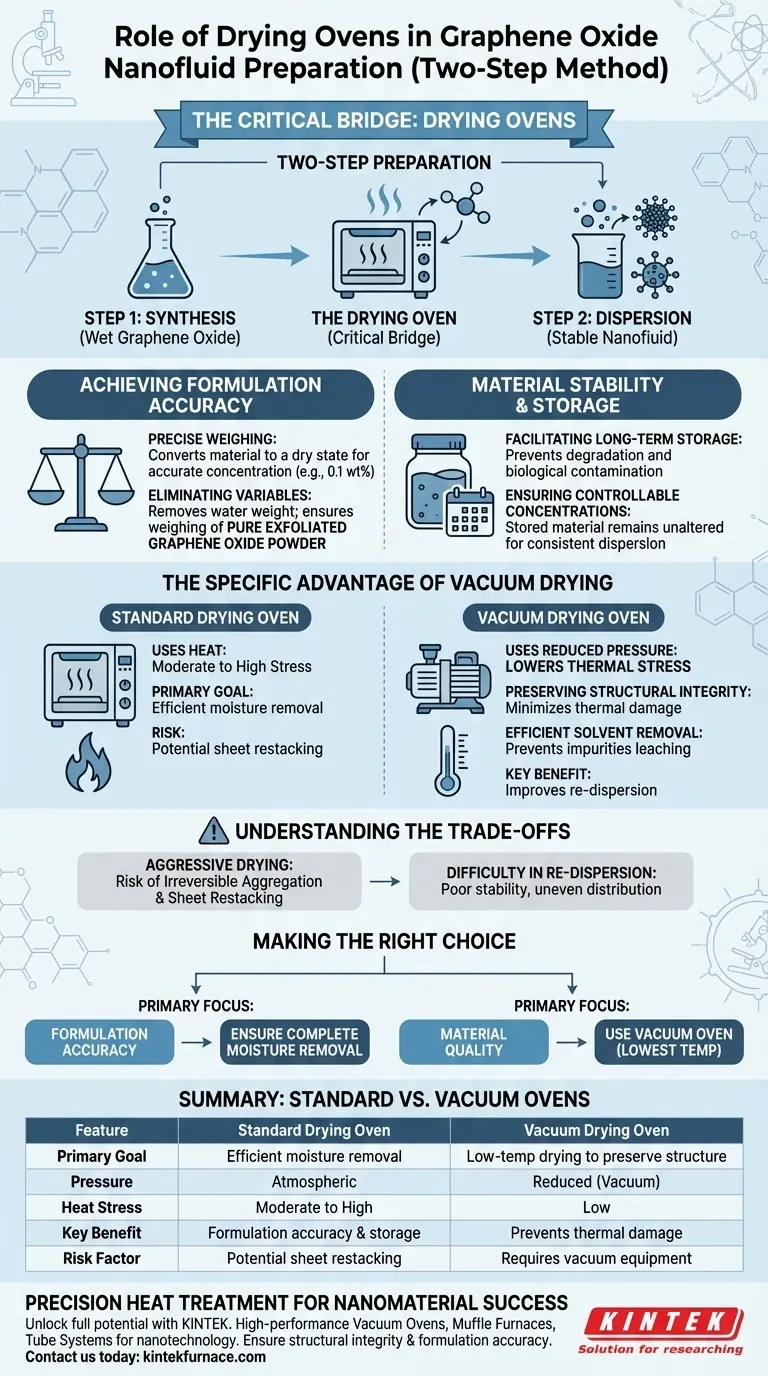
In the 'two-step' preparation method for graphene oxide nanofluids, the laboratory drying oven or vacuum oven acts as the critical bridge between synthesis and formulation. Its primary function is the controlled removal of excess moisture and residual solvents from exfoliated graphene oxide to produce a stable, dry powder.
By converting the synthesized material into a dry state, this step enables the precise weighing required to achieve accurate concentrations when re-dispersing the nanoparticles into base fluids like water or ethylene glycol.

