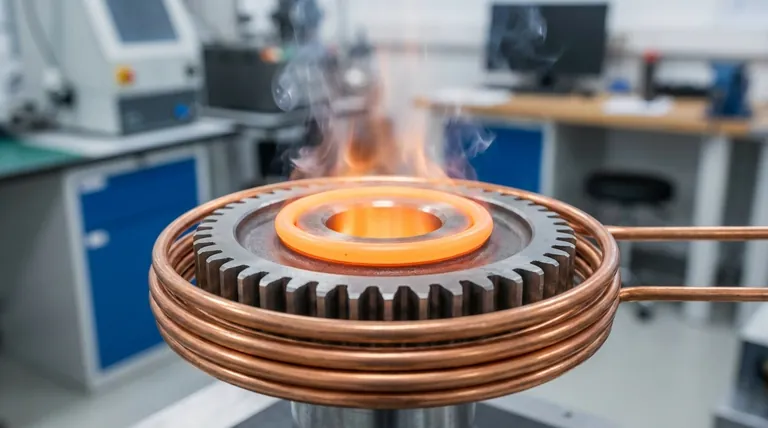
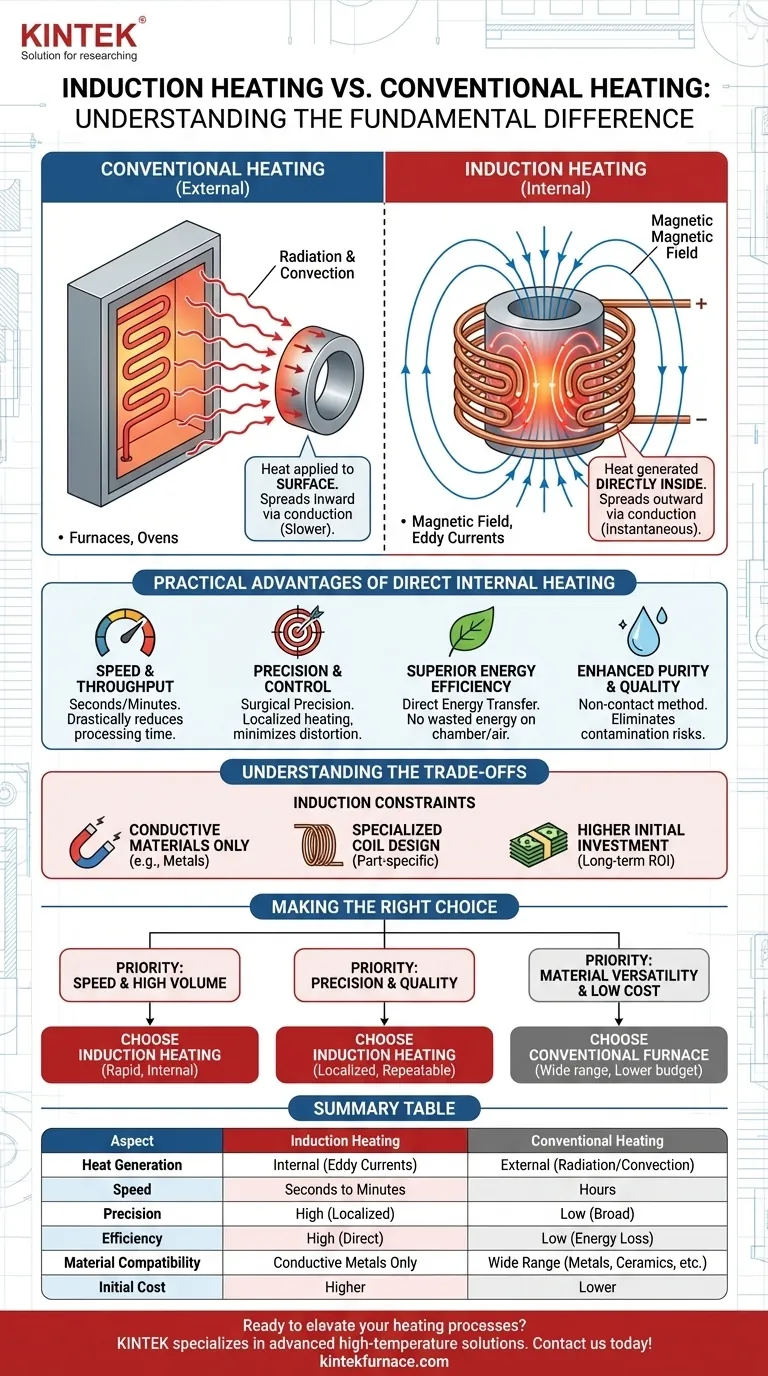
The fundamental difference lies in where the heat is generated. Traditional heating methods, like furnaces, apply heat to the surface of an object using radiation and convection. In contrast, induction heating uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly inside the object itself, which then spreads outward via conduction.
