In material processing, a chemically reactive atmosphere is a tool for targeted transformation. Its purpose is to intentionally introduce specific gases that react with a material's surface at high temperatures. This controlled chemical reaction fundamentally alters the material's properties, such as hardness or corrosion resistance, in a precise and predictable way.
The choice of atmosphere is not a passive background condition; it is an active ingredient in the process. While inert atmospheres are used to protect a material, a reactive atmosphere is used to deliberately modify its surface chemistry, adding or removing elements to achieve performance characteristics the bulk material does not possess.

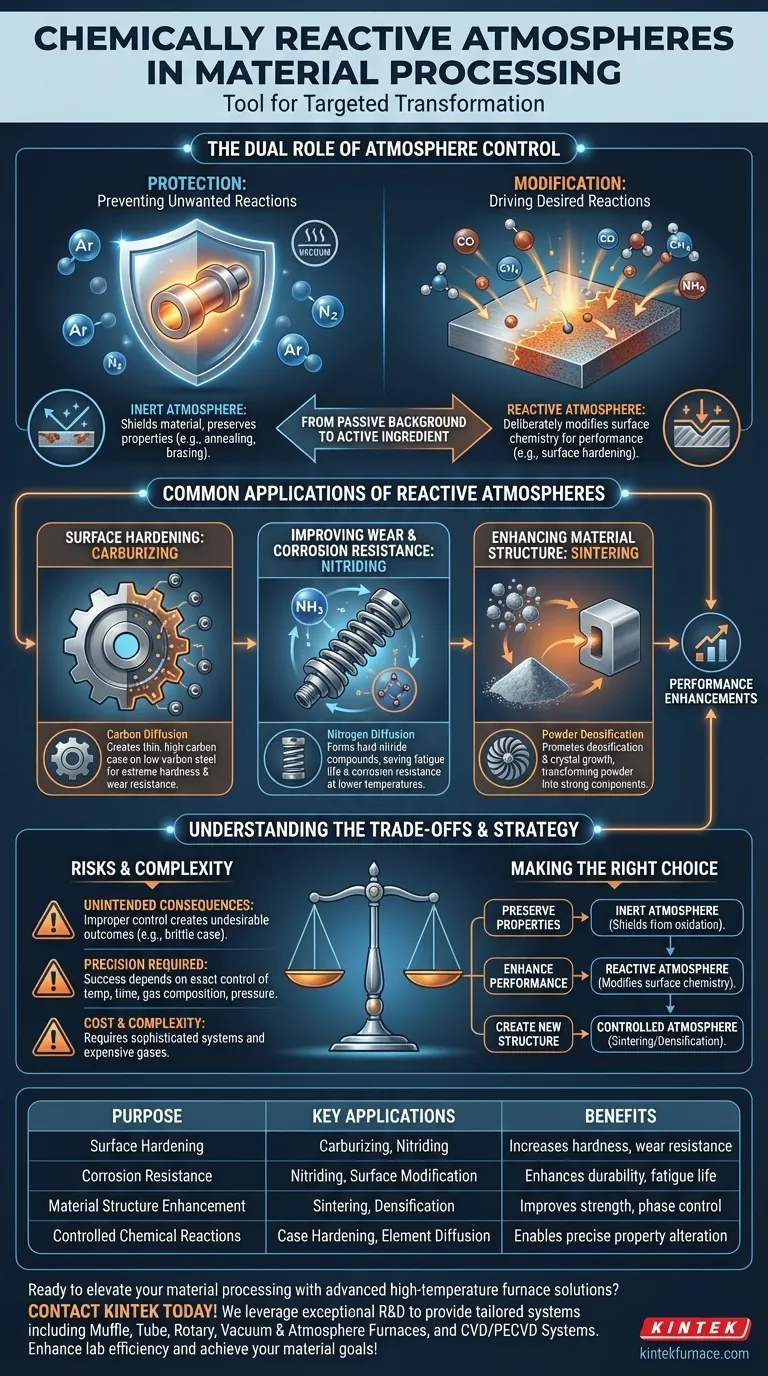
The Dual Role of Atmosphere Control
In any high-temperature process, the atmosphere inside the furnace is critical. Its role can be broadly divided into two distinct functions: protection or active modification. Understanding this distinction is key to material engineering.
