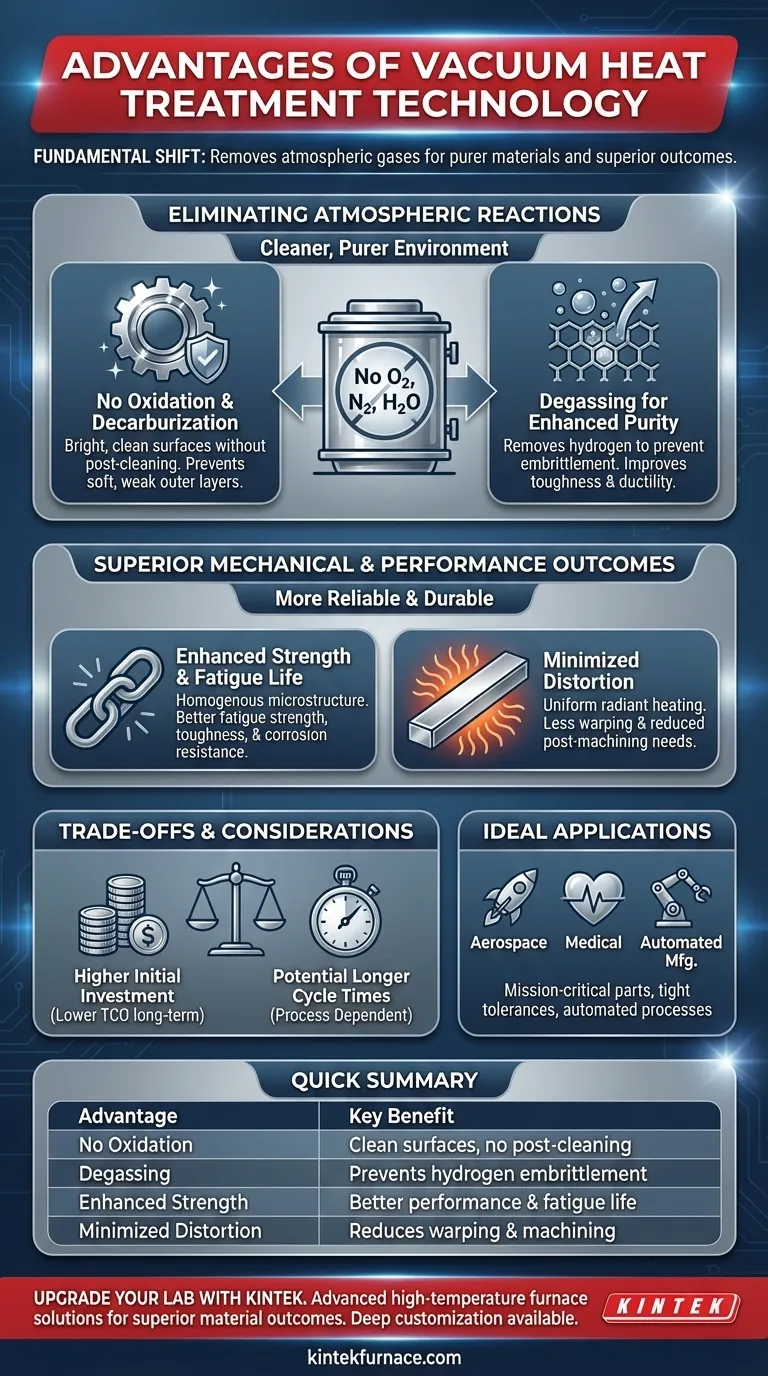
At its core, vacuum heat treatment provides superior material outcomes by fundamentally changing the processing environment. Instead of battling atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, it removes them entirely, resulting in unparalleled control over the final properties and surface finish of a component.
The primary advantage of vacuum heat treatment is not just one feature, but a cascade of benefits that stem from a single principle: by removing the atmosphere, you eliminate unwanted chemical reactions, leading to purer materials, cleaner surfaces, and more predictable results.

The Fundamental Advantage: Eliminating Atmospheric Reactions
Traditional heat treatment occurs in an atmosphere that actively reacts with the metal's surface. Vacuum technology sidesteps this entire problem by creating a controlled, inert environment.
No Oxidation or Decarburization
By removing oxygen, the process guarantees that parts emerge with a bright, clean surface, free from the oxide scale that plagues conventional methods. This eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning operations like sandblasting or pickling.
More importantly, it prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel—which can create a soft, weak outer layer and compromise the part's performance and wear resistance.
Degassing for Enhanced Purity
The vacuum environment actively pulls trapped gases, most notably hydrogen, out of the metal's internal structure.
This degassing effect is critical for preventing hydrogen embrittlement, a phenomenon that can cause catastrophic, brittle failure in high-strength steels. The result is a material with significantly improved toughness, ductility, and plasticity.
Superior Mechanical and Performance Outcomes
A cleaner, purer material processed with precise thermal control inherently delivers better and more reliable performance.
Enhanced Strength and Fatigue Life
By preventing surface and subsurface imperfections caused by oxidation and contamination, vacuum treatment produces a more homogenous microstructure.
This uniformity directly translates to improved fatigue strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, as there are fewer microscopic stress points where cracks can initiate.
Minimized Distortion
In a vacuum, heat is transferred primarily through radiation, which is inherently more uniform than convection at high temperatures. This slow, even heating minimizes thermal stress across the component.
Combined with controlled gas quenching, this precise thermal management results in significantly less distortion and warping. This reduces the need for costly post-heat-treat machining to bring parts back into tolerance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the advantages are significant, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. It involves a different set of operational and economic considerations compared to traditional furnace technologies.
Initial Capital Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a higher upfront capital cost than their atmospheric counterparts. The complexity of the vacuum pumps, chamber, and control systems contributes to this expense.
However, this cost can often be justified by a lower total cost of ownership when factoring in the elimination of post-processing, reduced scrap rates, and the lack of need for expensive consumable process gases like argon.
Cycle Time Variations
Heating via radiation can be slower at lower temperatures compared to forced convection methods. This can sometimes lead to longer overall cycle times for certain processes.
Modern vacuum furnaces often mitigate this with high-pressure gas quenching and optimized heating schedules, but it remains a key variable to consider during process planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use vacuum heat treatment should be driven by the specific requirements of your components and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: For aerospace, medical, or high-performance automotive parts, the material purity and prevention of hydrogen embrittlement make vacuum treatment the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is reducing post-processing costs: For complex geometries or parts with tight tolerances, the minimal distortion and clean surface finish can deliver a significant return on investment by eliminating grinding and cleaning steps.
- If your primary focus is process control and automation: The high degree of repeatability, safety, and clean operation makes vacuum technology ideal for modern, data-driven manufacturing environments.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum heat treatment is an investment in process control, quality, and predictability.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| No Oxidation/Decarburization | Bright, clean surfaces without post-treatment cleaning |
| Degassing | Removes hydrogen to prevent embrittlement and improve toughness |
| Enhanced Strength/Fatigue Life | Homogenous microstructure for better performance |
| Minimized Distortion | Uniform heating reduces warping and machining needs |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable vacuum and atmosphere furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior material outcomes and cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your heat treatment processes and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















