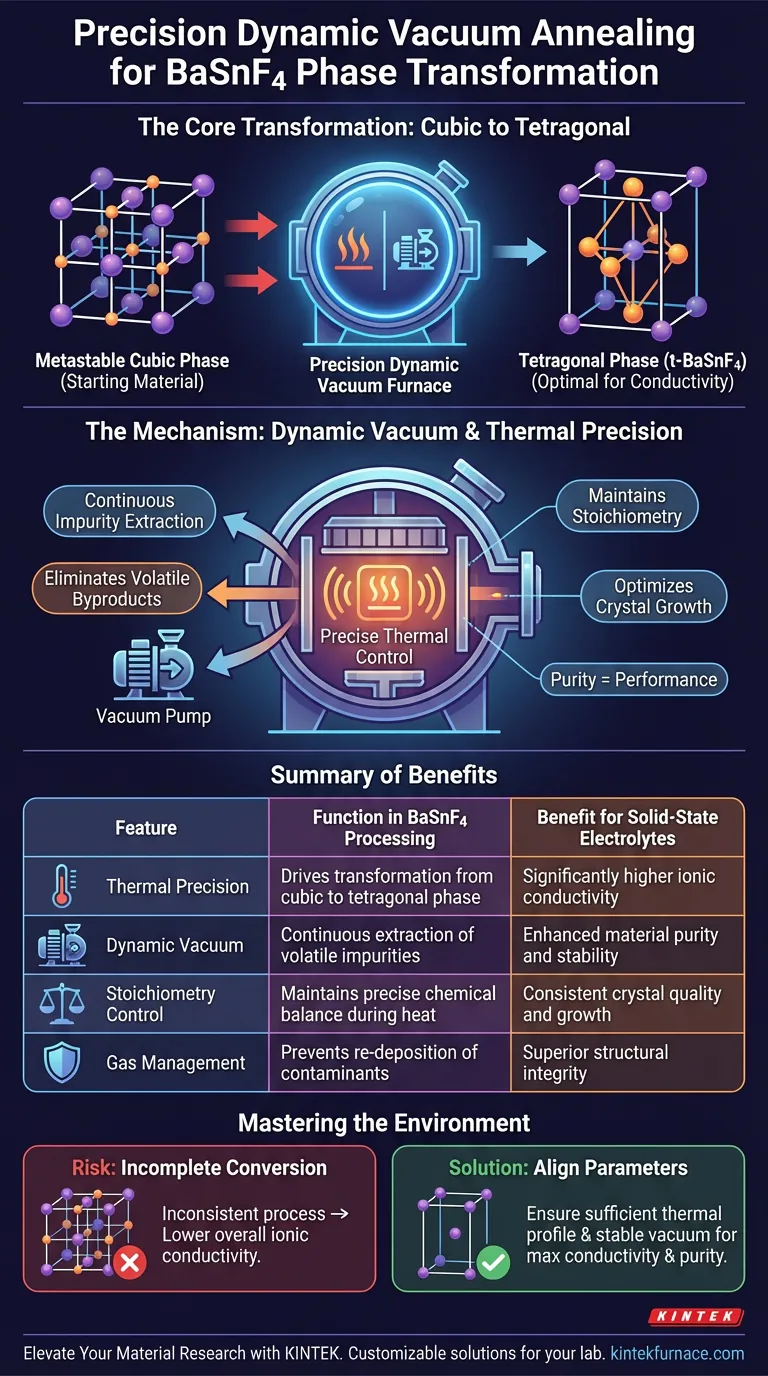
A precision dynamic vacuum annealing furnace acts as the critical catalyst for optimizing BaSnF4 solid-state electrolytes by orchestrating a specific structural change. It provides the controlled thermal energy required to convert metastable cubic-phase BaSnF4 into the tetragonal phase (t-BaSnF4), which is essential for high performance. Furthermore, the "dynamic" nature of the vacuum system actively manages the chemical environment to ensure purity and correct crystal growth.
