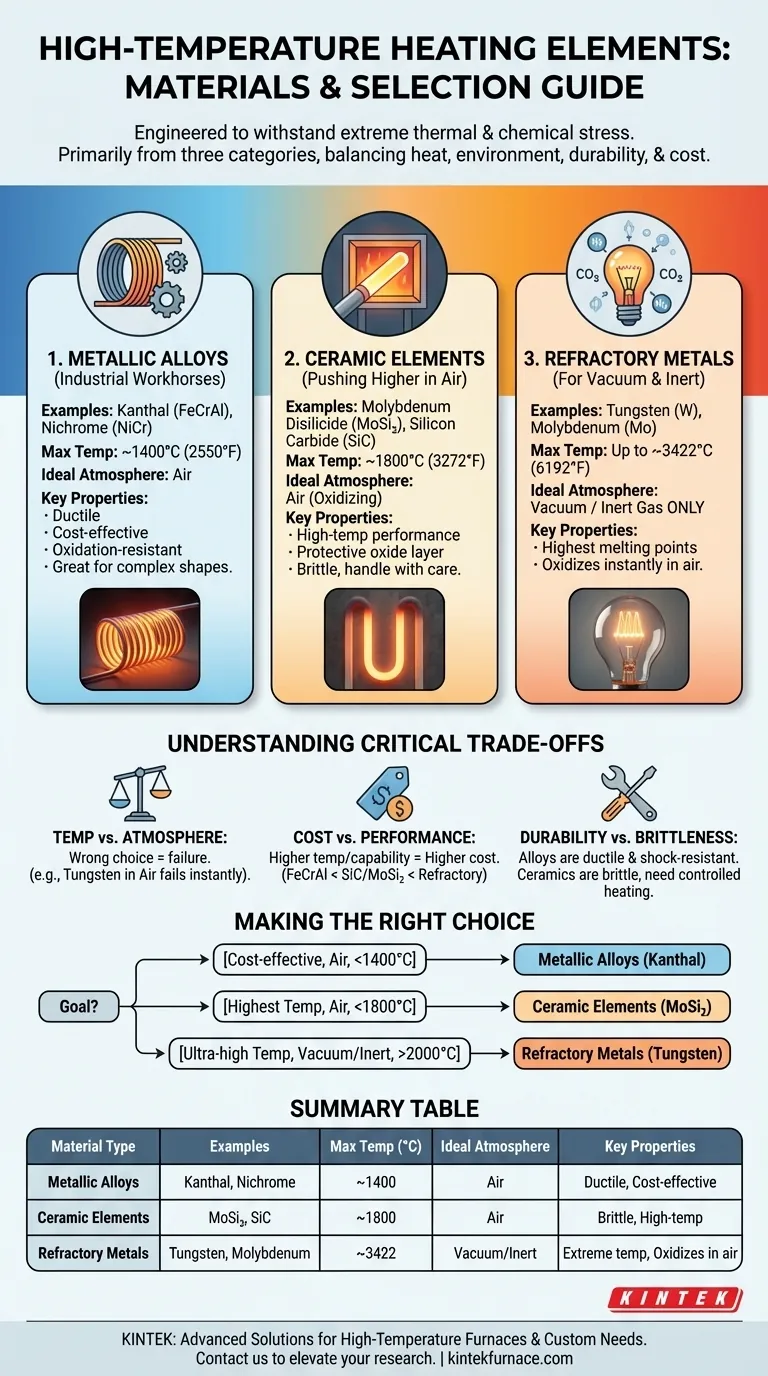
High-temperature heating elements are engineered from a select group of materials capable of withstanding extreme thermal and chemical stress. They are primarily made from three categories: specialized metallic alloys like Kanthal (FeCrAl) and Nichrome (NiCr), advanced ceramics such as Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC), and refractory metals like Tungsten (W) and Molybdenum (Mo).
The choice of material is not merely about reaching a target temperature. It is a critical engineering decision that balances maximum heat, the chemical environment (air vs. vacuum), mechanical durability, and overall system cost.
