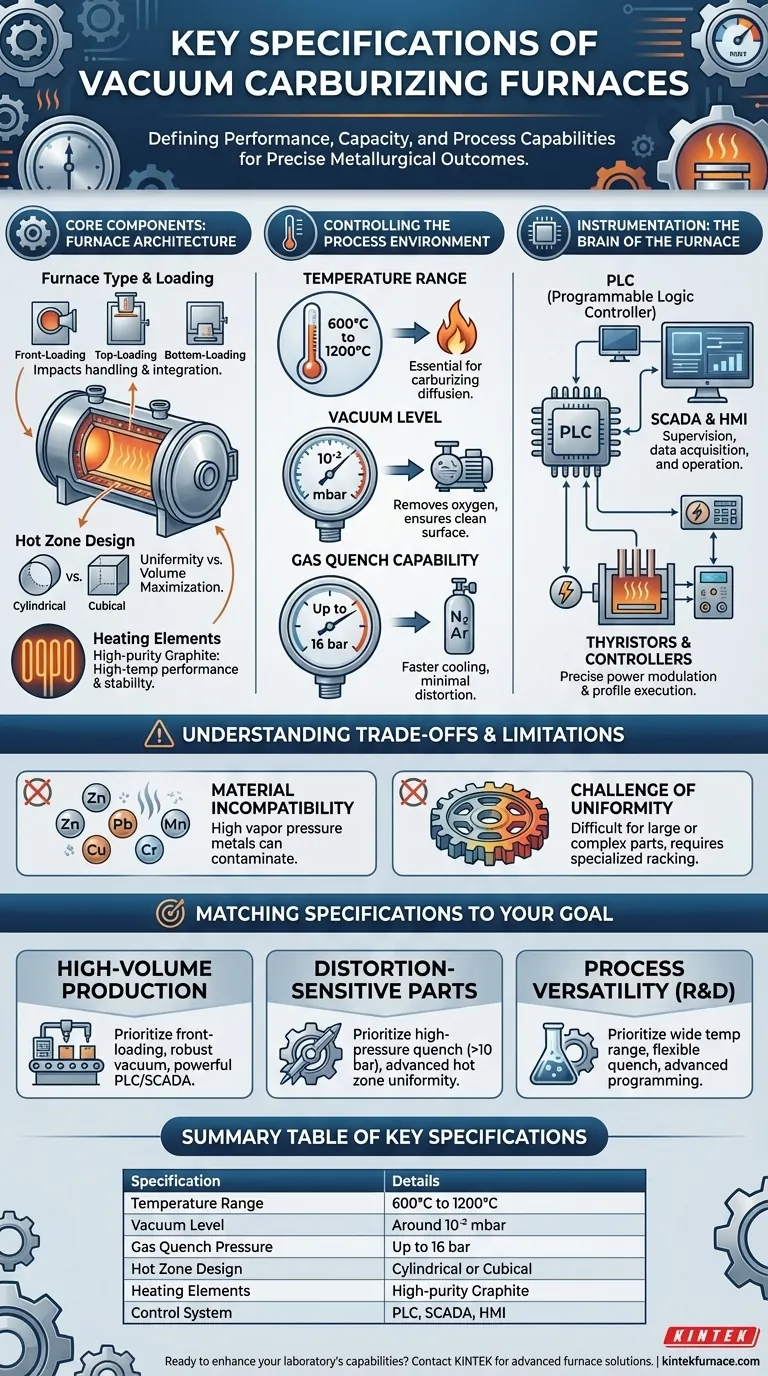
The key specifications of a vacuum carburizing furnace define its performance, capacity, and the types of materials it can process. These include the furnace type and hot zone design, temperature range (typically up to 1200°C), vacuum level (around 10⁻² mbar), the type of vacuum system used, and the pressure of its gas quench capability, which can reach up to 16 bar.
Choosing a vacuum carburizing furnace is not about finding the highest specifications, but about matching a precise set of controls—from the vacuum pump to the quench pressure—to your specific metallurgical goal. The right furnace provides control over the entire heat treatment process, ensuring consistent quality and minimal part distortion.

