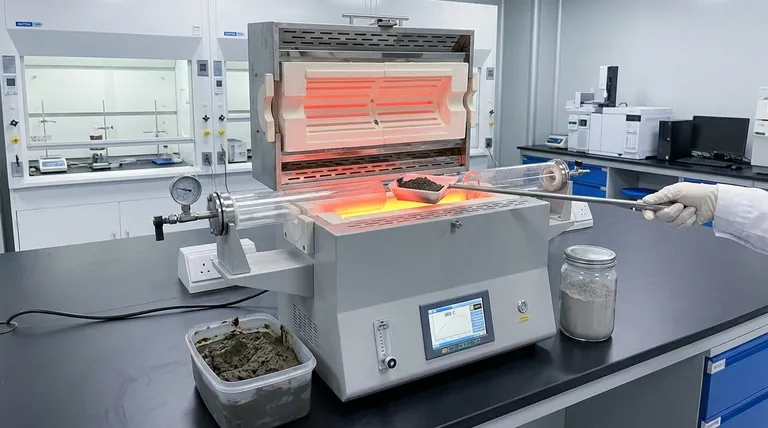
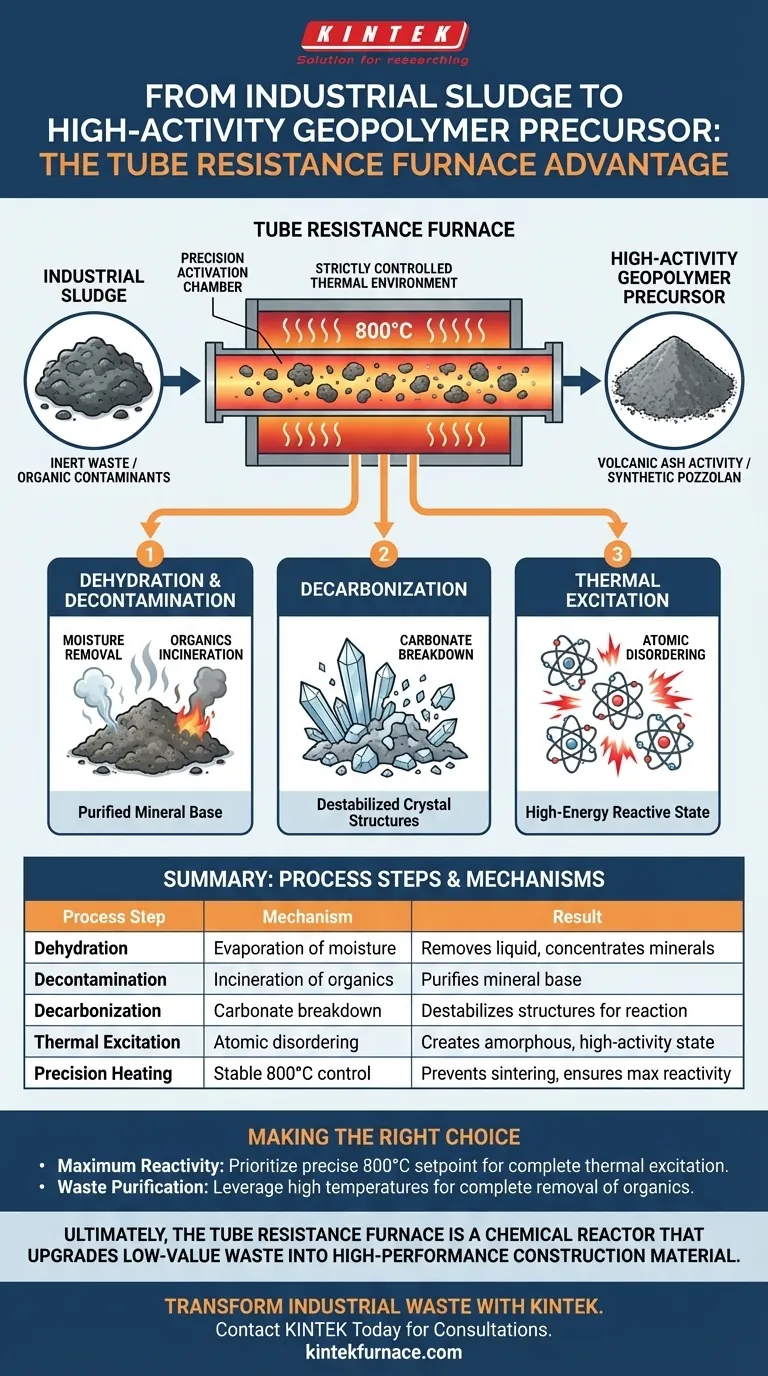
A tube resistance furnace serves as a precision activation chamber that converts industrial sludge into useful materials by subjecting it to a strictly controlled thermal environment, typically around 800°C. This high-temperature treatment triggers specific chemical changes—specifically calcination and thermal excitation—that strip away impurities and fundamentally alter the mineral structure of the sludge to make it chemically reactive.
