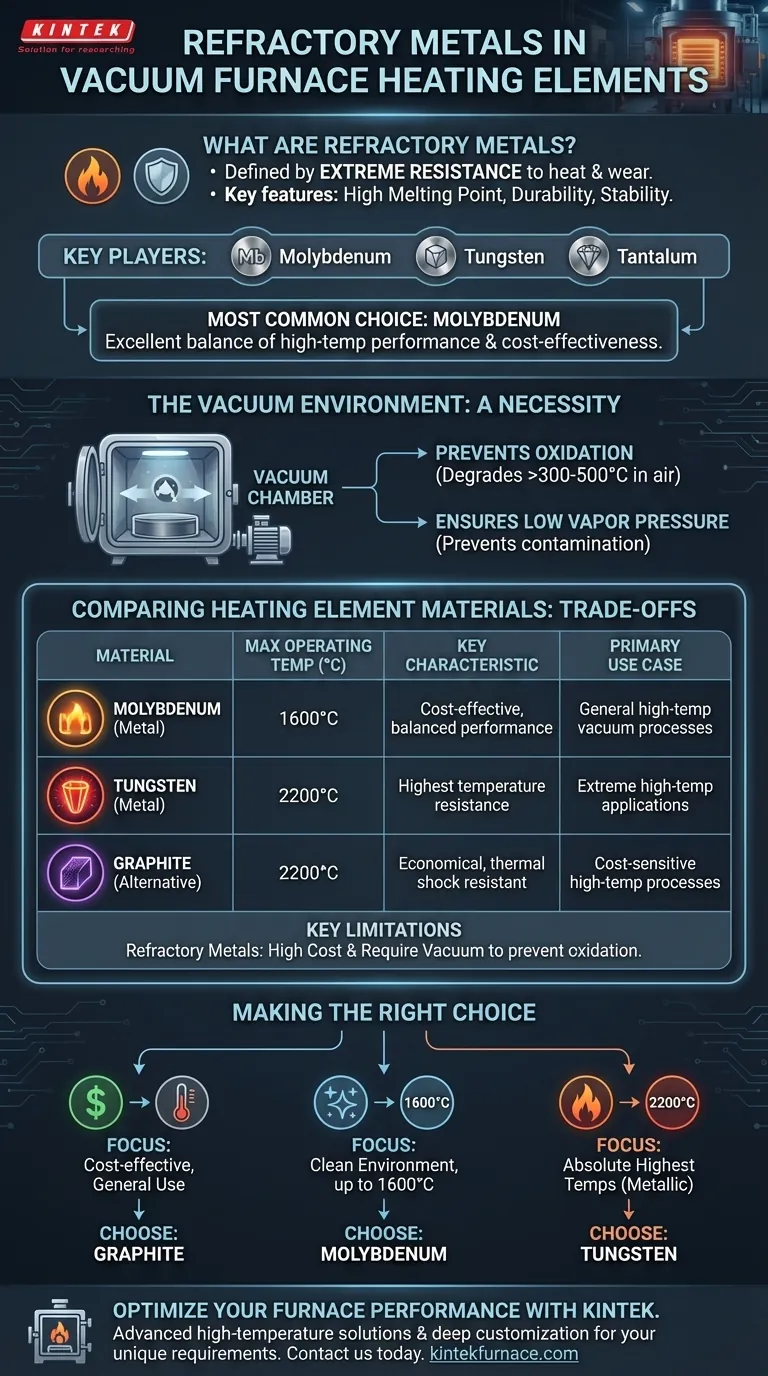
In short, refractory metals are a class of metals defined by their extreme resistance to heat and wear, with molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum being primary examples. For heating elements in vacuum furnaces, molybdenum is the most commonly used refractory metal because it offers an excellent balance of high-temperature performance and cost-effectiveness compared to its peers.
The choice of a heating element for a vacuum furnace is a critical engineering decision. It hinges on a trade-off between the required operating temperature, the need for a non-contaminating environment, and the total cost of the material.
What Defines a Refractory Metal?
Refractory metals are not defined by a single property but by a collection of characteristics that make them suitable for extreme environments. They are the materials of choice when both high temperatures and mechanical stability are required.
Extreme Heat Resistance
The defining characteristic is an exceptionally high melting point. This allows these metals to maintain their structural integrity and function as heating elements at temperatures that would cause most other metals to fail.
Durability and Stability
Beyond just heat, these metals resist wear, corrosion, and deformation under stress. This ensures a long operational life for critical components like heating elements.
The Key Players
While there are several refractory metals, three are most relevant to vacuum furnaces: molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum. Each offers a unique profile of temperature tolerance and cost.
The Unique Demands of a Vacuum Environment
Using a refractory metal as a heating element is only possible within a vacuum. The vacuum is not just for the process; it's essential for protecting the element itself.
Why a Vacuum is Necessary
Refractory metals have a strong affinity for oxygen. In open air, they begin to oxidize and degrade at temperatures as low as 300-500°C, far below their useful operating range. A vacuum removes the oxygen, preventing this destructive reaction.
The Importance of Low Vapor Pressure
A critical requirement for any material inside a vacuum furnace is low vapor pressure. This means the material does not readily turn into a gas at high temperatures, which is crucial for preventing the heating element from contaminating the product being processed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Metals vs. Graphite
While refractory metals are excellent, they are not the only option. Graphite, a non-metallic material, is a common and highly effective alternative. The best choice depends entirely on the specific application.
The Case for Molybdenum
Molybdenum is the workhorse of refractory metal heating elements. It offers excellent stability in clean environments for temperatures up to 1600°C. It is significantly less expensive than tungsten, making it the default choice for a wide range of vacuum heat-treating processes.
When to Use Tungsten
When an application requires the absolute highest temperatures a metallic element can provide, tungsten is the answer. It can operate reliably up to 2200°C. This extreme performance, however, comes at the highest cost.
The Graphite Alternative
Graphite is a non-metallic competitor that can also withstand temperatures up to 2200°C. It is durable, resistant to thermal shock, and considerably less expensive than either molybdenum or tungsten, making it a popular choice for many high-temperature applications.
Key Limitations of Refractory Metals
The primary drawbacks of refractory metals are their high cost and their absolute requirement for a vacuum to prevent oxidation. If the process does not demand a metallic element for reasons of purity or specific reactions, graphite is often a more economical solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element material is fundamental to the performance and efficiency of your vacuum furnace. Your decision should be guided by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general high-temperature use: Graphite is often the most practical and economical choice, offering a wide temperature range and excellent durability.
- If your primary focus is a clean environment with temperatures up to 1600°C: Molybdenum provides the ideal balance of high-purity performance and manageable cost.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute highest temperatures (up to 2200°C) with a metallic element: Tungsten is the necessary, albeit most expensive, option for your application.
Ultimately, understanding these material properties empowers you to select the most effective and efficient solution for your specific thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Refractory Metal | Max Operating Temp (°C) | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum | 1600°C | Cost-effective, balanced performance | General high-temperature vacuum processes |
| Tungsten | 2200°C | Highest temperature resistance | Extreme high-temperature applications |
| Graphite (Alternative) | 2200°C | Economical, resistant to thermal shock | Cost-sensitive high-temperature processes |
Optimize your vacuum furnace performance with the right heating element. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, or CVD/PECVD Systems, our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and precision with a tailored solution. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control



















