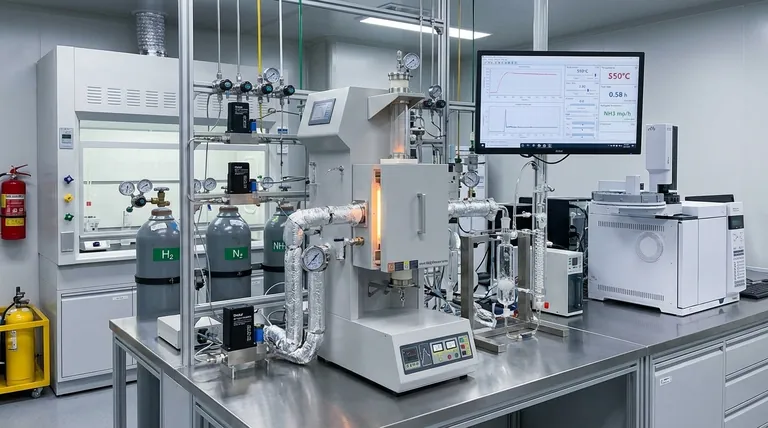
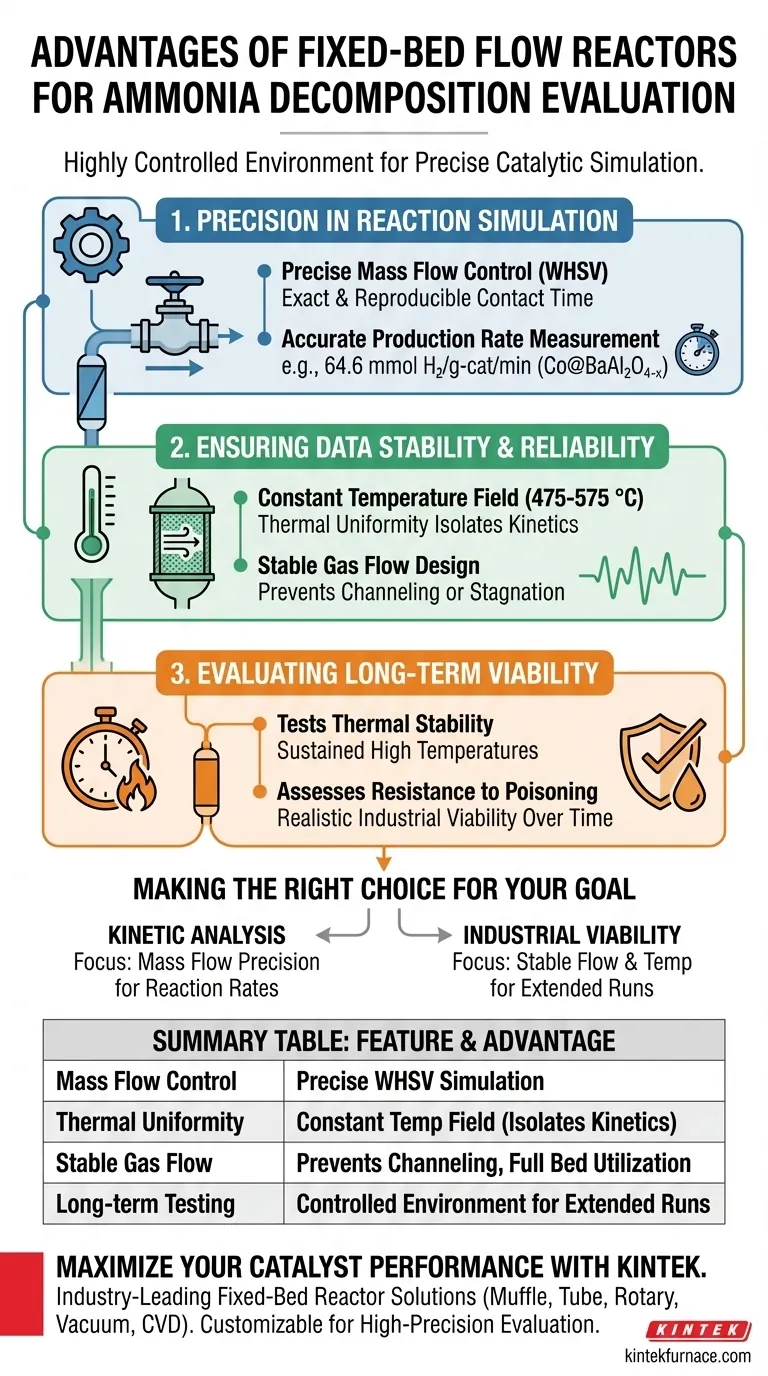
The primary advantage of a fixed-bed flow reactor is its ability to create a highly controlled environment for precise catalytic simulation. By utilizing mass flow controllers and a constant temperature design, these reactors allow for the rigorous evaluation of hydrogen production rates and catalyst longevity under specific operational conditions.
