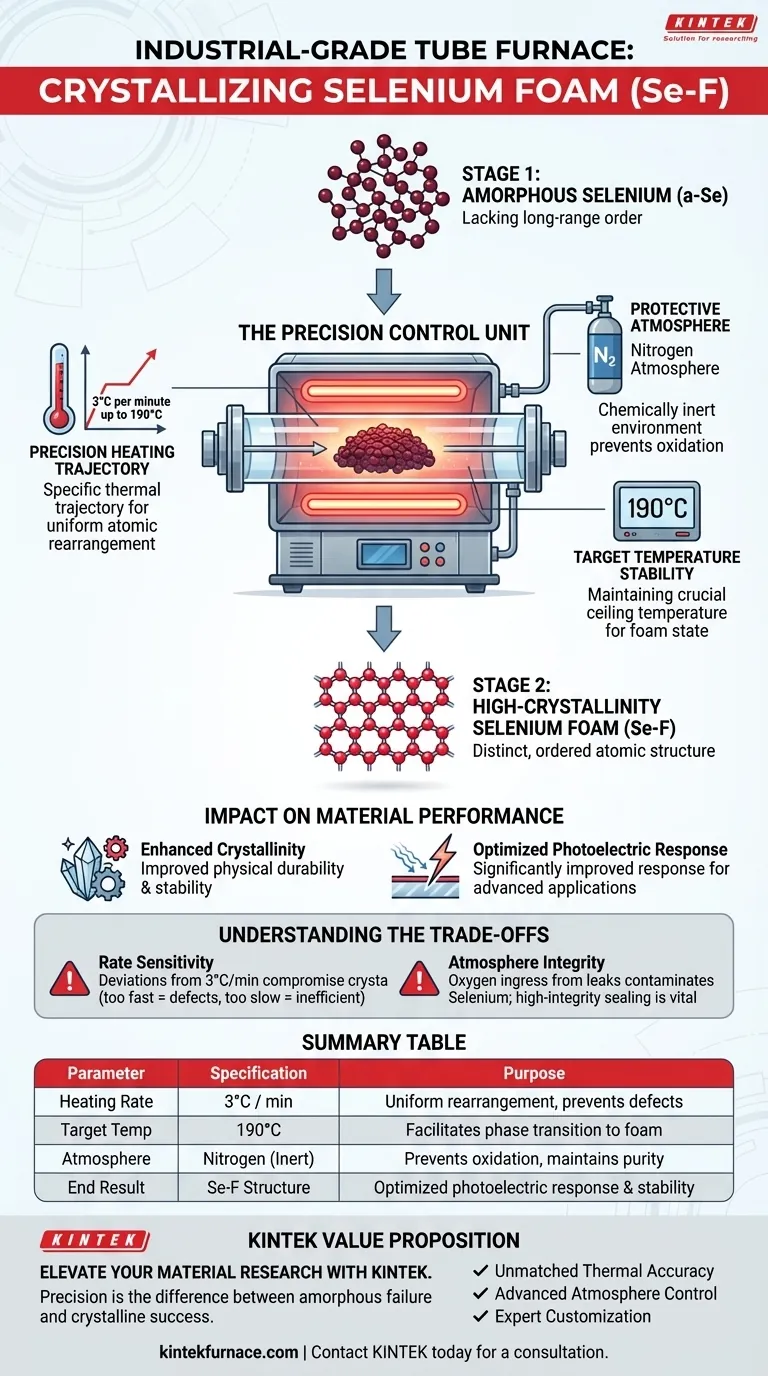
An industrial-grade tube furnace acts as the precision control unit necessary for transforming amorphous Selenium (a-Se) films into high-crystallinity Selenium foam (Se-F). This equipment provides a specific thermal trajectory—a heating rate of 3°C per minute up to 190°C—under a nitrogen atmosphere to facilitate atomic rearrangement and enhance the material's photoelectric properties.
The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is an instrument of structural definition. By strictly controlling the environment and heating rate, it drives the specific atomic rearrangement required to turn low-performance amorphous films into highly responsive crystalline foam.

The Mechanics of Transformation
From Amorphous to Crystalline
The crystallization process begins with amorphous Selenium (a-Se), a material lacking a defined long-range order.
