In essence, a box type resistance furnace is a high-temperature workhorse for laboratories and industrial settings. Its most common applications include the sintering of metals and ceramics, the heat treatment of materials, and the analytical testing of samples, such as ashing or studying shrinkage properties.
The box furnace's value lies not in a single function, but in its versatility. Its simple, robust design provides a highly controlled and uniform high-temperature environment, making it an essential tool for a wide range of material synthesis, treatment, and analysis processes.
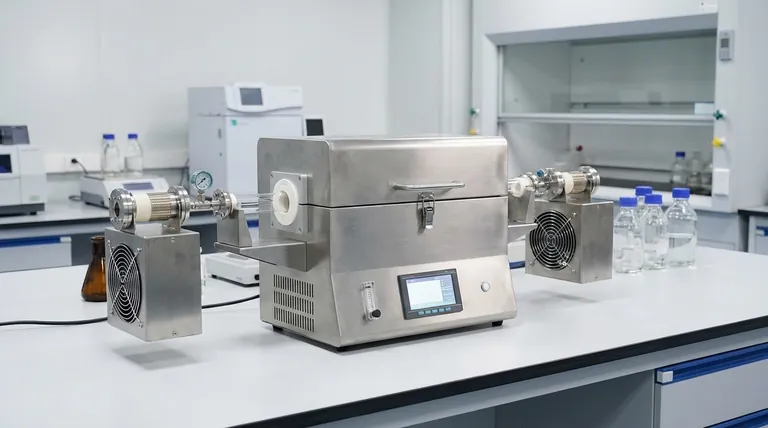

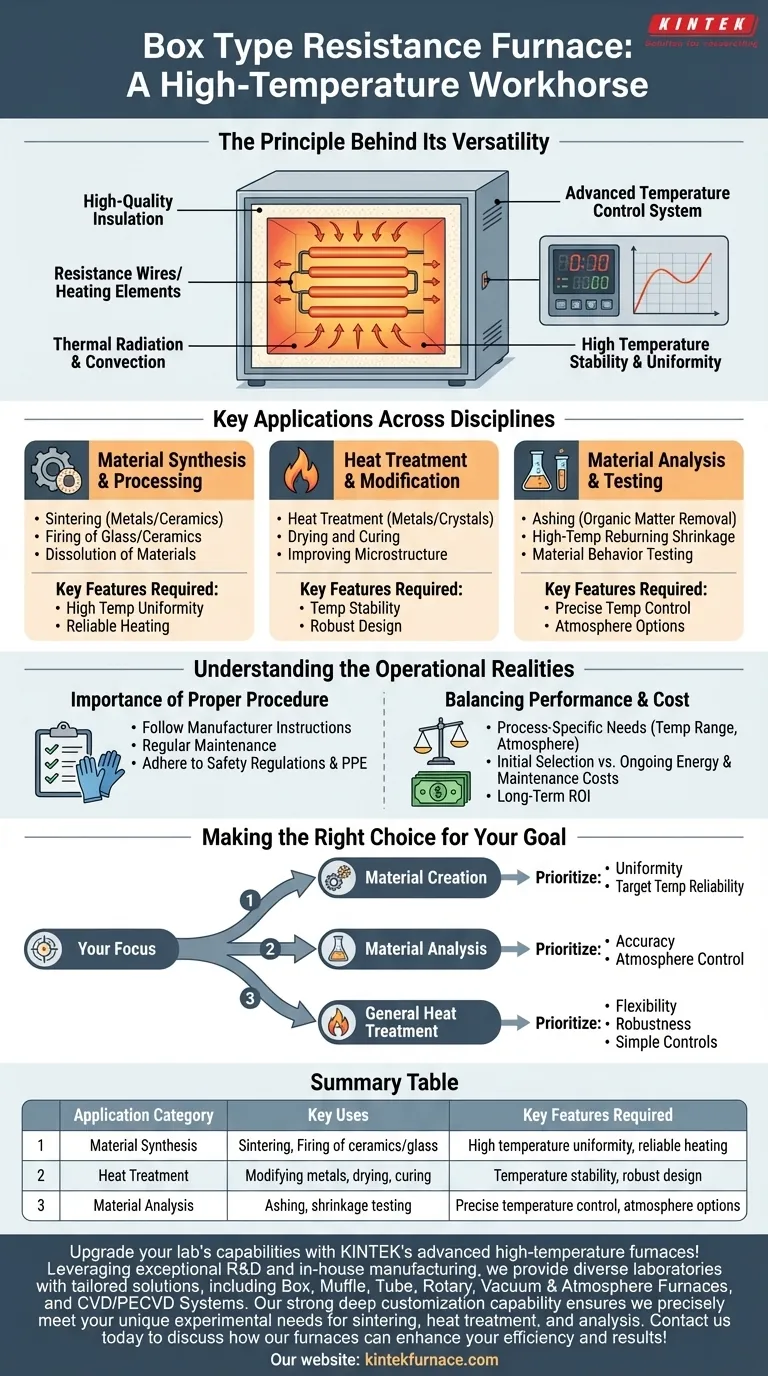
The Principle Behind Its Versatility
How It Achieves High Temperatures
A box type resistance furnace is a fundamentally simple yet effective piece of equipment. It generates heat using resistance wires or other electric heating elements inside an insulated chamber.