By combining precise thermal control with continuous gas extraction, this equipment facilitates the vital transition from cubic to tetragonal phases, directly unlocking the high ionic conductivity required for effective solid-state electrolytes.

The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
Targeting the Tetragonal Phase
The primary function of this furnace is to drive a specific crystallographic shift. The synthesis process initially yields BaSnF4 in a metastable cubic phase.
Why Transformation Matters
While the cubic phase is the starting point, it is not the optimal state for performance. The furnace utilizes controlled heat to force the material into the tetragonal phase (t-BaSnF4). This specific structure possesses significantly higher ionic conductivity, making it the superior choice for electrolyte applications.
The Critical Role of Dynamic Vacuum
Continuous Impurity Extraction
A "dynamic" vacuum is distinct from a static sealed environment. It involves continuous pumping to remove gases as they are generated.
Eliminating Volatile Byproducts
During the annealing process, volatile impurity gases are often released. The dynamic vacuum immediately extracts these contaminants from the chamber, preventing them from re-depositing on or reacting with the material.
Maintaining Stoichiometry
The precise chemical balance, or stoichiometry, of the electrolyte is vital for its function. By selectively removing impurities without depleting essential elements, the vacuum environment ensures the material retains the correct chemical composition.
Optimizing Crystal Growth
A pure, contaminant-free environment allows for superior crystal formation. The reduction of interference from foreign gases leads to higher quality crystal growth, which directly correlates to the stability and efficiency of the final electrolyte.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Sensitivity
While this method yields high-quality results, it requires rigorous control. If the vacuum pressure fluctuates or the thermal profile is inconsistent, the phase conversion may be incomplete.
Risk of Incomplete Conversion
An inadequate process can leave residual cubic-phase material within the sample. This results in a mixed-phase product with lower overall ionic conductivity than a pure tetragonal sample.
How to Apply This to Your Project
To maximize the effectiveness of your BaSnF4 synthesis, align your processing parameters with your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is maximizing ionic conductivity: Ensure your thermal profile is sufficient to drive a complete transformation from the cubic to the tetragonal phase.
- If your primary focus is crystal purity and consistency: Prioritize the stability of the dynamic vacuum to ensure continuous removal of volatile impurities and maintenance of stoichiometry.
Mastering the environment inside the furnace is the single most effective way to guarantee the performance of your solid-state electrolyte.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in BaSnF4 Processing | Benefit for Solid-State Electrolytes |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Precision | Drives transformation from cubic to tetragonal phase | Significantly higher ionic conductivity |
| Dynamic Vacuum | Continuous extraction of volatile impurities | Enhanced material purity and stability |
| Stoichiometry Control | Maintains precise chemical balance during heat | Consistent crystal quality and growth |
| Gas Management | Prevents re-deposition of contaminants | Superior structural integrity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise phase transformation control is the key to unlocking the full potential of your solid-state electrolytes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of specialized solutions, including Vacuum, CVD, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs.
Whether you are refining BaSnF4 synthesis or developing next-generation battery materials, our high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal stability and dynamic environment required for success. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Hong Chen, Oliver Clemens. Revealing an Intercalation Nature of High‐Capacity Conversion Cathode Materials for Fluoride‐Ion Batteries by Operando Studies. DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202500374
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is low-temperature calcination in a vacuum furnace necessary for Yb:CaF2 nanopowders? Achieve Optical Perfection
- What are the primary functions of an industrial-grade vacuum furnace? Optimize Magnet Recycling Performance
- How does an ultra-high vacuum preparation chain assist in the preparation of RCu samples? Ensure Pristine Data
- What safety features are included in the vacuum furnace system? Essential Protection for Your Lab and Materials
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum annealing furnace? Achieve Clean, Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What are the key characteristics of high-temperature vacuum furnaces? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Precision in Material Processing
- How does vacuum heat treating work in terms of temperature and time control? Master Precise Material Transformations
- What role does the quench tank play in a drop-bottom quench furnace? Unlock Precision in Heat Treatment



















