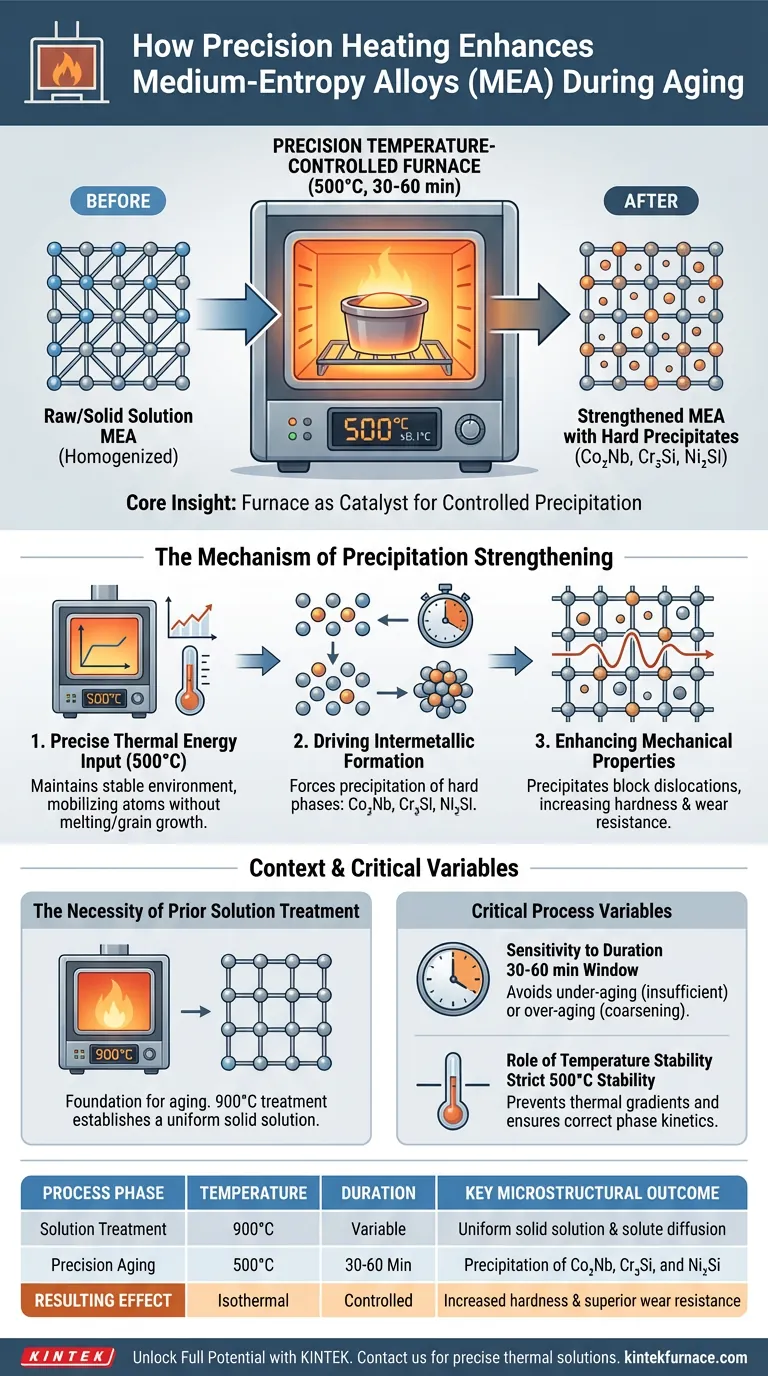
A precision temperature-controlled heating furnace significantly enhances medium-entropy alloys by maintaining a strict isothermal environment, typically at 500°C, for specific short durations like 30 or 60 minutes. This precise thermal regulation drives the precipitation of high-hardness intermetallic phases—specifically Co2Nb, Cr3Si, and Ni2Si—which directly improves the material's hardness and wear resistance.
Core Insight: The furnace does not merely heat the metal; it acts as a catalyst for specific microstructural changes. By delivering exact thermal energy, it transforms a solid solution into a structurally strengthened alloy through controlled precipitation, a process that fails without strict temperature stability.

The Mechanism of Precipitation Strengthening
Precise Thermal Energy Input
To achieve optimal aging, the furnace must maintain a constant temperature of 500°C.
