In essence, the heating mechanism difference between vertical and horizontal tube furnaces is subtle but significant, stemming from the furnace's orientation and its effect on heat transfer. While both use surrounding heating elements, vertical furnaces leverage natural convection for superior temperature uniformity, whereas horizontal furnaces rely more heavily on radiation, which can introduce slight temperature variations along the tube's length.
The choice between a vertical and horizontal tube furnace is not about which has a "better" heating mechanism, but which orientation's heat transfer characteristics and physical layout best serve your specific material, process, and desired outcome.

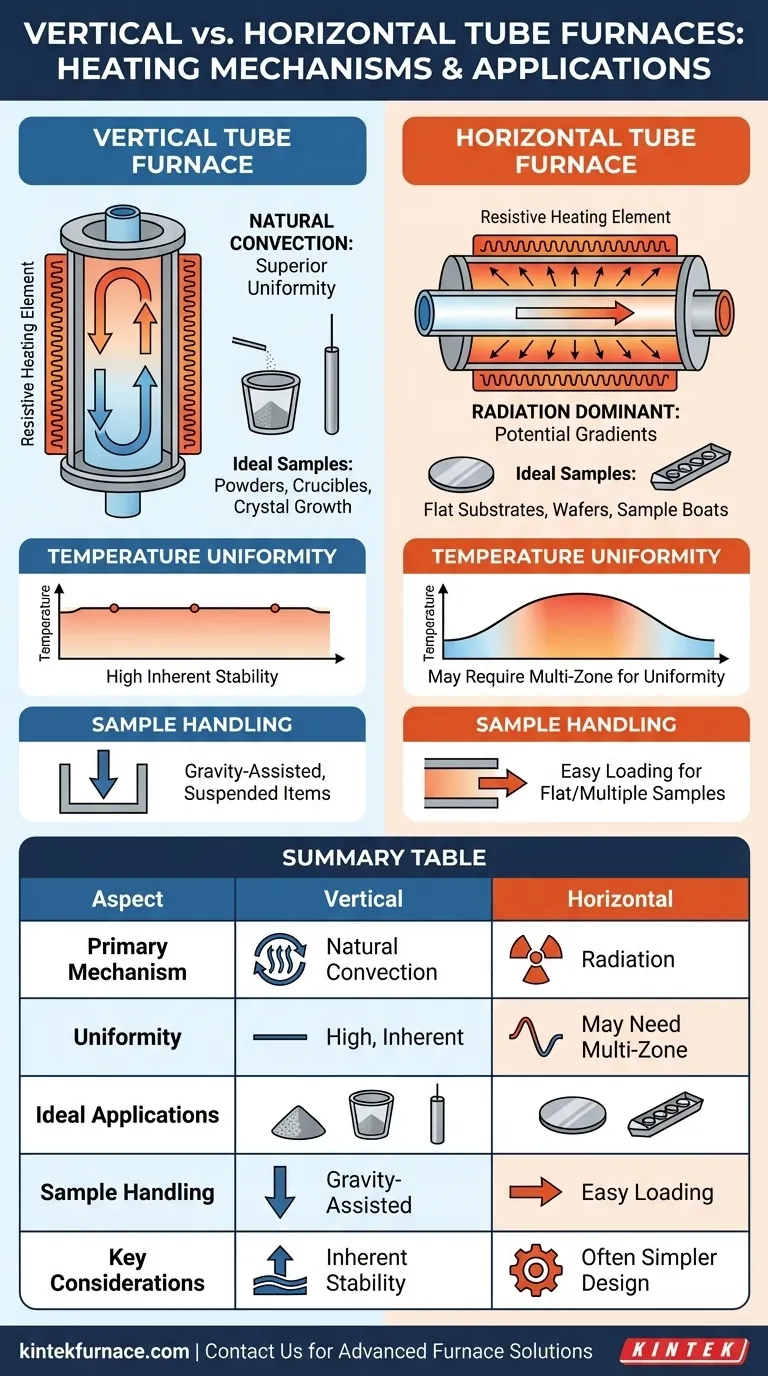
Deconstructing the Heat Transfer Process
The core design of both furnace types is identical: a resistive heating element encircles a process tube. The critical difference is how gravity interacts with the heated atmosphere inside that tube.
