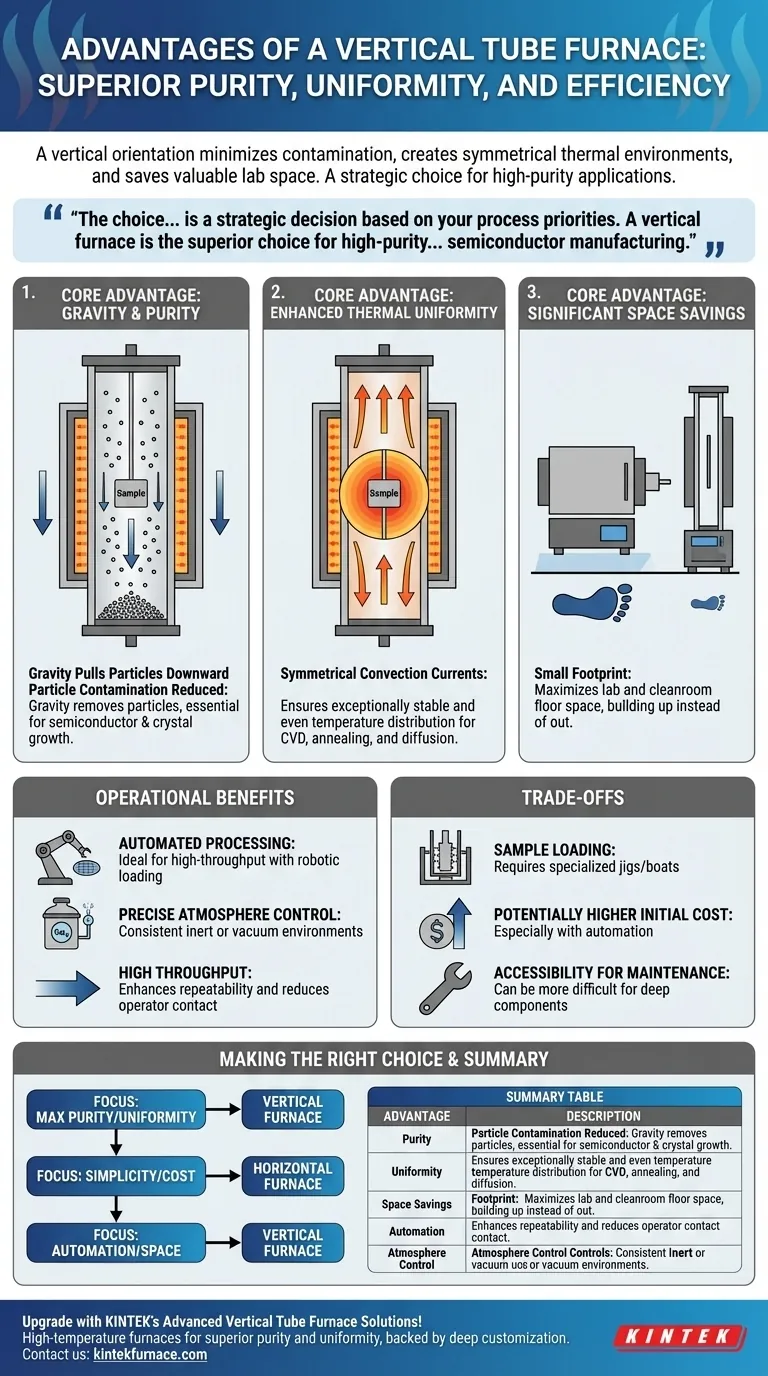
In short, a vertical tube furnace offers superior process purity and thermal uniformity. Its key advantages stem from its vertical orientation, which minimizes particle contamination by allowing particulates to fall away from the sample, creates a more symmetrical thermal environment, and saves valuable laboratory floor space.
The choice between a vertical and horizontal tube furnace is not merely about orientation; it's a strategic decision based on your process priorities. A vertical furnace is the superior choice for high-purity, high-uniformity applications like semiconductor manufacturing, whereas a horizontal furnace often provides a simpler, more cost-effective solution for general-purpose heating.