This specific thermal window provides the necessary energy to mobilize atoms within the alloy lattice without melting the material or causing unwanted grain growth.
Driving Intermetallic Formation
The primary function of this thermal control is to force the precipitation of specific strengthening phases.
During the 30 to 60-minute holding period, the furnace environment facilitates the formation of hard intermetallic compounds, including Co2Nb, Cr3Si, and Ni2Si.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
These precipitated phases act as obstacles to dislocation movement within the metal's structure.
The direct result is a significant increase in the alloy's macroscopic hardness and wear resistance, achieving what is known as precise structural strengthening.
The Broader Context of Heat Treatment
The Necessity of Prior Solution Treatment
While the aging process occurs at 500°C, it relies on a foundation set by high-temperature solution treatment.
Before aging, alloys are often heated to 900°C in a high-temperature electric furnace to facilitate the full diffusion of solute elements.
Establishing a Uniform Foundation
This high-temperature step creates a uniform solid solution state.
Without this homogenization, the subsequent aging process in the precision furnace would result in uneven precipitation and inconsistent mechanical properties.
Critical Process Variables
Sensitivity to Duration
The effectiveness of the aging treatment is highly dependent on time; the primary reference notes durations of 30 or 60 minutes.
Deviating from these specific timeframes can lead to "under-aging" (insufficient precipitation) or "over-aging" (where particles coarsen and lose their strengthening effect).
The Role of Temperature Stability
The term "precision" is not marketing language; it is a metallurgical requirement.
If the furnace creates thermal gradients or fluctuates from 500°C, the kinetics of the phase transformation change, potentially preventing the formation of the critical Ni2Si or Cr3Si phases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of medium-entropy alloys, align your heat treatment strategy with your specific microstructural targets:
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: Ensure your furnace can hold exactly 500°C for 30–60 minutes to maximize the density of Co2Nb and Cr3Si precipitates.
- If your primary focus is material uniformity: Verify that the alloy undergoes a comprehensive solution treatment at 900°C prior to aging to redistribute solute elements.
- If your primary focus is stress relief: utilize the furnace's precision to provide a stable isothermal environment, effectively eliminating casting stresses before final hardening.
Precision in thermal processing is the bridge between raw material potential and verified engineering performance.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature | Duration | Key Microstructural Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution Treatment | 900°C | Variable | Uniform solid solution & solute diffusion |
| Precision Aging | 500°C | 30 - 60 Min | Precipitation of Co2Nb, Cr3Si, and Ni2Si |
| Resulting Effect | Isothermal | Controlled | Increased hardness & superior wear resistance |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Alloys with KINTEK
Precise thermal regulation is the difference between a standard material and a high-performance engineering alloy. At KINTEK, we understand that maintaining a strict 500°C isothermal environment or 900°C homogenization requires uncompromising equipment reliability.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems are engineered to prevent thermal gradients, ensuring uniform precipitation strengthening.
- Customizable Solutions: Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, we tailor our high-temp furnaces to your specific metallurgical targets.
- Proven Performance: We empower labs and manufacturers to achieve precise structural strengthening through superior temperature stability.
Ready to elevate your heat treatment precision? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and let KINTEK provide the precision your materials deserve.
Visual Guide
References
- Denis Ariel Ávila-Salgado, José Luis Camacho-Martínez. Evolution of Microstructure, Hardness, and Wear Behavior of Medium-Entropy CuNiSiCrCoTiNbx Alloy. DOI: 10.3390/lubricants13040164
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a flash furnace in sludge treatment? Essential Thermal Preparation for Phosphorus Recovery
- How does a circulating mineral oil jacket heating system function? Ensure Precision in Wood Thermal Modification
- How does a sputtering system contribute to the preparation of electrodes? Enhance Bismuth Telluride Characterization
- Why are aluminum alloy castings subjected to high-temperature testing in an industrial blister oven? Reveal Defects
- Why are c-Si wafers with pyramid structures chosen for MoS2 solar cells? Boost Efficiency with Light Trapping
- Why is stepped temperature control in a laboratory precision oven necessary? Mastering Porous TiCO Ceramic Curing
- What are the three types of dental ceramics? A Guide to Material Selection
- How are magnetic stirrers and constant temperature drying ovens utilized in the wet chemical synthesis of copper selenide nanorods?



















