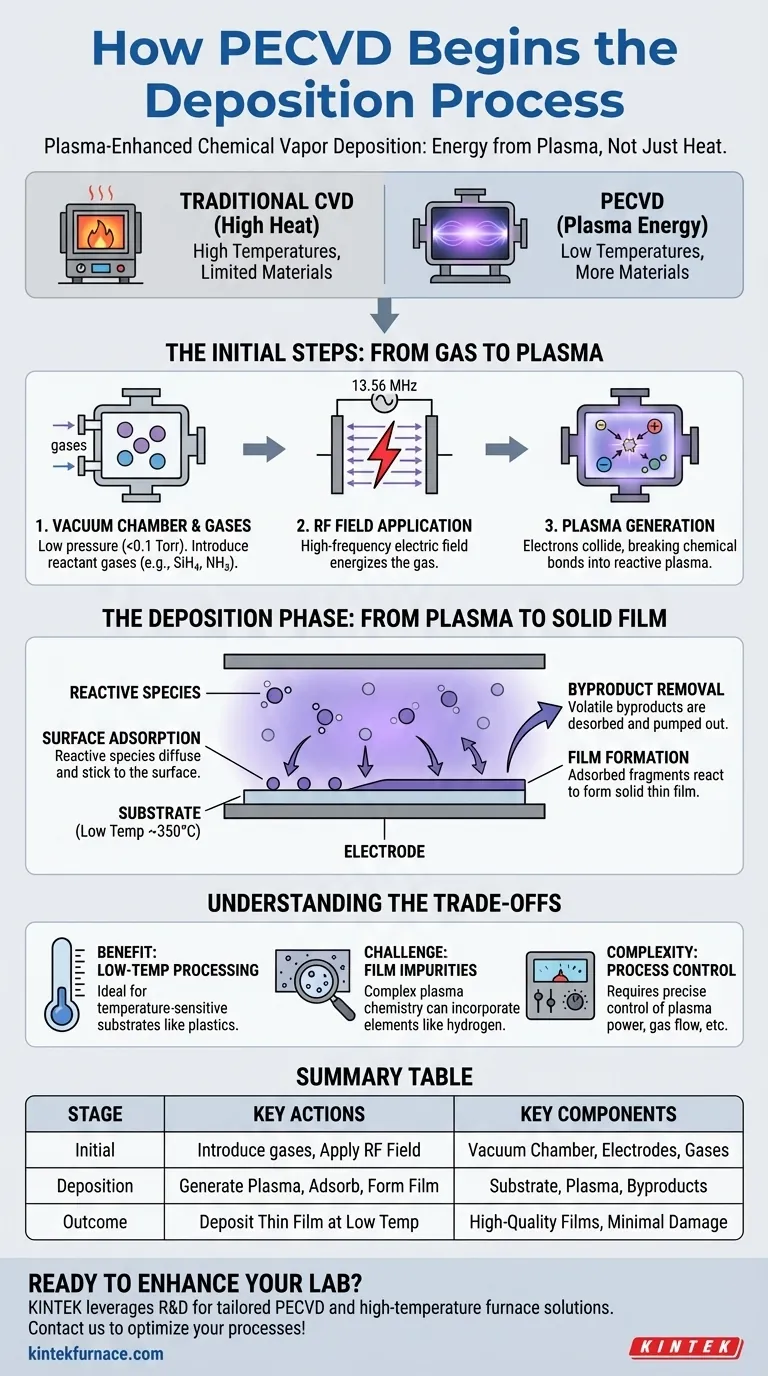
At its core, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) begins in two distinct stages. First, reactant gases, which are the precursors for the film, are introduced into a low-pressure vacuum chamber. Immediately after, a high-frequency electric field is applied between two electrodes within the chamber, energizing the gas and igniting it into a plasma, which is the key to the entire process.
The fundamental difference between PECVD and other methods is its use of energy from a plasma, rather than high heat, to drive the chemical reactions. This allows for the deposition of high-quality thin films at significantly lower temperatures, making it possible to coat materials that would be damaged by thermal processes.
