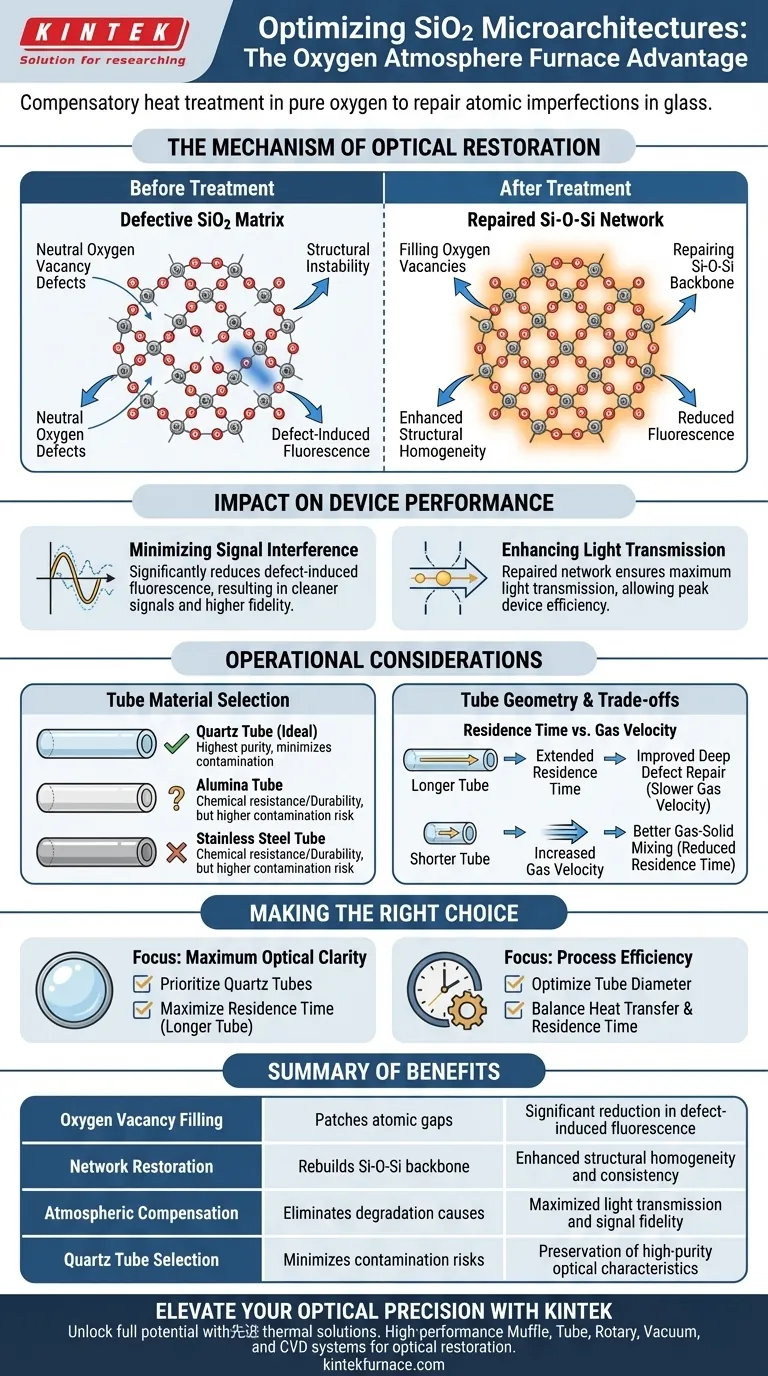
An oxygen atmosphere furnace optimizes SiO2 microarchitectures by subjecting the material to a compensatory heat treatment in a pure oxygen environment. This process directly targets atomic-level imperfections by filling neutral oxygen vacancy defects within the glass matrix and repairing the fundamental Si-O-Si network structure. By restoring the integrity of the silica network, the furnace eliminates the structural causes of optical degradation.
The core function of this treatment is the significant reduction of defect-induced fluorescence. By healing the glass matrix, the process enhances light transmission and minimizes signal interference, which is non-negotiable for high-performance micro-optical devices.

The Mechanism of Optical Restoration
Filling Oxygen Vacancies
The primary challenge in annealed SiO2 microarchitectures is the presence of neutral oxygen vacancy defects. These are atomic gaps in the material where oxygen atoms are missing from the lattice.
Heating the structure in an oxygen-rich atmosphere forces oxygen into the matrix. This "compensatory" action fills these vacancies, effectively patching the holes in the atomic structure.
