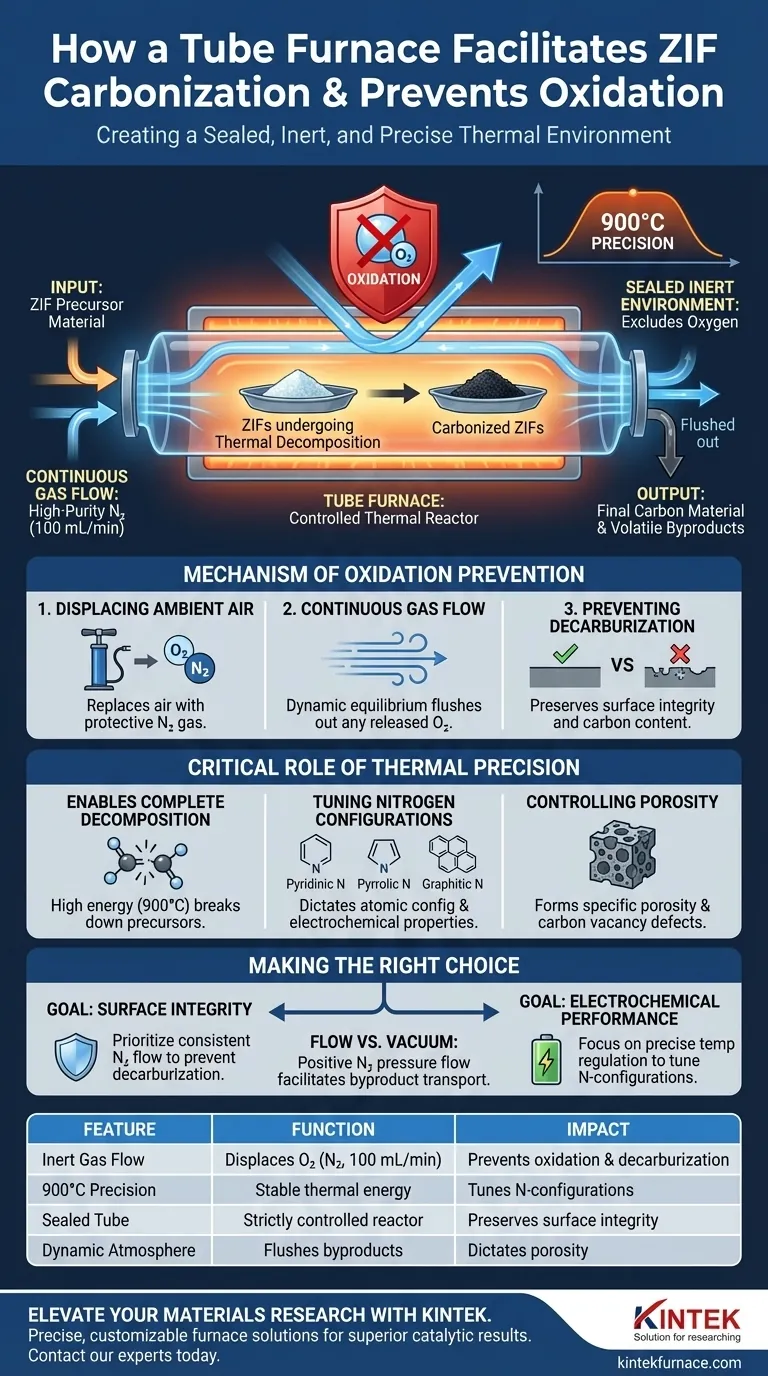
A tube furnace facilitates the carbonization of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIFs) by creating a sealed, inert environment that completely excludes oxygen. By continuously flowing high-purity nitrogen gas (typically at 100 mL/min) and maintaining precise temperatures (often around 900°C), the furnace ensures the material undergoes thermal decomposition rather than combustion.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace acts as a strictly controlled thermal reactor, not just a heater. Its primary function is to replace the reactive ambient atmosphere with an inert gas, allowing you to precisely dictate the porosity, elemental composition, and structural stability of the final carbon material.

The Mechanism of Oxidation Prevention
Displacing Ambient Air
The fundamental risk during high-temperature treatment is the reaction of materials with oxygen, known as oxidation.
To prevent this, the tube furnace replaces the air inside the chamber with a protective gas, most commonly high-purity nitrogen.
