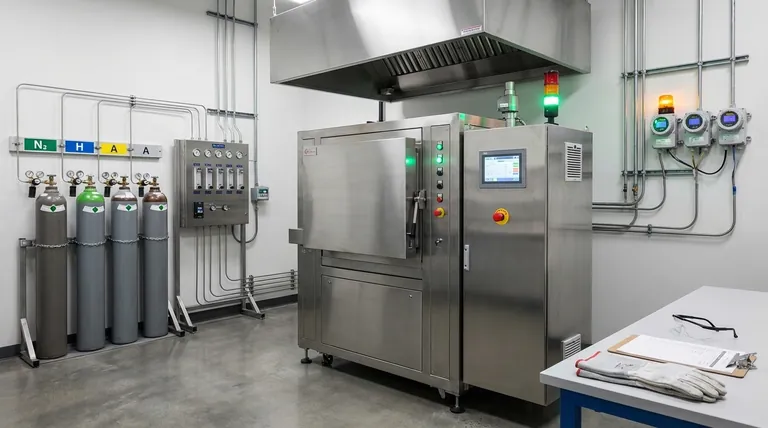
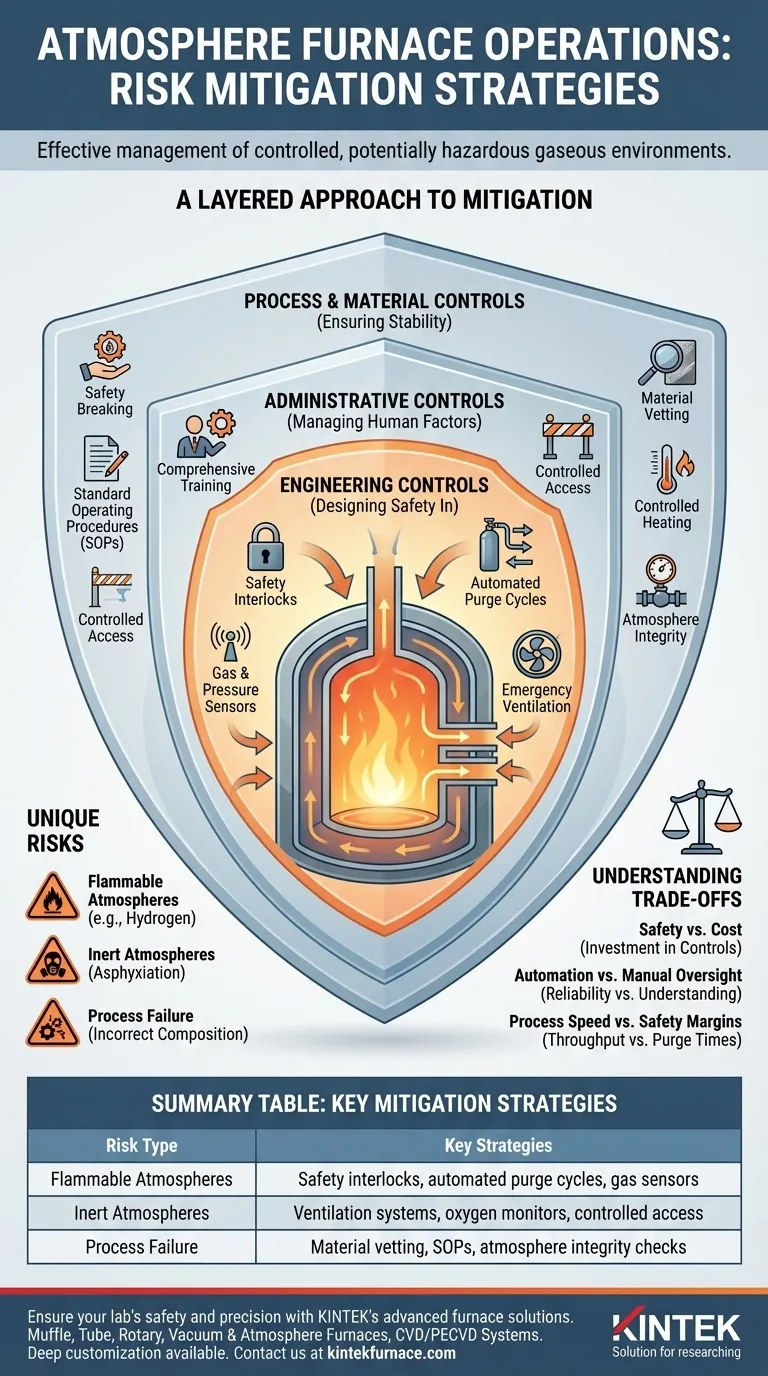
Effective risk mitigation for atmosphere furnace operations involves a multi-layered strategy that combines robust engineering controls, strict administrative procedures, and diligent process management. Key strategies include implementing safety interlocks and gas sensors, ensuring comprehensive operator training, using proper ventilation, and carefully controlling the materials and gaseous atmospheres introduced into the furnace to prevent explosions, asphyxiation, and process failures.
The unique dangers of atmosphere furnaces go beyond high temperatures. The core challenge is managing the controlled, often flammable or oxygen-displacing, gaseous environment itself. True safety is achieved not by a single solution, but by layering independent systems of engineering and procedural controls.