Repairing the Si-O-Si Network
Beyond simple vacancy filling, the thermal energy combined with the oxygen atmosphere actively rebuilds the Si-O-Si network. This network is the backbone of the glass's structural stability.
A continuous, repaired network ensures the material behaves consistently when interacting with light. This structural homogeneity is the physical basis for improved optical performance.
Impact on Device Performance
Minimizing Signal Interference
Defects in the silica structure often lead to unwanted fluorescence. When light passes through a defective matrix, the material absorbs and re-emits light, creating background noise.
By eliminating these defects, the oxygen furnace treatment drastically reduces this fluorescence. This results in a cleaner signal and higher fidelity in optical applications.
Enhancing Light Transmission
Optical purity is directly linked to the material's structural perfection. A repaired Si-O-Si network offers a clear path for photons.
This reduction in scattering and absorption allows for maximum light transmission, ensuring the micro-optical device operates at peak efficiency.
Operational Considerations for Furnace Configuration
Tube Material Selection
The choice of the furnace tube is critical for maintaining the high purity required for optical silica. Quartz tubes are typically the ideal choice for these high-purity processes.
While alumina offers chemical resistance and stainless steel offers durability, quartz minimizes the risk of introducing contaminants that could negate the benefits of the oxygen treatment.
The Role of Tube Geometry
The physical dimensions of the furnace tube—specifically length and diameter—dictate the efficiency of the treatment. These dimensions control the heat transfer dynamics and the gas flow.
A longer tube generally promotes longer residence times. This extended exposure is often necessary to ensure the oxygen has sufficient time to diffuse into the matrix and complete the repair reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Residence Time vs. Gas Velocity
There is an inherent trade-off in the design of the furnace tube regarding reaction efficiency.
A longer tube increases residence time, which improves reaction efficiency for deep defect repair. However, this may reduce gas velocity, potentially leading to stagnant zones if not managed correctly.
Conversely, a shorter tube increases gas velocity and improves gas-solid mixing. The downside is a reduced residence time, which may be insufficient for thoroughly healing deep-seated oxygen vacancies in denser microarchitectures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the optical performance of SiO2 structures, you must align your furnace configuration with your specific purity requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum optical clarity: Prioritize the use of quartz tubes to prevent contamination and utilize a longer tube design to ensure maximum residence time for defect repair.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Consider optimizing tube diameter to balance heat transfer rates against the residence time required to reduce fluorescence.
The oxygen atmosphere furnace is not just a heating tool; it is a restorative instrument that rebuilds the atomic foundation of silica to ensure pristine optical performance.
Summary Table:
| Optimization Mechanism | Impact on SiO2 Material | Resulting Optical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Vacancy Filling | Patches atomic gaps in the glass matrix | Significant reduction in defect-induced fluorescence |
| Network Restoration | Rebuilds the fundamental Si-O-Si backbone | Enhanced structural homogeneity and consistency |
| Atmospheric Compensation | Eliminates structural causes of degradation | Maximized light transmission and signal fidelity |
| Quartz Tube Selection | Minimizes chemical contamination risks | Preservation of high-purity optical characteristics |
Elevate Your Optical Precision with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your silica microarchitectures with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of optical material restoration.
Whether you require high-purity quartz tube configurations for defect repair or customizable laboratory furnaces for unique research needs, our engineering team is ready to deliver the precision you deserve. Contact us today to optimize your heat treatment process.
Visual Guide
References
- Joel Arriaga‐Dávila, Arturo Susarrey‐Arce. From Single to Multi‐Glass/Ceramic Microarchitectures via Two‐Photon Lithography. DOI: 10.1002/adom.202501658
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a lab calcination furnace in CoO synthesis? Engineer High-Performance Nanoparticles
- What role does an industrial oven play in the pre-treatment of Licuri bark? Optimize Activated Carbon Production
- Why are sealing mechanisms critical in atmosphere furnaces? Ensure Purity, Safety, and Efficiency
- What are the key applications of low vacuum atmosphere furnaces? Boost Efficiency in Heat Treatment
- How does a precision high-temperature furnace ensure the densification of MgO? Master Low-Temp Ceramic Sintering
- Why is inert atmosphere heat treating important for steel? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Finish and Performance
- How does the temperature control system work in the box type annealing atmosphere furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Management
- What is the purpose of a chemically reactive atmosphere in material processing? Achieve Precise Surface Modification for Enhanced Performance



