The Core Transformation By providing a stable high-temperature environment, the furnace transforms inert waste into a valuable resource. It achieves this by burning off organic contaminants and "waking up" the mineral components, imbuing the sludge with volcanic ash activity—the critical property required for geopolymer production.

The Mechanics of Thermal Activation
Precision Temperature Control
The primary contribution of the tube resistance furnace is its ability to maintain an exacting temperature profile.
For industrial sludge, the target temperature is often 800°C. This precision prevents the material from under-reacting (remaining inert) or over-reacting (melting or sintering), ensuring optimal activation.
Creating a Controlled Reaction Environment
Tube furnaces provide a sealed or semi-sealed environment that isolates the sludge during processing.
This isolation is crucial for consistent heat distribution. It ensures that every particle of sludge is subjected to the same thermal conditions, leading to a uniform product.
Chemical Transformations Inside the Furnace
Dehydration and Decontamination
Before chemical activation can occur, the sludge must be purified.
The furnace's heat effectively removes residual moisture and incinerates organic matter. This leaves behind a cleaner mineral base, ready for structural transformation.
Decarbonization
As the temperature rises, the furnace facilitates decarbonization.
This process breaks down carbonate minerals present in the sludge. It is a necessary step to destabilize the crystal structures that lock the minerals in an inert state.
Thermal Excitation
This is the most critical function of the furnace regarding geopolymer potential.
The thermal energy "excites" the mineral components. It forces the atoms into a disordered, amorphous state. This high-energy state is what makes the final precursor reactive, allowing it to bond with other materials to form strong geopolymers.
Achieving Volcanic Ash Activity
The cumulative result of these processes is the generation of volcanic ash activity.
In this context, "activity" refers to the material's ability to react with alkali activators in the presence of water. The furnace turns the sludge into a synthetic pozzolan, mimicking the reactive properties of natural volcanic ash.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Energy Intensity vs. Material Value
While the furnace adds significant value to the waste, it is energy-intensive.
Operating at 800°C requires substantial power input. The economic viability depends on balancing this energy cost against the high value of the resulting geopolymer precursor and the savings from reduced waste disposal.
Throughput Limitations
Tube resistance furnaces offer high precision but often sacrifice volume compared to massive rotary kilns.
They are ideal for high-value, high-specification applications where quality control is paramount. However, for massive-scale industrial waste processing, the throughput speed of a tube furnace can be a limiting factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The tube resistance furnace is a specialized tool that prioritizes quality and reactivity over sheer volume.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Reactivity: Prioritize the precise 800°C setpoint to ensure complete thermal excitation and the highest level of volcanic ash activity.
- If your primary focus is Waste Purification: Leverage the high-temperature capabilities to ensure complete removal of organic matter and moisture before further processing.
Ultimately, the tube resistance furnace is not just an incinerator; it is a chemical reactor that upgrades low-value waste into high-performance construction material.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Mechanism | Result for Sludge Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | Evaporation of moisture | Removes liquid waste and concentrates minerals |
| Decontamination | Incineration of organics | Purifies the mineral base by removing carbon/contaminants |
| Decarbonization | Carbonate breakdown | Destabilizes crystal structures for easier reaction |
| Thermal Excitation | Atomic disordering | Creates an amorphous state with high volcanic ash activity |
| Precision Heating | Stable 800°C control | Prevents sintering while ensuring maximum chemical reactivity |
Transform Industrial Waste into High-Value Resources
Don’t let valuable minerals go to waste. KINTEK’s high-precision Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnace systems provide the exacting thermal environments required for superior material activation and chemical transformation. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet the unique requirements of your sludge-to-geopolymer project.
Ready to achieve maximum reactivity in your lab or production line?
Contact KINTEK Today to Consult with our Experts
Visual Guide
References
- Hajar Jeniah, Laïla Ben Allal. Recovery of Plastic Waste in the Production of Industrial Sludge-Based Geopolymer Mortars. DOI: 10.18280/rcma.350205
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a multi-stage programmable tube furnace necessary for sintering spinel hollow fiber membrane green bodies?
- How do researchers utilize the heating elements in tubular furnaces? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials Research
- What is the role of a Tube Furnace in the preparation of ferromagnetic MoS2? Master Defect Engineering & Magnetism
- How do vertical tube furnaces contribute to advancements in material science and industrial production? Unlock Precision in Material Innovation
- What is the design advantage of a split tube furnace? Unlock Easy Access for Complex Lab Setups
- How is sealing and atmosphere control achieved in a tube furnace? Master Precise Gas Environments for Your Lab
- Why is uniform heating important in tubular furnaces? Ensure Process Reliability and Predictable Results
- What role does a high-vacuum tube furnace play in helium bubble studies? Master Thermal Activation & Material Purity



