The Core Design Advantage: Gravity as an Ally
The primary benefits of a vertical tube furnace are a direct result of its orientation. By aligning the process tube with the force of gravity, the furnace creates a fundamentally different and often superior processing environment compared to its horizontal counterpart.
Superior Purity and Reduced Contamination
In a vertical furnace, any particles generated during the process or introduced into the tube are pulled downward by gravity. They fall to the bottom of the tube, away from the sample being processed.
This is a critical advantage in applications like semiconductor wafer fabrication or crystal growth, where even microscopic particles can cause fatal defects in the final product. In a horizontal furnace, these same particles can settle directly onto the sample surface.
Enhanced Thermal Uniformity
Heat naturally rises, creating convection currents within the furnace tube. In a vertical orientation, these currents are symmetrical and flow uniformly up the tube walls, creating an exceptionally stable and even temperature zone around the sample.
This radial uniformity ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is essential for consistent chemical vapor deposition (CVD), annealing, and diffusion processes.
Significant Space Savings
By building up instead of out, a vertical tube furnace occupies a much smaller footprint. This is a major practical benefit in modern laboratories and cleanrooms where floor space is a premium and expensive commodity.
Operational and Process-Specific Benefits
Beyond the core physics, the vertical design enables tangible improvements in productivity and process control.
Ideal for Automated Processing
The top- or bottom-loading configuration of a vertical furnace is perfectly suited for automated wafer and boat transfer systems. Robotic arms can precisely load and unload samples with minimal human intervention.
This automation dramatically increases throughput, improves repeatability, and reduces the risk of contamination from operators, making it standard in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Like all tube furnaces, vertical models excel at maintaining a controlled atmosphere. The sealed tube can easily accommodate inert gases (like Argon or Nitrogen) or be operated under a vacuum.
The vertical design helps prevent gas stratification that can sometimes occur in horizontal tubes, ensuring a consistent atmosphere throughout the critical process zone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No design is perfect for every application. To make an informed decision, you must also consider the potential downsides of a vertical furnace.
Sample Loading and Handling
Loading a sample into a vertical furnace can be more mechanically complex than simply sliding it into a horizontal tube. It often requires specialized jigs, fixtures, or "boats" to hold the sample securely in the center of the heat zone.
Potentially Higher Initial Cost
While basic tube furnaces are relatively inexpensive, vertical systems—especially those equipped with automated loading capabilities—typically represent a higher initial investment compared to simpler horizontal models.
Accessibility for Maintenance
Depending on the design, accessing the central heating elements or the middle of the process tube for cleaning and maintenance can be more difficult in a tall, vertical furnace than in an easily accessible horizontal one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal is the most important factor in selecting the right furnace.
- If your primary focus is maximum sample purity and uniformity: A vertical tube furnace is the unequivocal choice, especially for sensitive semiconductor, electronics, or advanced materials research.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness for general heating: A horizontal tube furnace is often a more practical and economical solution for basic annealing, drying, or synthesis.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput automation and space efficiency: The vertical furnace is superior due to its small footprint and compatibility with automated loading systems.
Ultimately, choosing a vertical furnace is an investment in process control, purity, and precision.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Purity | Gravity pulls particles away from samples, minimizing contamination in high-purity applications like semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Enhanced Thermal Uniformity | Symmetrical convection currents ensure even temperature distribution, ideal for CVD and annealing processes. |
| Space Savings | Vertical design reduces floor space usage, beneficial for compact labs and cleanrooms. |
| Automation Compatibility | Top- or bottom-loading supports robotic systems for high-throughput, repeatable processing. |
| Precise Atmosphere Control | Prevents gas stratification, maintaining consistent inert or vacuum environments. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced vertical tube furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces tailored for superior purity and uniformity. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