To create functional Selenium foam, the material must undergo a phase transition. The tube furnace provides the thermal energy required to break the amorphous bonds and allow the material to restructure.
Facilitating Atomic Rearrangement
Heat allows the Selenium atoms to mobilize and align into a structured lattice.
The furnace ensures this atomic rearrangement occurs uniformly. This transition is what converts the disordered film into a high-quality crystalline structure.
Precise Environmental Control
The Critical Heating Trajectory
Success depends on the rate of temperature change, not just the final temperature.
The primary reference indicates a specific heating rate of 3 degrees Celsius per minute. Deviating from this ramp rate could result in uneven crystallization or structural defects.
Target Temperature Stability
The process targets a precise ceiling temperature of 190 degrees Celsius.
Reaching and maintaining this temperature is crucial for the material to achieve its final "foam" state. The tube furnace’s ability to hold this temperature steadily ensures the reaction is complete throughout the entire sample.
Atmosphere Management
Thermal treatment must occur in a chemically inert environment.
The furnace operates under a protective nitrogen atmosphere. This prevents oxidation and ensures that the Selenium interacts only with the thermal energy, preserving the purity of the final foam.
Impact on Material Performance
Enhanced Crystallinity
The primary output of this controlled process is "high-crystallinity" Selenium foam.
A high degree of crystallinity means the atomic structure is distinct and ordered. This directly influences the physical durability and stability of the material.
Optimized Photoelectric Response
The structural changes dictate the material's functional properties.
By refining the microstructure through precise heating, the furnace significantly improves the photoelectric response performance. This makes the final Se-F suitable for advanced applications where electrical response to light is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Rate Variances
The specific rate of 3°C per minute acts as a constraint as well as a feature.
If the furnace cannot maintain this precise ramp rate, the crystallinity may be compromised. Faster heating might lock in amorphous defects, while slower heating could be inefficient.
Dependence on Atmosphere Integrity
The process relies heavily on the nitrogen seal.
If the tube furnace has leaks or poor gas flow control, oxygen ingress can contaminate the Selenium. This dependence makes the quality of the furnace's sealing mechanisms just as important as its heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Selenium foam, you must align the furnace capabilities with your specific processing needs.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Prioritize a furnace with high-integrity vacuum sealing to maintain the nitrogen atmosphere and prevent oxidation during the atomic rearrangement.
- If your primary focus is Structural Consistency: Ensure the furnace controller can strictly enforce the 3°C/min ramp rate to guarantee uniform crystallinity across the entire sample.
Precision control of the thermal environment is the defining factor in extracting high-performance properties from raw Selenium materials.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Purpose in Selenium Crystallization |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | 3°C per minute | Ensures uniform atomic rearrangement & prevents defects |
| Target Temp | 190°C | Facilitates phase transition to high-crystallinity foam |
| Atmosphere | Nitrogen (Inert) | Prevents oxidation and maintains material purity |
| End Result | Se-F Structure | Optimized photoelectric response and structural stability |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between amorphous failure and crystalline success. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of Selenium foam production and other advanced lab processes.
Our value to you:
- Unmatched Thermal Accuracy: Maintain strict ramp rates (like 3°C/min) for perfect structural definition.
- Advanced Atmosphere Control: High-integrity sealing for pure nitrogen environments.
- Expert Customization: Tailored high-temp furnace solutions for unique material science applications.
Ready to optimize your photoelectric material performance? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let our technical team build the ideal furnace for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yuxin Huang, Pingping Yu. CNT:TiO2-Doped Spiro-MeOTAD/Selenium Foam Heterojunction for High-Stability Self-Powered Broadband Photodetector. DOI: 10.3390/nano15120916
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of controlled thermal processing for YIG thin films? Unlock Magnetic Order in Spintronics
- How does a two-stage sintering process in a tube furnace contribute to high-performance sodium-ion battery cathodes?
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- How does annealing in a tube vacuum furnace optimize WS2 thin films? Master Structural Integrity & Efficiency
- Why choose a vertical tube furnace over a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Purity
- Why is an industrial monitoring camera necessary for measuring aluminum powder ignition delay in a tube furnace?
- How does a tube furnace facilitate gas-phase hydrogenation for Zircaloy-4? Achieve Precise Hydride Precipitation
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in chromite reduction? Master Precision Solid-State Processing



















