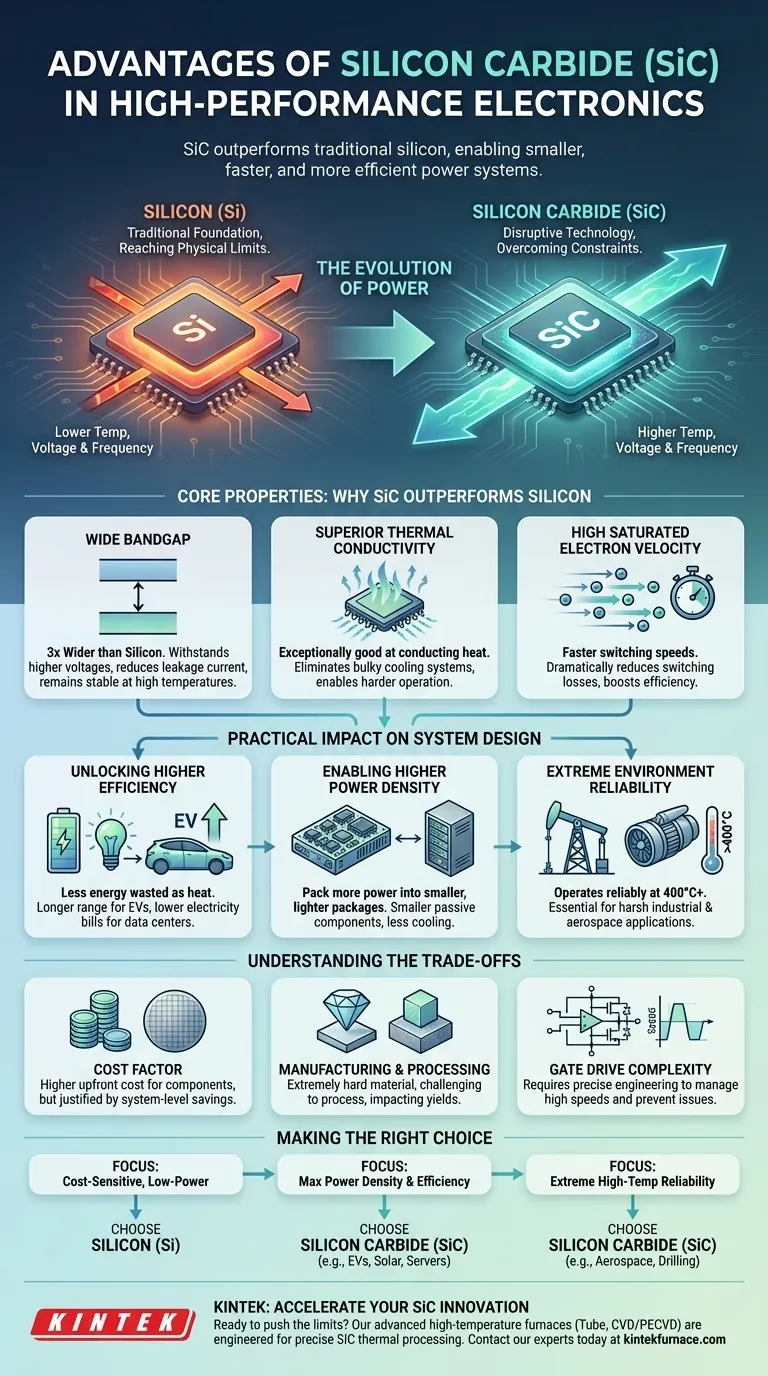
In the world of high-performance electronics, silicon carbide (SiC) stands out for its fundamental ability to operate at higher temperatures, voltages, and switching frequencies than traditional silicon. This allows for the creation of electronic systems that are significantly more efficient, compact, and reliable, especially under demanding conditions.
While silicon has been the foundation of the electronics industry for decades, it is reaching its physical limits in power applications. Silicon carbide is not an incremental improvement; it is a disruptive technology that overcomes silicon's core thermal and electrical constraints, enabling a new generation of smaller, faster, and more efficient power systems.
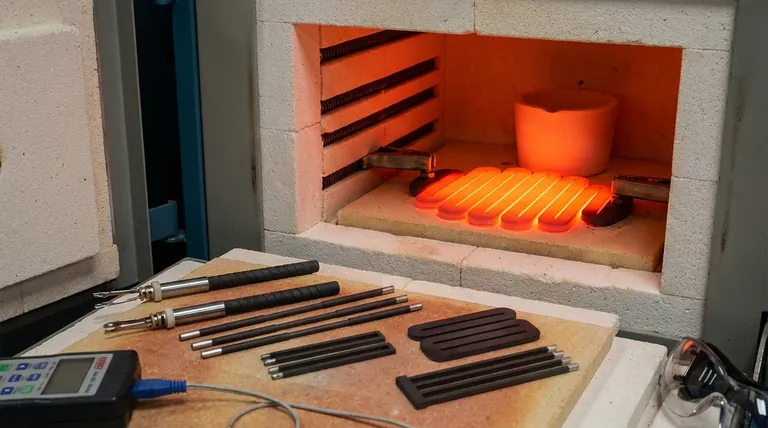

Why SiC Outperforms Silicon: The Core Properties
The advantages of SiC are not arbitrary; they stem directly from its fundamental material properties, which are vastly different from those of silicon.
