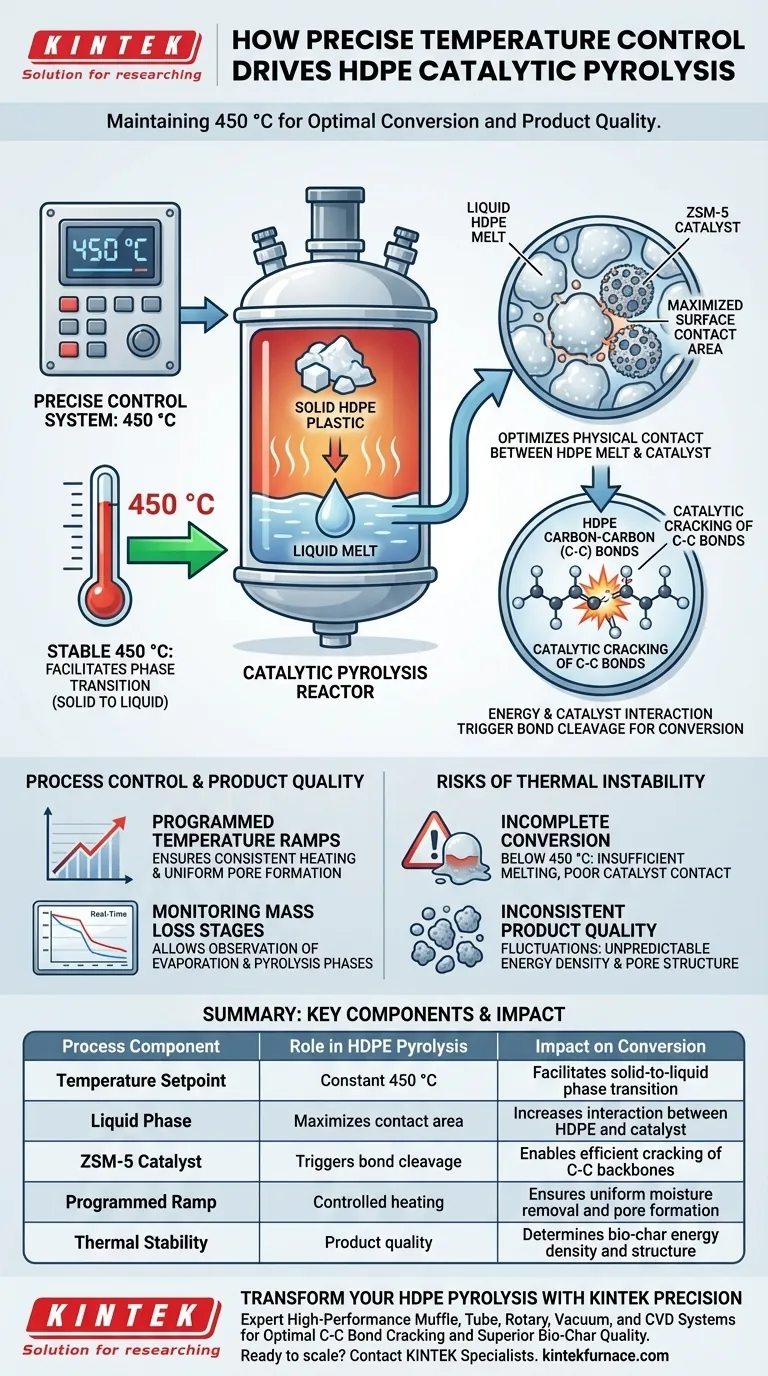
A precise temperature control system is the fundamental driver of efficiency in high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pyrolysis, specifically by maintaining the reaction environment at a stable 450 °C. This thermal precision forces the solid plastic to transition into a liquid melt, which maximizes the physical contact area between the HDPE and the ZSM-5 catalyst to trigger the necessary chemical breakdown.
Core Takeaway: Effective catalytic pyrolysis depends on phase transition, not just heat application. By holding a constant temperature, the control system optimizes the surface area interaction between the plastic melt and the catalyst, facilitating the cracking of Carbon-Carbon bonds that drives the entire conversion process.

The Mechanics of Catalytic Interaction
Creating the Liquid Phase
The primary function of the temperature control system is to reach and hold a constant 450 °C.
