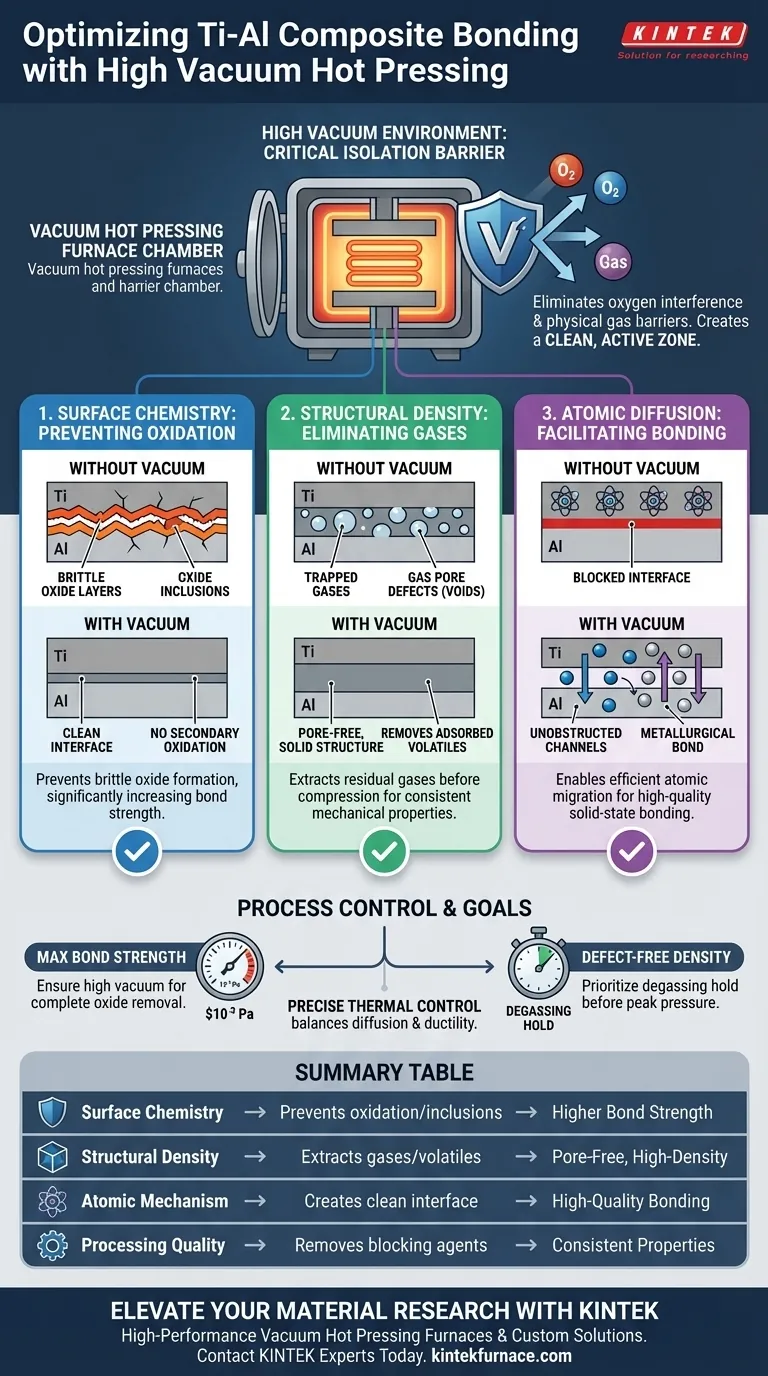
The high vacuum environment acts as a critical isolation barrier that prevents the chemical degradation of reactive metals during thermal processing. In the context of Ti-Al layered composites, this environment serves two primary functions: it halts the formation of brittle oxides and actively removes trapped gases that would otherwise create structural voids.
Core Takeaway: The structural integrity of Ti-Al composites is directly dependent on the purity of the bonding interface. The vacuum environment eliminates oxygen interference and physical gas barriers, converting the contact surface into a clean, active zone that allows metal atoms to diffuse freely and form a high-strength metallurgical bond.

The Role of Vacuum in Surface Chemistry
Preventing Secondary Oxidation
Titanium and aluminum are highly active metals that oxidize rapidly when exposed to high temperatures.
Without a vacuum, heating these metals results in the immediate formation of brittle oxide layers on the surface of the raw materials.