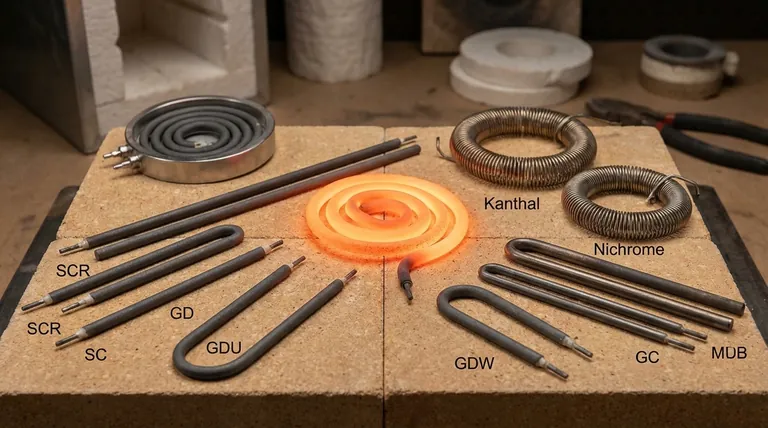

The Three Families of High-Temperature Materials
To understand high-temperature heating, it's best to group the materials by their fundamental properties and ideal operating conditions. Each family serves a distinct purpose in industrial and laboratory settings.
Metallic Alloys: The Industrial Workhorses
Metallic alloys are the most common and cost-effective choice for a wide range of heating applications in air.
They are valued for their ductility, making them easy to form into coils and complex shapes, and their excellent resistance to oxidation at high temperatures.
- Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl): Widely known by the brand name Kanthal, these alloys are the standard for industrial furnaces operating up to 1400°C (2550°F). They form a stable aluminum oxide layer that protects them from atmospheric corrosion.
- Nickel-Chromium (NiCr): Often called Nichrome, this alloy family is used in applications up to about 1250°C (2280°F). It offers better high-temperature strength and stability compared to FeCrAl in certain atmospheres.
Ceramic Elements: Pushing Higher in Air
When temperatures in an air-filled furnace must exceed the limits of metallic alloys, ceramic elements are the solution. They are brittle but offer exceptional performance.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): These elements are the top choice for reaching the highest possible temperatures in an oxidizing atmosphere, capable of operating at furnace temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). They form a protective silica glass layer at high temperatures.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Known for its high rigidity and thermal conductivity, SiC is chemically inert and can be used in furnaces up to 1625°C (2957°F). It is often used where high power density is required.
Refractory Metals: For Vacuum and Inert Atmospheres
Refractory metals have the highest melting points of all materials but come with a critical limitation: they oxidize and fail almost instantly in air at high temperatures.
Their use is exclusively reserved for vacuum furnaces or environments filled with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
- Tungsten (W): With a melting point of 3422°C (6192°F), tungsten allows for the highest operating temperatures of any common heating element, but only in a vacuum.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Molybdenum is another high-performance refractory metal used in vacuum furnaces, suitable for temperatures up to approximately 2200°C (3992°F).
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong element material doesn't just reduce performance; it can lead to catastrophic failure. The decision hinges on three key factors.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere
This is the single most important consideration. A MoSi₂ element designed for 1800°C in air will work perfectly, but a Tungsten element will burn out in seconds under the same conditions.
Conversely, a metallic alloy like Kanthal might not be suitable for the ultra-pure environment of a vacuum furnace where outgassing could be an issue.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between material cost and temperature capability.
FeCrAl alloys are the most economical. SiC and MoSi₂ elements represent a significant step up in both cost and performance. Refractory metals and the systems required to run them (vacuum pumps, inert gas supplies) are typically the most expensive.
Durability and Brittleness
Metallic alloys are ductile and resistant to mechanical and thermal shock. They can handle rapid heating and cooling cycles well.
Ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi₂ are very brittle when cold and must be handled carefully. They are also more susceptible to cracking from severe thermal shock, requiring more controlled heating and cooling profiles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific environment and temperature target will dictate the correct material.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating in air up to 1400°C: Metallic alloys like Kanthal (FeCrAl) are the clear and standard choice.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest temperatures in an air-filled furnace (up to 1800°C): Ceramic elements, particularly Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂), are required.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature operation in a vacuum or inert gas (>2000°C): Refractory metals like Tungsten are your only viable option.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is about matching the material's properties to the holistic demands of your entire thermal system.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Max Temperature (°C) | Ideal Atmosphere | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Kanthal (FeCrAl), Nichrome (NiCr) | Up to 1400 | Air | Ductile, cost-effective, oxidation-resistant |
| Ceramic Elements | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂), Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1800 | Air | Brittle, high-temperature performance, protective oxide layer |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten (W), Molybdenum (Mo) | Up to 3422 | Vacuum/Inert Gas | High melting point, oxidizes in air, for extreme temperatures |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab's high-temperature furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can elevate your research and industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















