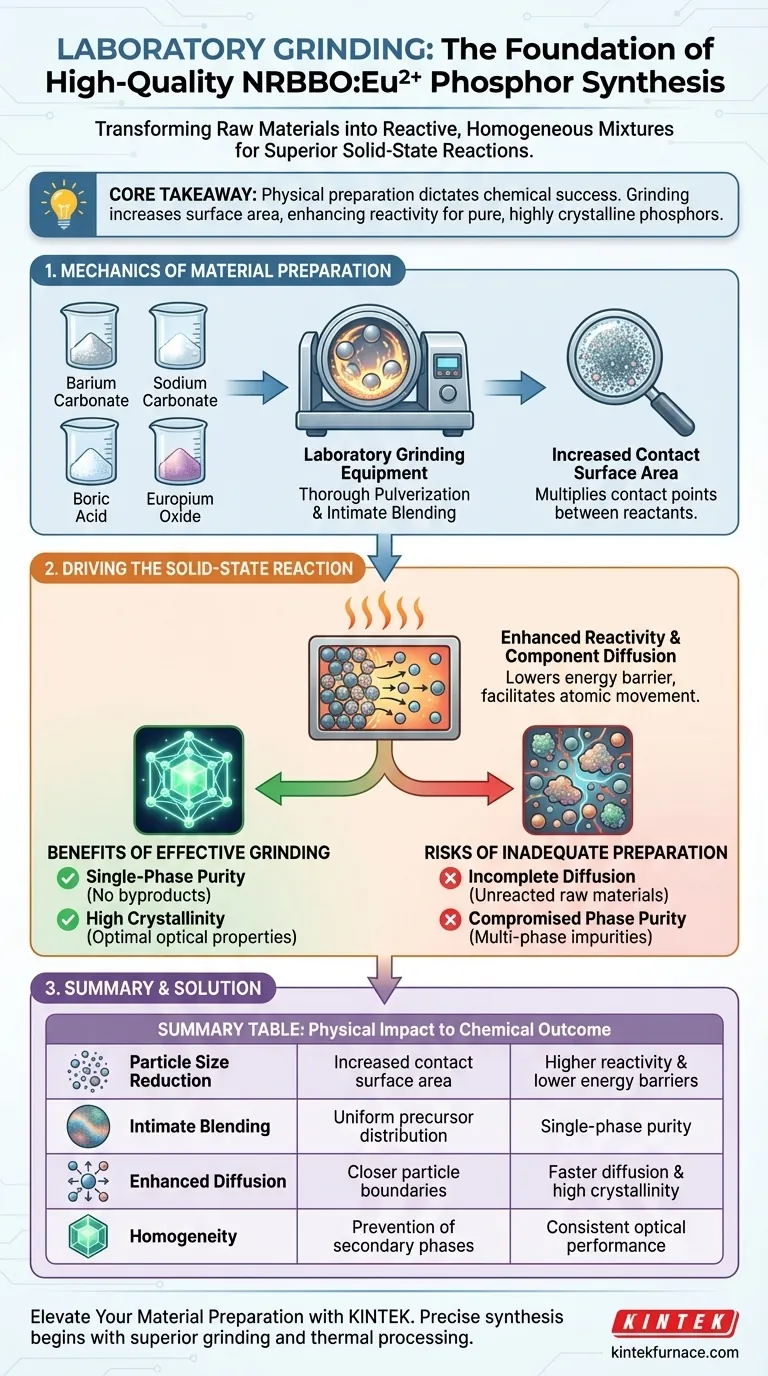
Laboratory grinding equipment serves as the critical foundation for synthesizing high-quality NRBBO:Eu2+ phosphors by transforming raw materials into a highly reactive, homogeneous mixture. By thoroughly pulverizing and blending precursors like barium carbonate and europium oxide, this equipment maximizes the contact surface area between particles, which is the primary driver for a successful solid-state reaction.
Core Takeaway The physical preparation of raw materials directly dictates the chemical success of the final product. Grinding increases particle surface area and enhances reactivity, facilitating the component diffusion necessary to produce pure, single-phase NRBBO crystals with high crystallinity.

The Mechanics of Material Preparation
Thorough Pulverization and Blending
The synthesis process begins with specific raw materials: barium carbonate, sodium carbonate, boric acid, and europium oxide. Laboratory grinding equipment is used to mechanically break these compounds down.