Achieving Formulation Accuracy
The Necessity of Dry Weighing
In scientific experimentation, accuracy is paramount. You cannot create a nanofluid with a specific concentration (e.g., 0.1 wt%) if the source material contains unknown amounts of moisture.
Eliminating Variables
The drying oven removes the variable of water weight. This ensures that every milligram measured on the balance consists of pure exfoliated graphene oxide powder, allowing for reproducible results across different batches.
Material Stability and Storage
Facilitating Long-Term Storage
Synthesized nanomaterials often need to be stored before they are converted into fluids. Wet materials are prone to degradation or biological contamination over time.
Ensuring Controllable Concentrations
Drying the material allows researchers to store the nanoparticles indefinitely. When ready for the "second step" (dispersion), the material can be retrieved and mixed into the base fluid without concern that the material has altered in composition during storage.
The Specific Advantage of Vacuum Drying
Lowering Thermal Stress
While a standard oven uses heat, a vacuum drying oven utilizes reduced pressure to lower the boiling point of liquids. This allows for thorough drying at significantly lower temperatures.
Preserving Structural Integrity
By drying at lower temperatures, you minimize the risk of thermally damaging the graphene oxide structure. This is crucial for maintaining the specific properties of the nanoparticles that make them effective in heat transfer applications.
Efficient Solvent Removal
As noted in similar purification processes, vacuum environments are highly effective at removing stubborn residual washing solvents from porous structures. This prevents these impurities from leaching into your final nanofluid and affecting its performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Irreversible Aggregation
There is a delicate balance in the drying process. If graphene oxide is dried too aggressively, the sheets may stack together tightly (restacking).
Difficulty in Re-dispersion
Once these sheets restack, they become extremely difficult to separate again during the re-dispersion step. This can lead to a nanofluid with poor stability and uneven particle distribution, negating the benefits of the "two-step" method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your nanofluid preparation, select your drying parameters based on your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is formulation accuracy: Ensure the drying time is sufficient to remove all moisture so your concentration calculations are precise.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Use a vacuum oven to dry at the lowest possible temperature to protect the chemical structure of the graphene oxide.
The drying step is not merely about removing water; it is a quality control measure that defines the consistency and reliability of your final nanofluid.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Drying Oven | Vacuum Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Efficient moisture removal for dry weighing | Low-temp drying to preserve structural integrity |
| Pressure | Atmospheric | Reduced (Vacuum) |
| Heat Stress | Moderate to High | Low (Reduces boiling point of solvents) |
| Key Benefit | Formulation accuracy & long-term storage | Prevents thermal damage & improves re-dispersion |
| Risk Factor | Potential sheet restacking | Requires specific vacuum-rated equipment |
Precision Heat Treatment for Nanomaterial Success
Unlock the full potential of your graphene oxide research with KINTEK. As a leader in laboratory thermal solutions, we provide high-performance Vacuum Ovens, Muffle Furnaces, and Tube Systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of nanotechnology. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable systems that ensure your materials maintain their structural integrity and formulation accuracy.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and discover how our expert-engineered high-temp solutions can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- José A. Rodríguez, Yuri Silva Vidal. A Short Overview on Aqueous Graphene Oxide Suspensions for Application in Thermal Heating Systems. DOI: 10.25103/jestr.184.03
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does hydrogen play in the operation of a vacuum sintering furnace? Unlock Superior Sintering Quality and Efficiency
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is the contamination risk in low vacuum versus high vacuum furnaces? Balance Purity, Cost, and Throughput
- What are the key specifications of vacuum carburizing furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What innovations are being made in graphite for vacuum furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Coatings & Custom Parts
- What is the first step in the vacuum sintering process? Master the Key to High-Performance Parts
- In what way does a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system inhibit grain growth? Achieve Precision Nanostructures
- What are the general advantages of vacuum heat treatment technology? Achieve Superior Material Performance and Purity



