This heat is transferred to the sample primarily through thermal radiation and convection, allowing it to reach very high temperatures efficiently.
Why Control is Critical
The furnace's core components include a sturdy metal shell, high-quality aluminum oxide fiber insulation, and an advanced temperature control system.
This combination of robust insulation and precise digital control ensures high temperature stability and uniformity throughout the furnace chamber. This is critical for achieving repeatable and reliable results in sensitive processes.
Key Applications Across Disciplines
Material Synthesis and Processing
The furnace is a cornerstone for creating and processing new materials. Sintering, the process of forming a solid mass of material from powder using heat, is a primary application for both metals and ceramics.
It is also used for the firing of glass and ceramics, where controlled heat transforms raw materials into finished, hardened products. Some processes also use it for the dissolution of materials at high temperatures.
Heat Treatment and Modification
Modifying the properties of existing materials is another key use. Heat treatment of metals and some single crystals is performed to alter their microstructure, improving hardness, strength, or ductility.
For less extreme processes, the furnace is also used for drying and curing samples, where a stable, elevated temperature is needed to remove moisture or trigger a chemical reaction in a coating.
Material Analysis and Testing
In research and quality control, the furnace is indispensable for analysis. Ashing is a common technique where the furnace is used to burn off all organic matter from a sample, leaving only the inorganic ash for measurement.
It is also vital for testing the properties of materials, such as conducting high-temperature reburning shrinkage detection to understand how refractory materials behave under extreme heat.
Understanding the Operational Realities
The Importance of Proper Procedure
The effectiveness and safety of a box furnace depend entirely on correct operation. Users must always follow the manufacturer's operating instructions and adhere to a strict regular maintenance schedule.
High-temperature operation presents inherent risks. Familiarity with all safety regulations and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment are non-negotiable to prevent accidents.
Balancing Performance and Cost
While versatile, not all furnaces are created equal. The initial selection must account for process-specific needs like maximum temperature range, atmospheric control (e.g., for inert or vacuum environments), and required temperature uniformity.
Beyond the purchase price, you must also consider the ongoing energy efficiency and maintenance costs. A more efficient furnace may have a higher upfront cost but deliver a better long-term return on investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its capabilities to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is Material Creation (Sintering/Firing): Prioritize a furnace with excellent temperature uniformity and the ability to reach your target processing temperature reliably.
- If your primary focus is Material Analysis (Ashing/Testing): You need superior temperature accuracy and may require features like atmosphere control for specific tests.
- If your primary focus is General Heat Treatment (Metals/Crystals): Look for a flexible, robust model with simple controls that can handle repeated heating and cooling cycles efficiently.
By aligning the furnace's specifications with your core task, you ensure it becomes a reliable and effective tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Key Features Required |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Firing of ceramics/glass | High temperature uniformity, reliable heating |
| Heat Treatment | Modifying metals, drying, curing | Temperature stability, robust design |
| Material Analysis | Ashing, shrinkage testing | Precise temperature control, atmosphere options |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions, including Box, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for sintering, heat treatment, and analysis. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment



















