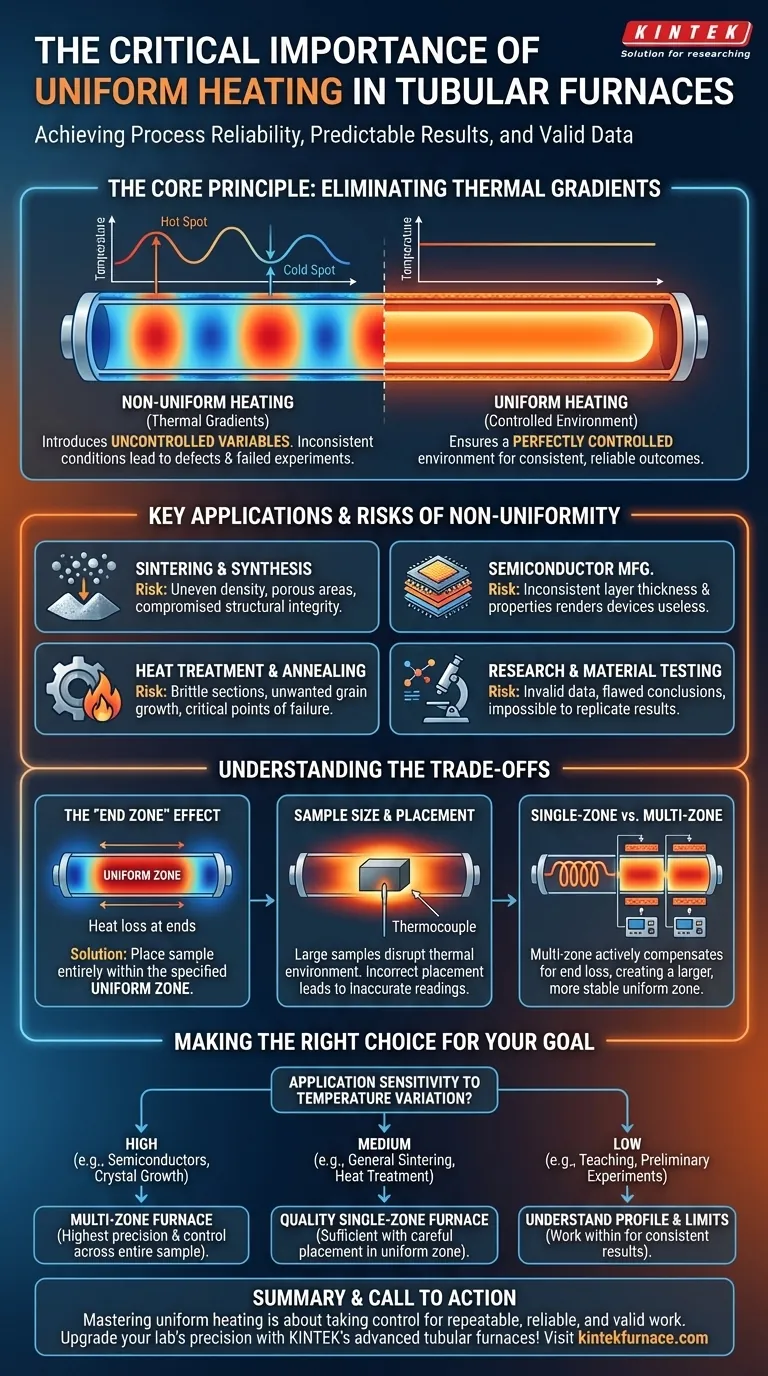
At its core, uniform heating in a tubular furnace is the single most important factor for ensuring process reliability and predictable results. Without it, every material or component placed inside is subjected to inconsistent thermal conditions, leading to defects, failed experiments, and compromised material integrity.
The central challenge in any high-temperature process is eliminating variables. Non-uniform heating introduces thermal gradients—hot and cold spots—that act as a major, uncontrolled variable, making consistent outcomes nearly impossible to achieve.
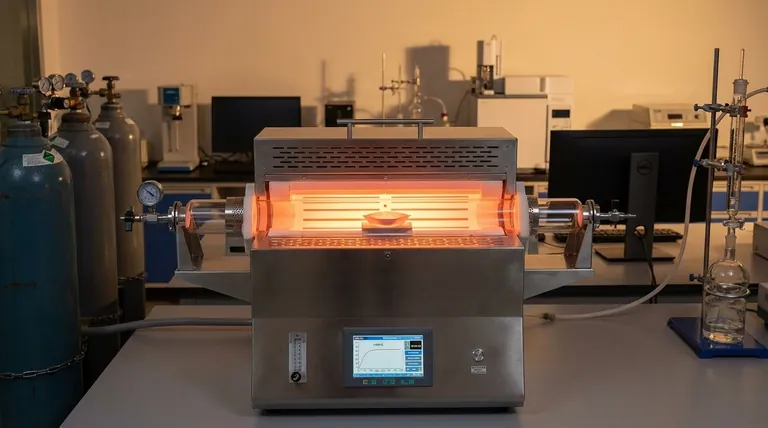

The Core Principle: Eliminating Thermal Gradients
The entire purpose of a precision furnace is to create a perfectly controlled environment. The primary threat to this control is a thermal gradient, which is simply a variation in temperature across a space.