The Core Components: Furnace Architecture
The physical design of the furnace dictates its workflow, capacity, and heating efficiency. These foundational choices impact every part that enters the system.
Furnace Type and Loading Configuration
Furnace designs are typically "cold wall," where the outer vessel remains cool. The loading style—front-loading, top-loading, or bottom-loading—is a primary specification that impacts material handling, floor space, and integration with automated production lines.
Hot Zone Design
The hot zone is where the heating occurs. It is commonly either cylindrical or cubical. Cylindrical zones often provide better temperature uniformity, while cubical zones can maximize the usable volume for stacking or arranging parts.
Heating Elements
High-purity graphite heating elements are the standard for these furnaces. They provide excellent high-temperature performance, rapid heating rates, and long-term stability in a vacuum environment.
Controlling the Process Environment
The unique benefits of vacuum carburizing come from the precise manipulation of the furnace's internal atmosphere, temperature, and cooling cycle.
Temperature Range
A typical operational range is 600°C to 1200°C. This range is essential to accommodate the various stages of heat treatment, including the high temperatures required for the diffusion of carbon into the steel's surface during carburizing.
Vacuum System and Level
The vacuum system, often a rotary-roots pump combination or a diffusion pump, creates a low-pressure environment of around 10⁻² mbar. This vacuum is not for the carburizing itself but to remove atmospheric contaminants like oxygen, ensuring a perfectly clean surface for a uniform, high-quality case.
Gas Quench Capability
Instead of oil, vacuum furnaces use high-pressure inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to cool parts. The gas quench pressure, which can be specified up to 16 bar, is a critical parameter. Higher pressure allows for faster cooling, enabling the hardening of lower-alloy steels and providing an adjustable quench intensity to minimize distortion.
Instrumentation: The Brain of the Furnace
Modern furnaces rely on sophisticated control systems to ensure that every cycle is precise and repeatable, which is essential for meeting stringent industry standards like CQI 9.
Process Automation
Control is managed through a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), often paired with SCADA for supervision and data acquisition, and an HMI (Human-Machine Interface) for operation. This suite ensures process automation, traceability, and consistency.
Temperature and Process Control
Thyristors provide precise power modulation to the heating elements, while programmable temperature controllers and recorders execute and document the exact heating and cooling profiles required for the desired metallurgical outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum carburizing technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Material Incompatibility
Vacuum furnaces are unsuitable for processing materials with high saturated vapor pressure at treatment temperatures. Metals like zinc, lead, copper, manganese, and chromium can evaporate, contaminating the furnace and altering the workpiece's surface properties.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving perfectly uniform heating and quenching can be difficult for very large parts or those with complex geometries. This often requires specialized part racking, advanced furnace baffling, and carefully designed gas quench nozzles to ensure all surfaces are treated evenly.
Matching Furnace Specifications to Your Goal
The ideal specifications are entirely dependent on your application. Use these guidelines to prioritize what matters most for your operation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Prioritize a front-loading design for easier automation, a robust vacuum system for fast pump-down cycles, and a powerful PLC/SCADA system for process repeatability.
- If your primary focus is distortion-sensitive parts (e.g., aerospace gears): A high-pressure gas quench (above 10 bar) and advanced temperature uniformity controls within the hot zone are your most critical specifications.
- If your primary focus is process versatility for R&D: Look for a furnace with a wide operating temperature range, flexible gas quench pressure settings, and advanced instrumentation that allows for easy programming of new cycles.
Ultimately, understanding these specifications empowers you to select a furnace that delivers not just heat, but precise and repeatable metallurgical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 600°C to 1200°C |
| Vacuum Level | Around 10⁻² mbar |
| Gas Quench Pressure | Up to 16 bar |
| Hot Zone Design | Cylindrical or Cubical |
| Heating Elements | High-purity Graphite |
| Control System | PLC, SCADA, HMI |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with precision-engineered high-temperature furnaces? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your heat treatment processes and achieve consistent, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