Protection: Preventing Unwanted Reactions
Many materials, especially metals, are highly susceptible to reacting with air at high temperatures. The most common unwanted reaction is oxidation (rusting or scaling).
An inert atmosphere, using gases like argon or nitrogen, or a vacuum, displaces oxygen. This shields the material, preserving its inherent properties and surface finish during processes like annealing or brazing.
Modification: Driving Desired Reactions
A chemically reactive atmosphere is the opposite. Here, the goal is not to prevent reactions but to force a specific one to occur.
Engineers carefully select gases that will diffuse elements into or out of the material's surface. This process, known as case hardening or surface modification, creates a composite material: a tough, ductile core with a functionally different outer shell.
Common Applications of Reactive Atmospheres
The ability to engineer a material's surface opens up a wide range of performance enhancements, often allowing the use of less expensive base materials.
Surface Hardening: Carburizing
Carburizing is a classic example. Low-carbon steel is heated in an atmosphere rich in carbon, often from gases like carbon monoxide or methane.
Carbon atoms diffuse into the surface of the steel. This creates a thin, outer case of high-carbon steel that is extremely hard and wear-resistant, while the inner core remains softer and tougher.
Enhancing Material Structure: Sintering
In the creation of advanced ceramics and powdered metals, the atmosphere plays a crucial role in sintering.
A controlled atmosphere can promote densification and crystal growth, transforming loose powder into a solid, strong component. It can also be reactive to burn off binders or facilitate specific phase transformations necessary for the final material's performance.
Improving Wear and Corrosion Resistance: Nitriding
Nitriding involves heating a material, typically steel, in a nitrogen-rich atmosphere (e.g., ammonia).
The nitrogen diffuses into the surface to form extremely hard nitride compounds. This process not only increases surface hardness but also significantly improves fatigue life and corrosion resistance without the high temperatures required for carburizing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using a reactive atmosphere is a powerful but complex technique. It requires precise control, and failure to manage the process can be more damaging than helpful.
The Risk of Unintended Consequences
An improperly controlled reactive atmosphere can create undesirable outcomes. Too much carbon can lead to a brittle case, and incorrect gas mixtures can cause unexpected and detrimental chemical reactions on the material's surface.
The Importance of Precision
Success depends on the exact control of multiple variables: temperature, time, gas composition, and pressure. These factors work together to determine the depth and concentration of the diffused elements, directly impacting the final properties of the component.
Cost and Complexity
Systems for managing reactive atmospheres are more complex and expensive than simple air or inert gas furnaces. The cost of the reactive gases, along with the sophisticated control and safety systems required, must be justified by the performance gains achieved.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your atmospheric strategy should be dictated entirely by the final properties you need to achieve in your component.
- If your primary focus is preserving the material's inherent properties: An inert or vacuum atmosphere is required to shield the part from oxidation and other unwanted surface reactions.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface performance: A chemically reactive atmosphere is the correct choice to deliberately modify the surface chemistry for improved hardness, wear, or corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is creating a new material structure: A precisely controlled atmosphere, which may be inert or reactive, is essential for processes like sintering to achieve the desired final density and phase.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace atmosphere allows you to treat it not as a processing condition, but as a final, critical ingredient in your material's design.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Hardening | Carburizing, Nitriding | Increases hardness, wear resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance | Nitriding, Surface Modification | Enhances durability, fatigue life |
| Material Structure Enhancement | Sintering, Densification | Improves strength, phase control |
| Controlled Chemical Reactions | Case Hardening, Element Diffusion | Enables precise property alteration |
Ready to elevate your material processing with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored furnace systems. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're aiming for superior surface hardening, corrosion resistance, or sintering, our expertise ensures optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve your material goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