At this precise thermal setpoint, the HDPE undergoes a complete phase change from solid to liquid. This liquefaction is the prerequisite for all subsequent chemical reactions in this specific process.
Maximizing Surface Contact
Once the HDPE is in a liquid melt state, the dynamics of the reactor change.
The liquid phase significantly increases the contact area between the hydrocarbon chains and the ZSM-5 catalyst particles. Without this intimate physical contact, the catalyst cannot effectively interact with the bulk material.
Triggering Bond Cleavage
The interaction between the liquid HDPE and the catalyst is what initiates the reaction.
This specific thermal state enables the catalytic cracking of C-C bonds. The precise 450 °C environment provides the energy required to break the carbon backbone of the polymer effectively.
Process Control and Product Quality
Programmed Temperature Ramps
Beyond maintaining a static setpoint, an automatic control system manages the approach to the target temperature.
The system follows a specific, programmed temperature ramp. This ensures the material is heated consistently, rather than being subjected to thermal shock or uneven heating rates.
Monitoring Mass Loss Stages
Precise control allows for real-time observation of the reaction's progress.
By providing temperature compensation, operators can monitor mass loss characteristics across different stages. This includes distinguishing between initial moisture evaporation and the primary or secondary pyrolysis phases.
Defining Bio-Char Characteristics
The stability of the thermal environment directly impacts the physical properties of the solid byproduct.
The level of control exerted during the process dictates the development of the pore structure in the resulting bio-char. Furthermore, this precision influences the overall energy density of the final product.
Risks of Thermal Instability
Incomplete Conversion
If the system fails to maintain the strict 450 °C requirement, the phase transition may be compromised.
Lower temperatures may result in insufficient melting, preventing the necessary contact with the ZSM-5 catalyst. This leads to unreacted material and inefficient C-C bond cracking.
Inconsistent Product Quality
Reliability in the temperature ramp is critical for product uniformity.
Fluctuations during the heating stages can alter how moisture evaporates and how pyrolysis initiates. This inconsistency often results in bio-char with unpredictable energy densities and irregular pore structures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your HDPE pyrolysis setup, focus on the specific outcomes you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is conversion efficiency: Ensure your system can rigidly maintain 450 °C to guarantee the liquid melt required for maximum catalyst contact and bond cracking.
- If your primary focus is bio-char quality: prioritize a system with programmable ramps and compensation to control pore structure development and energy density.
Precise thermal regulation transforms pyrolysis from a chaotic heating process into a controlled chemical engineering operation.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in HDPE Pyrolysis | Impact on Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Setpoint | Constant 450 °C | Facilitates solid-to-liquid phase transition |
| Liquid Phase | Maximizes contact area | Increases interaction between HDPE and catalyst |
| ZSM-5 Catalyst | Triggers bond cleavage | Enables efficient cracking of C-C backbones |
| Programmed Ramp | Controlled heating | Ensures uniform moisture removal and pore formation |
| Thermal Stability | Product quality | Determines bio-char energy density and structure |
Transform Your HDPE Pyrolysis with KINTEK Precision
Don’t let thermal instability compromise your conversion efficiency. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Our precise temperature control systems ensure your catalytic reactions achieve the exact 450 °C environment required for optimal C-C bond cracking and superior bio-char quality.
Ready to scale your research or production? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace solution for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Wei Xiong, Jun Zhao. Acidic Site-Controlled ZSM-5 Catalysts for Fast Molten-Phase Pyrolysis of Plastic Waste with Tunable Product Distribution. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c02781
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is 500°C thermal stabilization necessary for titania supports? Ensure Catalyst Stability and Performance
- How does a laboratory furnace operate? Master Heating Principles for Your Lab
- What problem does a fluidized bed address in ceramic molds? Ensure Uniform Shells for High-Temp Casting
- What technical advantages does Joule heating equipment offer? Achieving High-Efficiency Single-Atom Catalyst Synthesis
- What is the function of a high-temperature heating reactor in OPF delignification? Unlock High-Purity Cellulose
- What is the function of the heating device in the micro-Kjeldahl method? Master Protein Analysis in Mushrooms
- What is the purpose of a safety warning system in MDR? Ensure Reactor Integrity and Laboratory Safety
- What is the function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven for Fe-N-C catalysts? Preserve Nanoporous Structure



