Wide Bandgap: The Foundation of Power
The most critical property of SiC is its wide bandgap, which is approximately three times wider than silicon's. This single characteristic is the source of its primary benefits.
A wider bandgap allows the material to withstand a much stronger electric field before breaking down. This translates directly to devices that can handle significantly higher voltages in a smaller physical area.
Furthermore, this property drastically reduces leakage current, especially at high temperatures. Where silicon devices start to "leak" and fail as they heat up, SiC remains stable and efficient.
Superior Thermal Conductivity: Managing the Heat
Silicon carbide is exceptionally good at conducting heat, dissipating it much more effectively than silicon. This high thermal conductivity is a game-changing advantage.
When electronic components can shed heat efficiently, they can be run harder without overheating. This reduces or even eliminates the need for bulky cooling systems like large heatsinks, fans, and liquid cooling, which are often required for high-power silicon devices.
High Saturated Electron Velocity: The Speed Advantage
SiC allows electrons to move at high speeds, even under strong electric fields. This property, known as high saturated electron velocity, enables SiC devices to be switched on and off much faster than silicon-based counterparts like IGBTs.
This high-speed switching capability is crucial for efficiency. It dramatically reduces switching losses (energy wasted during the on/off transition), which are a major source of inefficiency in many power systems.
The Practical Impact on System Design
These material properties translate into tangible, system-level benefits that are revolutionizing industries from electric vehicles to renewable energy.
Unlocking Higher Efficiency
By minimizing both conduction losses (due to lower resistance) and switching losses (due to faster switching), SiC devices waste significantly less energy as heat.
This increased efficiency means more power from the source reaches its destination. In an electric vehicle, this can mean longer range; in a data center, it means lower electricity bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
Enabling Higher Power Density
The combination of high-temperature operation, superior heat dissipation, and high-frequency switching creates a powerful synergy.
Because SiC can run hotter, requires less cooling, and allows for the use of smaller passive components (like inductors and capacitors), engineers can pack much more power into a smaller and lighter package. This is the definition of higher power density.
Extreme Environment Reliability
As noted, SiC's stability at high temperatures is unmatched by silicon. It can operate reliably at temperatures of 400°C and beyond, where silicon electronics would instantly fail.
This makes SiC the only viable choice for electronics in ultra-harsh environments, such as down-hole drilling for oil and gas, aerospace engine controllers, and other demanding industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its challenges. Adopting silicon carbide requires a clear understanding of its current limitations.
The Cost Factor
The primary barrier to widespread SiC adoption has been cost. Growing high-quality SiC crystals is a more difficult and expensive process than producing silicon wafers.
While the price gap is narrowing, SiC components remain more expensive upfront than their silicon equivalents. However, this higher initial cost can often be justified by system-level savings in cooling, size, and long-term energy efficiency.
Manufacturing and Processing
Silicon carbide is an extremely hard material, making it more challenging to process and manufacture into finished devices. This complexity contributes to its higher cost and has historically impacted device yields and availability.
Gate Drive Complexity
The fast-switching nature of SiC devices, while a major benefit, also demands more careful engineering. The gate driver circuits that control them must be precisely designed to manage the high speeds and prevent issues like voltage overshoot and ringing, which can impact reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between silicon and silicon carbide depends entirely on the specific goals and constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, low-power applications: Proven and economical silicon technology remains the most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing power density and efficiency: SiC is the superior technology for applications like EV inverters, solar power converters, and server power supplies, where its benefits justify the cost.
- If your primary focus is reliability in extreme high-temperature environments: SiC is often the only viable option, enabling electronics to function in conditions far beyond silicon's limits.
Ultimately, adopting silicon carbide is a strategic decision to overcome the physical barriers of silicon, unlocking a new tier of performance for demanding power systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Core Property | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Voltage & Temperature Operation | Wide Bandgap (3x silicon) | Enables smaller, more reliable devices for extreme environments (e.g., EV, aerospace) |
| Efficient Heat Dissipation | Superior Thermal Conductivity | Reduces/eliminates bulky cooling systems, lowering system size and cost |
| High-Frequency Switching | High Saturated Electron Velocity | Minimizes energy loss (switching losses), boosting overall system efficiency |
| System-Level Benefits | Combination of all properties | Achieves higher power density, compact designs, and longer operational life |
Ready to push the limits of your power electronics?
At KINTEK, we understand that cutting-edge materials like silicon carbide demand equally advanced processing solutions. Our high-temperature furnaces, including Tube and CVD/PECVD Systems, are engineered to support the precise thermal processing required for SiC R&D and production.
Leveraging our deep customization capabilities, we can tailor a furnace solution to meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you unlock the full potential of SiC technology.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our advanced furnace solutions can accelerate your SiC innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