Continuous Gas Flow
A static environment is often insufficient; the furnace maintains a dynamic equilibrium using a steady gas flow, such as 100 mL/min.
This continuous flow flushes out any oxygen released during the heating process and ensures the environment remains strictly inert throughout the carbonization cycle.
Preventing Decarburization
Beyond simple oxidation, the presence of oxygen can lead to decarburization, where carbon is lost from the material's surface.
By maintaining an oxygen-free atmosphere, the furnace preserves the surface integrity of the ZIFs, ensuring the final structure retains the necessary carbon content.
Critical Role of Thermal Precision
Enabling Complete Decomposition
Carbonization of ZIFs requires high thermal energy, often reaching 900°C, to break down the precursor materials completely.
The tube furnace provides the stable, high-temperature environment necessary to drive this full thermal decomposition without temperature fluctuations that could lead to incomplete processing.
Tuning Nitrogen Configurations
The precise control of temperature and airflow does more than just burn off precursors; it dictates the atomic configuration of the final material.
Specific thermal conditions determine the ratios of critical nitrogen configurations—specifically pyridinic, pyrrolic, and graphitic nitrogen—which define the material's electrochemical properties.
Controlling Porosity
The stability of the heating profile directly impacts the physical structure of the carbonized ZIF.
Accurate temperature management allows for the formation of specific porosity levels and carbon vacancy defects, which are essential for applications requiring high conductivity or catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Flow Rate Sensitivity
While gas flow is essential, it introduces a variable that must be carefully managed.
Incorrect flow rates can lead to turbulence or thermal gradients within the tube, potentially causing uneven carbonization across the sample batch.
Vacuum vs. Flow Atmospheres
It is important to distinguish between inert flow (used here) and vacuum processing.
While a vacuum furnace removes oxygen to prevent oxidation, the tube furnace uses positive pressure from nitrogen flow. This is often preferred for ZIFs as it facilitates the transport of volatile byproducts away from the material surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your carbonized ZIFs, align your furnace settings with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is Surface Integrity: Prioritize a consistent, high-purity nitrogen flow (e.g., 100 mL/min) to aggressively flush oxygen and prevent decarburization.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Performance: Focus on precise temperature regulation (e.g., 900°C) to tune the ratios of pyridinic and graphitic nitrogen configurations.
Success in ZIF carbonization relies on viewing the tube furnace as an instrument of chemical control, where atmosphere and temperature are equally critical variables.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in ZIF Carbonization | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas Flow | Displaces oxygen using high-purity Nitrogen (100 mL/min) | Prevents oxidation and decarburization |
| 900°C Precision | Provides stable thermal energy for decomposition | Tunes nitrogen configurations (pyridinic, pyrrolic) |
| Sealed Tube | Creates a strictly controlled thermal reactor | Preserves surface integrity and elemental composition |
| Dynamic Atmosphere | Flushes out volatile thermal byproducts | Dictates porosity and carbon vacancy defects |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precise carbonization of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIFs) requires the highest standards of atmospheric control and thermal stability. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of lab-scale and industrial R&D.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our furnaces ensure uniform heating and airtight seals to prevent oxidation.
- Fully Customizable: Tailor flow rates, temperature profiles, and tube dimensions to your specific ZIF applications.
- Enhanced Performance: Achieve perfect nitrogen configurations and porosity levels for superior catalytic results.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact our thermal experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace solution for your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yan Yang, Gai Zhang. Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity for ORR Based on Synergistic Effect of Hierarchical Porosity and Co-Nx Sites in ZIF-Derived Heteroatom-Doped Carbon Materials. DOI: 10.3390/c11030070
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of heating elements are used in a 70mm tube furnace? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- How does the heating mechanism differ between vertical and horizontal tube furnaces? Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processing
- Why is a high-precision gas flow control system required for vermiculite heat treatment? Ensure Perfect Atmosphere
- What critical role does a tube furnace play in the final stage of catalyst preparation for FeOx@KCC-1? Expert Insights
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace ensure effective conversion during MOF selenization? Optimize Your Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace required for PET carbonization? Achieve High-Surface Area Activated Carbon with Precise Control
- What are the laboratory research applications of vacuum tube furnaces? Unlock Precise Material Synthesis and More
- How does the temperature zone layout of a horizontal tube furnace affect the synthesis quality of Bi2Se3 nanofilms?



