While conventional ovens heat the air around the food, induction heats the pan directly. This core distinction explains why induction offers unparalleled speed, precision, and efficiency for heating conductive materials.

The Core Mechanism: Internal vs. External Heating
To understand the practical benefits of induction, you must first grasp the fundamental difference in how heat is delivered to the workpiece.
How Conventional Heating Works (External)
Traditional furnaces, whether gas or electric, operate by heating a chamber or element to a very high temperature.
This heat is then transferred to the workpiece through two primary methods:
- Radiation: Infrared energy travels from the hot source to the object's surface.
- Convection: Hot gases in the chamber circulate and transfer heat to the object.
In this model, the heat must soak in from the outside, which is a comparatively slow and inefficient process.
How Induction Heating Works (Internal)
Induction heating is a non-contact process that turns the workpiece into its own heat source.
It uses an alternating electric current passed through a copper coil to create a powerful, oscillating magnetic field. When a conductive material (like steel) is placed within this field, it induces electrical currents—known as eddy currents—inside the part.
The material's natural electrical resistance fights these currents, generating precise and instantaneous heat from within.
Practical Advantages of Direct Internal Heating
Generating heat inside the material rather than applying it to the surface creates significant operational advantages.
Unmatched Speed and Throughput
Because heat is generated instantly and internally, induction can bring a material to temperature in seconds or minutes, whereas a furnace might take hours. This drastically reduces processing time and increases production output.
Surgical Precision and Control
The heat is only generated where the magnetic field is concentrated. By carefully designing the induction coil, you can heat a very specific area of a part without affecting adjacent components. This localized heating minimizes thermal distortion and extends the life of nearby tooling.
Superior Energy Efficiency
With induction, energy is applied directly to the workpiece. You are not wasting energy to heat a large furnace chamber, its insulation, or the surrounding air. This results in significantly higher energy efficiency and lower utility costs.
Enhanced Purity and Quality
As a non-contact method, induction heating eliminates the risk of contamination from fuel byproducts or contact with heating elements. The rapid and precise control also leads to superior consistency and higher-quality end products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
Material Constraints
The primary limitation of induction is that it only works on electrically conductive materials, primarily metals. It cannot directly heat insulators like ceramics, glass, or most polymers.
Equipment and Coil Design
Induction heating systems are specialized. The geometry of the induction coil is critical to performance and must be designed to match the specific part being heated. A change in product shape often requires a new, custom-designed coil.
Higher Initial Investment
The initial capital cost for an induction power supply and its associated coils can be higher than that of a simple gas furnace. The return on investment comes from long-term gains in speed, efficiency, and quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating technology requires aligning its strengths with your most important goals.
- If your primary focus is speed and high-volume production: Induction heating is the superior choice due to its rapid, internal heating capabilities.
- If your primary focus is precision, quality, and process control: Induction's localized heating and repeatability are unmatched for applications like surface hardening or brazing.
- If your primary focus is material versatility and low initial cost: A conventional furnace is more practical for heating a wide variety of materials, including non-metals, on a limited budget.
Ultimately, choosing induction is a strategic decision to prioritize operational efficiency and precision over flexibility and initial upfront cost.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Heating | Conventional Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Internal (via eddy currents) | External (via radiation/convection) |
| Speed | Seconds to minutes | Hours |
| Precision | High (localized heating) | Low (broad heating) |
| Efficiency | High (direct energy transfer) | Low (energy loss to surroundings) |
| Material Compatibility | Conductive metals only | Wide range (metals, ceramics, etc.) |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to elevate your heating processes with induction technology? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, manufacturing, or research, our induction heating systems can boost your speed, precision, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