What are Hot and Cold Spots?
Even in a high-quality furnace, some areas can be slightly hotter or cooler than the setpoint temperature. These are known as hot spots and cold spots.
These spots arise due to factors like proximity to heating elements, airflow patterns, or heat loss near the ends of the tube.
Why Gradients Invalidate Results
When a sample is placed across a thermal gradient, different parts of it undergo different processes. One section might be perfectly annealed while another remains brittle, or one part of a chemical reaction may complete while another lags behind.
This inconsistency makes it impossible to draw reliable conclusions from research or produce a product with uniform quality. It undermines the very reason for using a precision furnace.
Key Applications Demanding Uniformity
While important in all applications, uniform heating becomes non-negotiable in processes where slight temperature deviations have significant consequences.
For Material Synthesis and Sintering
In processes like sintering, powdered materials are heated to bond together. If heating is uneven, some areas may become fully dense while others remain porous and weak, compromising the structural integrity of the final part.
For Semiconductor Manufacturing
Creating semiconductor devices involves depositing microscopic layers of material. The temperature during this deposition directly affects the layer's thickness, crystal structure, and electronic properties. Any variation can render the entire microchip useless.
For Heat Treatment and Annealing
Heat treating metals like steel or aluminum is done to alter their mechanical properties, such as hardness or ductility. A cold spot can leave a section brittle, while a hot spot can cause unwanted grain growth, creating a critical point of failure in a finished component.
For Research and Material Testing
When scientists study how a material behaves at a specific high temperature, they must be certain the entire sample is at that temperature. Uniform heating ensures the data collected is valid and represents the material's true properties, which is essential for developing new alloys and ceramics for aerospace or automotive use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving perfect uniformity across the entire length of a furnace tube is a significant engineering challenge. Understanding the practical limitations is key to successful operation.
The "End Zone" Effect
The ends of the furnace tube are the most difficult areas to heat uniformly due to heat loss to the outside environment. Most furnaces specify a "uniform zone" in the center where the temperature is most stable.
Crucially, your sample must be placed entirely within this specified uniform zone to achieve the desired results.
Sample Size and Placement
A large sample can disrupt the thermal environment inside the tube, creating its own cold spots. Similarly, placing a sample too close to the thermocouple can lead to inaccurate temperature readings for the rest of the sample.
Multi-Zone vs. Single-Zone Furnaces
A standard single-zone furnace has one set of heating elements and one controller. For higher precision, multi-zone furnaces use several independent heating zones (typically three) along the tube, each with its own controller.
This allows for active compensation for heat loss at the ends, creating a much larger and more stable uniform zone, but at a significantly higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of uniformity you need depends directly on your application's sensitivity to temperature variation.
- If your primary focus is high-yield production or foundational research (e.g., semiconductors, crystal growth): A multi-zone furnace is necessary to guarantee the highest level of temperature control across the entire sample.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment, sintering, or material testing: A quality single-zone furnace is often sufficient, provided you carefully place your sample within its documented uniform hot zone.
- If your primary focus is teaching or preliminary experiments: Prioritize understanding the furnace's specific thermal profile and work within its limitations to achieve consistent, if not perfectly uniform, results.
Ultimately, mastering uniform heating is about taking control of the thermal environment to ensure your work is repeatable, reliable, and valid.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Non-Uniform Heating | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Gradients | Causes hot/cold spots, leading to inconsistent material properties | Use precise furnace design and placement within uniform zone |
| Process Reliability | Results in defects, failed experiments, and unreliable data | Ensure uniform heating for repeatable outcomes |
| Key Applications | Critical in sintering, semiconductor manufacturing, and heat treatment | Choose furnace type (single-zone vs. multi-zone) based on sensitivity |
| Sample Placement | Incorrect placement disrupts thermal environment, invalidating results | Place samples entirely within specified uniform zone |
Upgrade your lab's precision with KINTEK's advanced tubular furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs for uniform heating and consistent results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process reliability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