The fixed-bed flow reactor removes environmental variability, providing the stable baseline necessary to accurately validate high-performance catalysts like Co@BaAl2O4-x.

Precision in Reaction Simulation
Controlling Space Velocity
The inclusion of mass flow controllers is critical for evaluating catalytic activity.
These devices allow researchers to precisely simulate ammonia decomposition under various Weight Hourly Space Velocities (WHSV). This control ensures that the contact time between the reactant and the catalyst is exact and reproducible.
Accurate Production Rate Measurement
The stability provided by this reactor design enables the accurate quantification of performance metrics.
For example, researchers have successfully used this setup to measure high hydrogen production rates, reaching 64.6 mmol H2 per gram of catalyst per minute for Co@BaAl2O4-x. This level of precision is essential for distinguishing between incremental and breakthrough catalyst improvements.
Ensuring Data Stability and Reliability
Maintaining a Constant Temperature Field
A major advantage of the fixed-bed flow reactor is the generation of a constant temperature field.
This thermal uniformity is vital for operating within specific windows, such as the 475 to 575 °C range used for ammonia decomposition. It ensures that observed activity changes are due to catalyst kinetics, not thermal fluctuations within the reactor bed.
Stable Gas Flow Design
In addition to thermal control, the reactor's design ensures stable gas flow throughout the experiment.
This stability prevents flow channeling or stagnation, ensuring that the entire catalyst bed is utilized effectively during the evaluation process.
Evaluating Long-Term Viability
Testing Thermal Stability
Beyond instantaneous activity, fixed-bed reactors are ideal for assessing long-term thermal stability.
Because the environment is strictly controlled, researchers can run extended experiments to observe how the catalyst structure holds up under sustained high temperatures without interference from external variables.
Assessing Resistance to Poisoning
The continuous flow nature of the reactor allows for the effective evaluation of a catalyst's resistance to poisoning.
By introducing potential contaminants into the stable flow stream, researchers can accurately measure performance degradation over time, providing a realistic picture of industrial viability.
Understanding the Operational Requirements
Critical Design Dependencies
While the fixed-bed flow reactor offers high precision, its effectiveness relies heavily on the quality of its peripheral components.
To achieve the "constant temperature field" mentioned, the reactor requires robust insulation and heating control to prevent radial or axial thermal gradients (hot spots). Without precise mass flow controllers, the WHSV data becomes unreliable, negating the reactor's primary advantage of simulation accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of a fixed-bed flow reactor for your specific research needs, consider the following focuses:
- If your primary focus is Kinetic Analysis: Prioritize the precision of your mass flow controllers to vary WHSV accurately and determine reaction rates.
- If your primary focus is Industrial Viability: Utilize the stable flow and temperature capabilities to perform extended runs testing for thermal degradation and poisoning resistance.
Success in evaluating ammonia decomposition relies on leveraging the reactor's stability to isolate the catalyst's true performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for Catalytic Evaluation | Impact on Research |
|---|---|---|
| Mass Flow Control | Precise simulation of Space Velocity (WHSV) | Accurate, reproducible contact time |
| Thermal Uniformity | Constant temperature field (e.g., 475-575 °C) | Isolates kinetics from thermal fluctuations |
| Stable Gas Flow | Prevention of flow channeling or stagnation | Ensures full utilization of the catalyst bed |
| Long-term Testing | Controlled environment for extended runs | Reliable data on thermal stability and poisoning |
Maximize Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Ready to elevate your ammonia decomposition research? KINTEK provides industry-leading fixed-bed reactor solutions designed for high-precision catalytic evaluation. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your lab's unique high-temperature requirements.
From achieving uniform heating to ensuring stable gas flow for long-term poisoning tests, our systems empower you to validate breakthroughs like high-rate hydrogen production with confidence.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your lab's efficiency and precision.
Visual Guide
References
- Pei Xiong, Molly Meng‐Jung Li. Efficient Low‐temperature Ammonia Cracking Enabled by Strained Heterostructure Interfaces on Ru‐free Catalyst. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202502034
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven utilized for ZnO-FL drying? Preserving Delicate Nanoparticle Morphologies
- How does the control of high-purity Argon gas flow affect Al/Ni film deposition? Master Precision Sputtering
- How does a high-precision Vertical Bridgman Furnace facilitate ZnGeP2 growth? Master Single Crystal Production
- What is the role of a precision annealing furnace in the preparation of ZnO or CuO doped phosphate glass?
- Why is industrial-grade isostatic pressing necessary for zirconia? Achieve Uniform Density & Structural Integrity
- What is the function of an ultra-high vacuum sputtering system with multi-target for CuGaO2? Precision Synthesis Guide
- How does the design of specialized industrial furnaces for hydrogen production contribute to extension of lifespan?
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace influence ZnO nanotube sensors? Unlock Peak Sensitivity and Stability



