The vacuum hot pressing furnace isolates these metals from oxygen, preventing "secondary oxidation" during the heating phase.
Eliminating Brittle Inclusions
Oxides are contaminants that act as barriers to bonding.
If oxide layers are allowed to form, they become trapped within the composite as oxide inclusions.
These inclusions significantly reduce the interfacial bond strength and can serve as initiation sites for material failure.
The Role of Vacuum in Structural Density
Removal of Adsorbed Gases
Microscopic amounts of gas are often adsorbed onto the surface of metal foils or trapped between stacked layers.
Under normal pressure, these gases would be sealed inside the composite during compression.
The vacuum environment extracts these residual gases and volatile impurities before the material is fully compressed, promoting pore closure.
Preventing Gas Pore Defects
The evacuation of interlayer gases is essential for achieving high material density.
By removing these volatiles, the process avoids the formation of gas pore defects (voids) within the final composite.
This ensures the production of a solid, crack-free layered structure with consistent mechanical properties.
Facilitating Atomic Diffusion
Creating a Clean Interface
The fundamental mechanism of solid-state bonding is atomic diffusion—atoms moving from one material into the other.
This process requires a pristine, clean contact interface to function correctly.
The vacuum environment ensures that the surface remains free of blocking agents like oxide films or contaminants.
Unobstructed Elemental Channels
When the interface is clean, it creates "unobstructed elemental diffusion channels."
This allows titanium and aluminum atoms to migrate across the boundary efficiently.
The result is a high-quality metallurgical bond formed at temperatures below the melting point of the metals.
Understanding the Process Constraints
The Necessity of Precise Control
While the vacuum environment creates the potential for a perfect bond, it does not guarantee the mechanical properties on its own.
The vacuum creates a highly active surface that is primed for diffusion, but this activity must be managed.
Balancing Diffusion and Ductility
The vacuum allows for unobstructed diffusion, but the thickness of the diffusion layer must still be controlled via temperature and pressure.
If diffusion is too aggressive (allowed by the clean vacuum interface), the material may form excessive intermetallic compounds.
Therefore, the vacuum is a prerequisite for bonding, but thermal control determines the final balance between material strength and ductility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If your primary focus is Maximum Bond Strength:
- Ensure the vacuum level reaches at least $10^{-3}$ Pa to guarantee the complete removal of oxide barriers, allowing for maximum atomic interlock.
If your primary focus is Defect-Free Density:
- Prioritize a vacuum cycle that includes a "degassing hold" to fully exhaust adsorbed gases and volatiles between layers before applying peak mechanical pressure.
The vacuum environment is not merely a protective measure; it is the active enabler that transforms separate metal layers into a unified, high-performance composite.
Summary Table:
| Effect Category | Impact of Vacuum on Ti-Al Bonding | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Chemistry | Prevents secondary oxidation and brittle inclusions | Higher interfacial bond strength |
| Structural Density | Extracts adsorbed gases and eliminates volatiles | Pore-free, high-density composite |
| Atomic Mechanism | Creates clean interface for unobstructed diffusion | High-quality metallurgical bonding |
| Processing Quality | Removes blocking agents like oxide films | Consistent mechanical properties |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect Ti-Al metallurgical bond requires more than just heat; it requires an uncompromising vacuum environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, and CVD systems designed to eliminate contaminants and maximize atomic diffusion. Whether you need a standard solution or a system customized for your unique needs, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the precision control your composites demand.
Ready to eliminate defects and boost material density? Contact KINTEK Experts Today
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a hot press machine work? Master Heat, Pressure, and Time for Perfect Results
- What is the purpose of vacuum hot pressing? Achieve Superior Material Density and Purity
- Why are graphite molds necessary during the hot pressing sintering process of Fe-Cu-Ni-Sn-VN? Essential Sintering Tools
- What are the different types of heating methods in vacuum hot press sintering furnaces? Compare Resistance vs. Induction
- What are the technical advantages of using a HIP furnace for MgB2 wires? Unlock Peak Superconducting Density
- What are the processing advantages of SPS systems for LaFeO3 ceramics? Achieve High Density with Precision
- What are the typical operational steps when using a vacuum press? Master Flawless Bonding and Forming
- What are the advantages of industrial SPS vs traditional sintering for SiC? Superior Density and Fine-Grain Structure



