Vertical Furnaces: Harnessing Natural Convection
In a vertical tube furnace, the air or process gas inside heats up, becomes less dense, and naturally rises. This creates a continuous convective loop within the tube.
This constant circulation of gas actively mixes the heat, smoothing out hot spots and distributing thermal energy evenly along the length of the processing zone. This natural assistance makes achieving excellent temperature uniformity an inherent feature of the vertical design.
Horizontal Furnaces: A Primary Reliance on Radiation
In a horizontal tube, gravity prevents a large-scale convective loop from forming along the tube's axis. While small convection cells exist, they don't effectively transfer heat from the middle to the ends.
Therefore, heat transfer is dominated by thermal radiation from the hot walls of the heating element to the sample. While effective, this can be less uniform. Areas of the sample closer to the center of the heating elements may get slightly hotter, and heat loss at the ends of the tube can create noticeable temperature gradients.
Practical Implications of the Difference
The subtle shift from a convection-assisted process to a radiation-dominant one has direct consequences for your work.
Temperature Uniformity and Control
Vertical furnaces have a natural advantage in temperature uniformity. The self-mixing nature of convection provides a highly stable and consistent thermal environment with minimal engineering.
Horizontal furnaces can achieve excellent uniformity, but often require multiple heating zones. These are independent sections of the heating element that can be set to different temperatures to compensate for heat loss at the ends and create a flat thermal profile across the central zone.
Sample Handling and Application
The orientation dictates how samples can be loaded and processed.
Vertical furnaces are ideal for:
- Processing powders or molten materials in crucibles.
- Growing crystals or annealing long rods/wires that can be suspended.
- Applications where gravity assists in sample loading and positioning.
Horizontal furnaces are necessary for:
- Processing flat substrates, such as silicon wafers in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Loading multiple smaller samples arranged in a "boat."
- Many Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes where gas flow over a flat surface is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior. The right choice is always a function of your specific application and priorities.
The Myth of Perfect Uniformity
Even in vertical furnaces, perfect uniformity is an ideal. Multi-zone heating is often used in high-precision vertical systems to achieve the tightest possible temperature control, just as it is in horizontal ones. The key difference is that vertical furnaces start from a more uniform baseline.
When Horizontal is the Optimal Choice
Despite the potential for gradients, horizontal furnaces are the standard in many industries. Their ease of loading for flat materials and compatibility with established processes (like wafer fabrication) make them the default and most practical choice. For general-purpose lab heating, their simpler design is often sufficient.
When Vertical is Non-Negotiable
For applications like crystal growth, certain types of annealing, or material synthesis in a crucible, the uniform heating and gravitational stability offered by a vertical furnace are essential for achieving repeatable and high-quality results. The sample's physical form or process requirements make a horizontal orientation impractical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your decision should be guided by your primary experimental or production goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum intrinsic temperature uniformity: Choose a vertical tube furnace, as natural convection provides an inherent advantage in distributing heat evenly.
- If your primary focus is processing flat substrates or multiple samples in a boat: A horizontal tube furnace is the necessary and standard configuration for this type of handling.
- If your primary focus is high-precision control over a long uniform zone: Consider a multi-zone furnace, whether vertical or horizontal, to actively compensate for heat loss and engineer a precise temperature profile.
Understanding how orientation impacts heat transfer empowers you to select the furnace that is not just a heat source, but the correct tool for your specific scientific objective.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vertical Tube Furnace | Horizontal Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Heating Mechanism | Natural convection for superior uniformity | Radiation, with potential gradients |
| Temperature Uniformity | High, due to convective loops | May require multi-zone heating for uniformity |
| Ideal Applications | Powders, crucibles, crystal growth, annealing rods | Flat substrates, wafer processing, CVD, sample boats |
| Sample Handling | Gravity-assisted loading, suitable for suspended items | Easy loading of flat or multiple samples |
| Key Considerations | Inherent stability, minimal engineering for uniformity | Often simpler design, standard for many industries |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with the perfect tube furnace?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're processing powders, growing crystals, or handling flat substrates, our experts can help you select or customize a furnace for optimal temperature control and performance. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