This process ensures that these distinct components are not just mixed, but intimately blended. The goal is to create a uniform distribution of reactants before any heat is applied.
Increasing Contact Surface Area
The primary physical outcome of this grinding process is a drastic increase in the contact surface area between the powders.
In solid-state chemistry, reactions only occur where particles touch. By pulverizing the materials into finer powders, the equipment multiplies the number of contact points between the reactants.
Driving the Solid-State Reaction
Enhancing Reactivity
Because the precursors remain in a solid state during the initial reaction phases, their ability to react is limited by their proximity.
The increased surface area achieved through grinding significantly enhances the reactivity of the mixture. This lowers the energy barrier required for the reaction to initiate.
Promoting Component Diffusion
For the NRBBO crystal to form, atoms must physically move (diffuse) across particle boundaries.
The close contact and fine particle size facilitate efficient component diffusion during high-temperature treatment. This diffusion is the mechanism that transforms the separate raw ingredients into a unified compound.
The Impact on Final Product Quality
Ensuring Single-Phase Purity
The uniformity provided by laboratory grinding helps prevent the formation of unwanted byproducts.
When diffusion is efficient and the mix is homogeneous, the result is a single-phase product. This means the material consists entirely of the desired NRBBO structure, without impurities that could degrade performance.
Achieving High Crystallinity
The structural order of the final phosphor is paramount.
The thorough mixing and enhanced diffusion allow the crystal lattice to form correctly and completely. This results in high crystallinity, a quality marker that indicates a well-ordered atomic structure essential for optimal optical properties.
The Risks of Inadequate Preparation
The Consequence of Poor Diffusion
If the grinding process is bypassed or performed poorly, the contact surface area remains low.
This leads to incomplete diffusion. Without sufficient contact, the high-temperature reaction may fail to fully integrate the europium or other components, leaving unreacted raw materials in the final batch.
Compromised Phase Purity
A lack of homogeneity in the raw mix often results in multi-phase products.
Instead of a pure NRBBO crystal, you may end up with a mixture containing secondary phases. These impurities disrupt the crystal lattice and generally result in a phosphor with inferior structural integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of NRBBO:Eu2+ phosphors, you must prioritize the physical state of your precursors.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your grinding protocol is sufficient to create a perfectly homogeneous blend, eliminating the risk of secondary impurity phases.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Maximize the pulverization duration to achieve the finest possible particle size, which promotes the diffusion required for high crystallinity.
Effective grinding is not merely a mixing step; it is the essential catalyst that enables the formation of a pure, highly crystalline phosphor.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Physical Impact | Chemical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Increased contact surface area | Higher reactivity & lower energy barriers |
| Intimate Blending | Uniform precursor distribution | Single-phase purity (no impurities) |
| Enhanced Diffusion | Closer particle boundaries | Faster component diffusion & high crystallinity |
| Homogeneity | Prevention of secondary phases | Consistent optical performance |
Elevate Your Material Preparation with KINTEK
Precise phosphor synthesis begins with superior material preparation. At KINTEK, we understand that high crystallinity and phase purity depend on the quality of your grinding and thermal processing.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces and grinding solutions—all customizable for your unique research needs.
Don't let inadequate diffusion compromise your results. Contact us today to discover how our equipment can streamline your laboratory workflow and deliver the high-performance materials your project demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Runtian Kang, Yuhua Wang. Chemical Pressure‐Induced FWHM Narrowing in Narrowband Green Phosphors for Laser Displays with Ultra‐High Saturation Thresholds. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202505385
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is lab vacuum used for? Mastering Environmental Control for Purity and Precision
- How does the hardness of alumina ceramics compare to other materials? Discover Its Superior Wear Resistance
- Why is the selection of high-purity crucibles critical for niobate sintering? Ensure Precision in High-Temp Synthesis
- What are the primary functions of a quartz tube reactor? Enhance Hydrogen Production and Induction Efficiency
- What is the critical role of the vacuum filter in a waste magnesium vacuum distillation system? The Essential Protection for Your Vacuum Pump
- Why are high-purity alumina boats utilized as precursor containers in MoS2 synthesis? Ensure High-Quality 2D Materials
- What are the technical advantages of using a high-purity alumina crucible for the synthesis of MnBi2Te4?
- How does a vacuum pump facilitate the pre-treatment of modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes? Optimize Surface Activation


















