At its core, a refinery furnace functions as a powerful industrial heater. It uses burners to combust fuel, such as natural gas or fuel oil, to generate immense heat. This heat is transferred to a network of tubes running through the furnace, raising the temperature of the crude oil inside them to a precise point just before it enters the distillation column for separation.
The purpose of a refinery furnace is not simply to heat crude oil, but to do so with extreme precision. It is the critical first step that energizes the crude oil, preparing it for separation into valuable products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
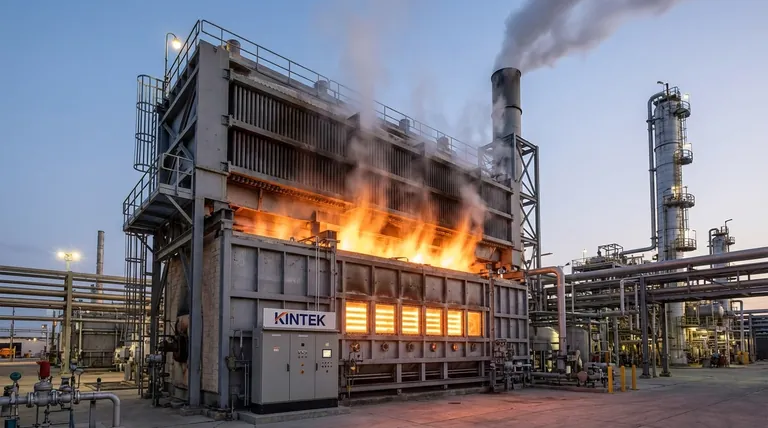

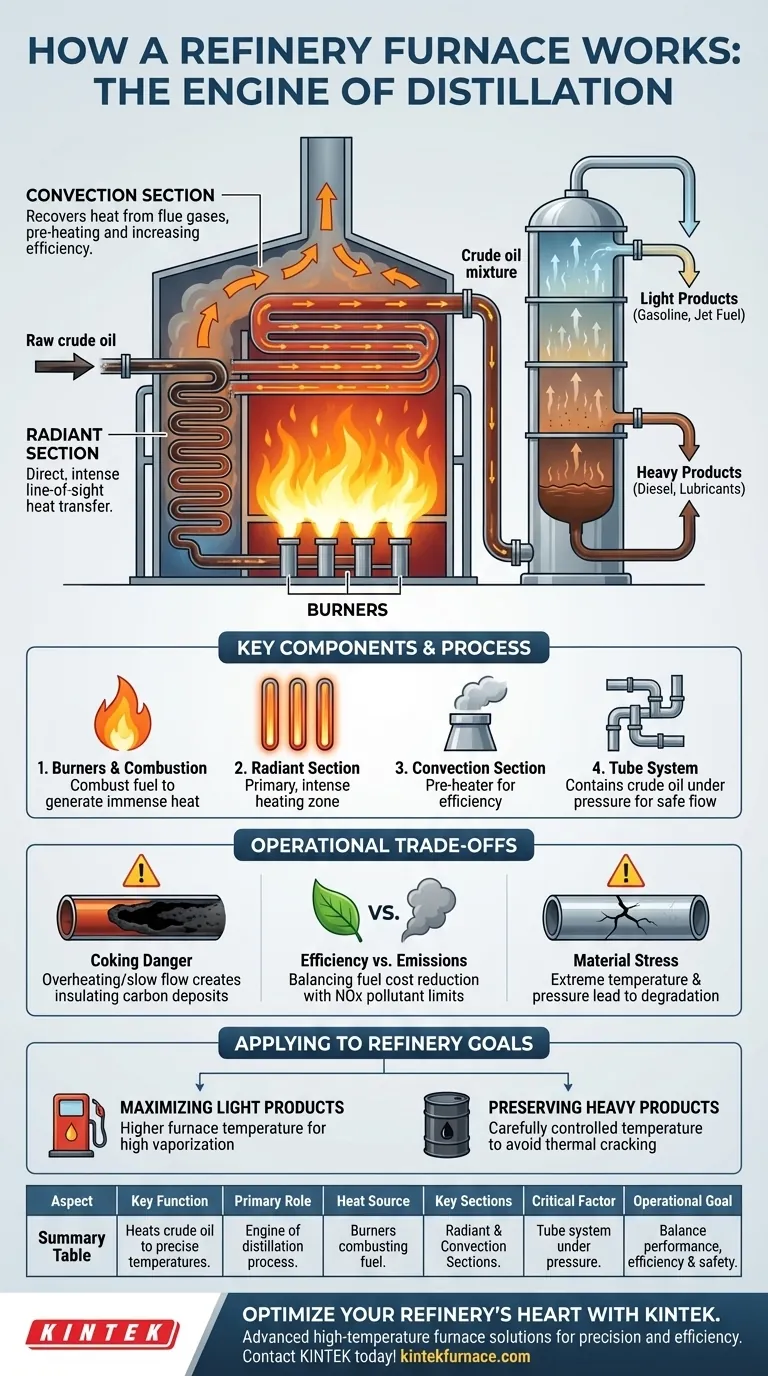
The Furnace's Role in Distillation
A refinery furnace is the engine that drives the entire atmospheric distillation process. Its job is to heat the raw crude oil feedstock to a specific, high temperature (typically around 350-400°C or 660-750°F).