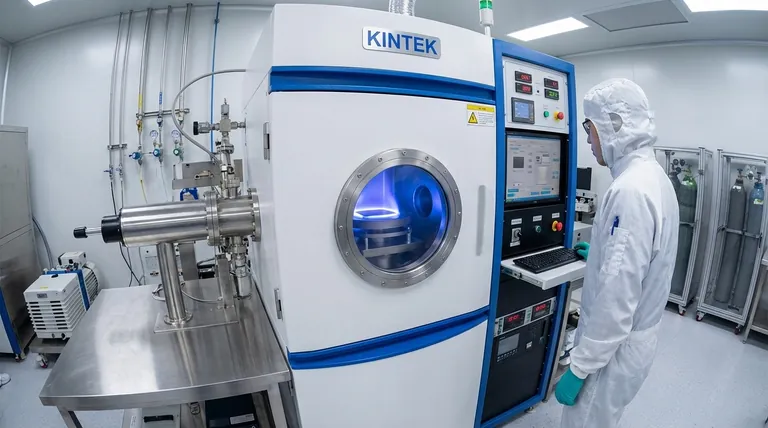

The Initial Steps: From Gas to Plasma
To understand PECVD, you must first understand how the reactive environment is created. The process is not driven by heat alone, but by the energetic state of matter known as plasma.
Step 1: Establishing the Environment
The process starts within a vacuum chamber held at a very low pressure, typically below 0.1 Torr. Into this controlled environment, a precise mixture of reactant gases is introduced. These gases, such as silane (SiH4) and ammonia (NH3) for depositing silicon nitride, serve as the chemical building blocks for the final film.
Step 2: Generating the Plasma
Once the gases have stabilized, a powerful, high-frequency electric field is applied across a pair of parallel electrodes. This is often an RF (Radio Frequency) field, commonly at 13.56 MHz. This electrical energy does not heat the gas directly in the traditional sense.
Step 3: Creating Reactive Species
Instead, the electric field accelerates free electrons within the chamber. These highly energetic electrons (100-300 eV) collide with the neutral precursor gas molecules. These collisions are powerful enough to break the molecules' chemical bonds, creating a volatile mix of ions, radicals, and other excited, reactive fragments. This ionized gas is the plasma, often visible as a characteristic glow discharge.
The Deposition Phase: From Plasma to Solid Film
With the reactive plasma established, the focus shifts to building the film on the target material, known as the substrate.
The Role of the Substrate
The substrate is placed on one of the electrodes, which is often heated. However, this temperature is relatively low (around 350°C), far below what would be required for purely thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This low temperature is the primary advantage of PECVD.
Surface Reactions and Adsorption
The highly reactive species generated in the plasma diffuse and travel towards the substrate. Upon reaching the substrate, they "stick" to the surface in a process called chemical adsorption. Their high reactivity means they are primed to form new chemical bonds.
Film Formation and Byproduct Removal
On the surface, these adsorbed fragments react with each other to form a stable, solid thin film. As the desired film material is formed, other volatile byproducts are also created. These byproducts are desorbed (released) from the surface and are continuously pumped out of the vacuum chamber, leaving behind only the deposited film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its inherent benefits and challenges is critical for proper application.
The Benefit: Low-Temperature Processing
The most significant advantage of PECVD is its ability to deposit films on temperature-sensitive substrates. Materials like plastics, organic electronics, or certain semiconductor devices cannot withstand the high heat of traditional CVD. PECVD bypasses this limitation by using plasma energy.
The Challenge: Film Impurities
The chemical reactions in a plasma are complex and can lead to the incorporation of unwanted elements into the film. For instance, when using hydrogen-containing precursors like silane, it is common for hydrogen to be embedded in the final film, which can alter its electrical or optical properties.
The Complexity: Process Control
PECVD introduces more process variables than thermal CVD. In addition to temperature, pressure, and gas flow, one must also precisely control plasma power. Each parameter affects the plasma density and chemistry, which in turn influences deposition rate, film uniformity, and material properties, making process optimization more intricate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use PECVD should be driven by the specific requirements of your substrate and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is depositing a film on a temperature-sensitive material: PECVD is the definitive and often only choice, as it protects the substrate from thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest film purity for a heat-resistant substrate: You might consider traditional high-temperature CVD, which can produce films with fewer incorporated impurities like hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is balancing deposition speed with moderate quality: Optimizing PECVD's plasma power and gas flow offers a highly effective path for achieving rapid film growth at low temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding that PECVD separates the energy source (plasma) from the thermal environment (substrate) is the key to leveraging its unique capabilities for advanced materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Actions | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | Introduce reactant gases, apply RF electric field | Vacuum chamber, electrodes, gases (e.g., SiH4, NH3) |
| Deposition | Generate plasma, adsorb reactive species, form film | Substrate, plasma, byproducts |
| Outcome | Deposit thin film at low temperatures (e.g., 350°C) | High-quality films, minimal thermal damage |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced PECVD systems? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs for low-temperature deposition and more. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