The Unique Risks of Atmosphere Furnaces
Standard furnaces present a thermal hazard. Atmosphere furnaces add chemical and pressure-related risks because they operate by replacing air with a specific gaseous medium to achieve desired metallurgical properties. Understanding these specific risks is the first step toward mitigating them.
The Hazard of Flammable & Reactive Atmospheres
Many heat-treating processes use atmospheres containing high concentrations of flammable gases like hydrogen or endothermic gas (a mix of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen).
If this flammable mixture combines with oxygen from a leak or an improper purge cycle, it can create a highly explosive environment inside the hot furnace chamber.
The Hazard of Inert Atmospheres
Other processes use inert gases like nitrogen or argon to create an oxygen-free environment and prevent oxidation.
While not flammable, these gases are asphyxiants. A significant leak in an enclosed space can displace oxygen, creating a life-threatening environment for personnel.
The Hazard of Process Failure
The furnace atmosphere is a critical process variable. An incorrect gas composition, pressure, or flow rate will not only ruin the product but can also damage the furnace itself.
For example, improper carbon potential can lead to unwanted carburization or decarburization, rendering expensive components useless.
A Layered Approach to Mitigation
A robust safety program relies on the "hierarchy of controls," prioritizing engineered solutions over procedural ones because they are inherently more reliable.
Engineering Controls: Designing Safety In
This is the most critical layer of protection. These are physical systems designed to automatically prevent a hazardous state.
Key controls include:
- Safety Interlocks: These systems prevent unsafe actions, such as opening the furnace door before a purge cycle is complete or introducing flammable gas when the temperature is below its autoignition point.
- Automated Purge Cycles: A programmed system that uses an inert gas (like nitrogen) to safely remove all oxygen before flammable gas is introduced, and to remove all flammable gas before the door is opened to the air.
- Gas & Pressure Sensors: Continuous monitoring of the atmosphere composition, chamber pressure, and gas flow rates. These sensors should be tied to alarms and automatic shutdown procedures.
- Emergency Ventilation: A dedicated, high-capacity ventilation system that can be activated to quickly exhaust hazardous gases from the work area in the event of a leak.
Administrative Controls: Managing Human Factors
These controls are the procedures and policies that govern how people work with the equipment.
They are essential but are considered less reliable than engineering controls because they depend on human adherence.
- Comprehensive Training: Only authorized and thoroughly trained personnel should operate the equipment. Training must cover normal operations, shutdown procedures, and detailed emergency response for fire, explosion, or gas leaks.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Clear, written instructions must be available for every phase of operation, including startup, shutdown, loading/unloading, and emergency stops.
- Controlled Access: The area around the furnace should be restricted to trained and authorized personnel to minimize uninformed interference.
Process & Material Controls: Ensuring Stability
This layer focuses on what you put into the furnace and how you run the cycle.
- Material Vetting: Never heat materials that could release hazardous vapors, excessive smoke, or volatile contaminants. Unidentified substances on parts can poison the atmosphere or create unexpected reactions.
- Controlled Heating: Avoid overheating materials beyond their required processing temperature, as this can cause unforeseen reactions or damage the product and furnace.
- Atmosphere Integrity: Ensure the supply gases meet purity specifications and that flow controls are properly calibrated to maintain the precise atmosphere required for the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Implementing a comprehensive safety strategy requires balancing competing priorities. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for making informed decisions.
Safety vs. Cost
Advanced engineering controls like fully automated purge systems and extensive gas detection represent a significant upfront capital investment. However, this cost is an investment against catastrophic failure, equipment loss, and serious injury, which are far more expensive in the long run.
Automation vs. Manual Oversight
While automation is a powerful tool for safety and consistency, it is not infallible. Operators must be trained to understand the process well enough to recognize when an automated system is malfunctioning, rather than trusting it blindly.
Process Speed vs. Safety Margins
There is often pressure to increase throughput by shortening cycle times. Rushing critical steps like inert gas purges is a common cause of furnace incidents. Safety procedures must define and enforce minimum purge times and flow rates, which should never be compromised for productivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Your mitigation strategy should be tailored to your specific equipment, processes, and organizational goals.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: Prioritize investment in engineering controls like automated purge cycles and continuous gas detection for both flammable gases and oxygen displacement.
- If your primary focus is process integrity and product quality: Focus on rigorous atmosphere control through high-quality sensors, regular calibration, and detailed operator training on the metallurgical impact of gas chemistry.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new safety program: Start with a formal risk assessment, then build a layered strategy based on the hierarchy of controls, beginning with the most effective engineering solutions.
Ultimately, a proactive and vigilant approach to managing the unique risks of controlled atmospheres is the foundation of a safe and successful furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Risk Type | Key Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Flammable Atmospheres | Safety interlocks, automated purge cycles, gas sensors |
| Inert Atmospheres | Ventilation systems, oxygen monitors, controlled access |
| Process Failure | Material vetting, SOPs, atmosphere integrity checks |
Ensure your lab's safety and precision with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing risk mitigation and operational efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