Preparing for Separation
The goal is to vaporize a large portion of the crude oil before it is pumped into the bottom of the distillation tower. As this hot liquid and vapor mixture enters the tower, the vapors rise, cool, and condense at different levels according to their boiling points.
Without the furnace, the crude oil would be too cool for this separation to occur effectively. The furnace provides the necessary thermal energy to break the crude down into its constituent fractions.
The Key Components and Process
A refinery furnace, often called a fired heater, has several critical parts working in concert.
1. Burners and Fuel Combustion The heat source is a series of high-intensity burners located on the floor or walls of the furnace. These burners are designed to combust various fuels, including natural gas, fuel oil, or even off-gases produced by other refinery processes.
2. The Radiant Section This is the lower, hotter part of the furnace where the tubes are directly exposed to the flame's radiant heat. This "line-of-sight" heat transfer is intense and responsible for the majority of the heating. The crude oil flows rapidly through these tubes to absorb the energy.
3. The Convection Section Above the radiant section, hot flue gases from the combustion process are channeled past more banks of tubes. This section recovers additional heat through convection before the gases are exhausted through a stack. It acts as a pre-heater, increasing the overall thermal efficiency of the furnace.
4. The Tube System The crude oil is always contained within a continuous network of metal alloy tubes. This design ensures the fluid is heated evenly and under controlled pressure, preventing uncontrolled reactions and ensuring a safe flow to the next processing unit.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Operating a refinery furnace is a constant balancing act between performance, efficiency, and safety. Miscalculations can have significant consequences for the entire refinery.
The Danger of Coking
If the oil is heated too much or flows too slowly through the tubes, hydrocarbon molecules can "crack" and form solid carbon deposits known as coke. This coke insulates the inside of the tube, drastically reducing heat transfer efficiency and potentially causing dangerous hot spots on the tube metal.
Efficiency vs. Emissions
Maximizing thermal efficiency to reduce fuel costs is a primary goal. However, running the furnace at the highest possible temperature or with a specific air-to-fuel ratio can increase the production of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx). Engineers must constantly optimize firing conditions to meet both production targets and strict environmental regulations.
Material Stress and Lifespan
The metal tubes inside the furnace operate under extreme temperature and pressure. Over time, this stress can lead to material degradation, creep, and potential failure. The choice of metallurgy and rigorous inspection schedules are critical to ensuring the furnace's long-term integrity and safety.
Applying This to Your Refinery Goals
The way a furnace is operated is directly tied to the slate of products the refinery aims to produce. The furnace's outlet temperature is one of the most important control variables in the entire facility.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light products like gasoline and kerosene: The furnace must be operated at higher temperatures to ensure a high degree of vaporization before the crude enters the distillation column.
- If your primary focus is preserving valuable heavy products like lubricants or asphalt: The furnace temperature must be carefully controlled to be hot enough for separation but not so hot that it thermally cracks these long-chain molecules into less valuable, lighter products.
Understanding the furnace is to understand the foundational control point for transforming crude oil into the products that power our world.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Heats crude oil to precise temperatures for distillation. |
| Heat Source | Burners combusting fuel (natural gas, fuel oil). |
| Key Sections | Radiant Section (intense heating), Convection Section (efficiency). |
| Critical Factor | Tube system containing crude oil under controlled pressure. |
| Operational Goal | Balance performance, efficiency (avoid coking), and emissions control. |
Optimize your refinery's heart with a high-performance furnace solution.
At KINTEK, we understand that your refinery furnace is a critical control point for product yield and operational efficiency. Our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube and Rotary Furnaces, are engineered for precision, durability, and thermal efficiency to meet the demanding environment of oil refining.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide robust designs that help manage operational trade-offs, minimize coking risks, and extend equipment lifespan. Our strong deep customization capability ensures the furnace solution is tailored to your specific product slate, whether maximizing gasoline or preserving heavy lubricants.
Ready to enhance your distillation process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our furnace technology can be engineered for your unique refinery goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials



















