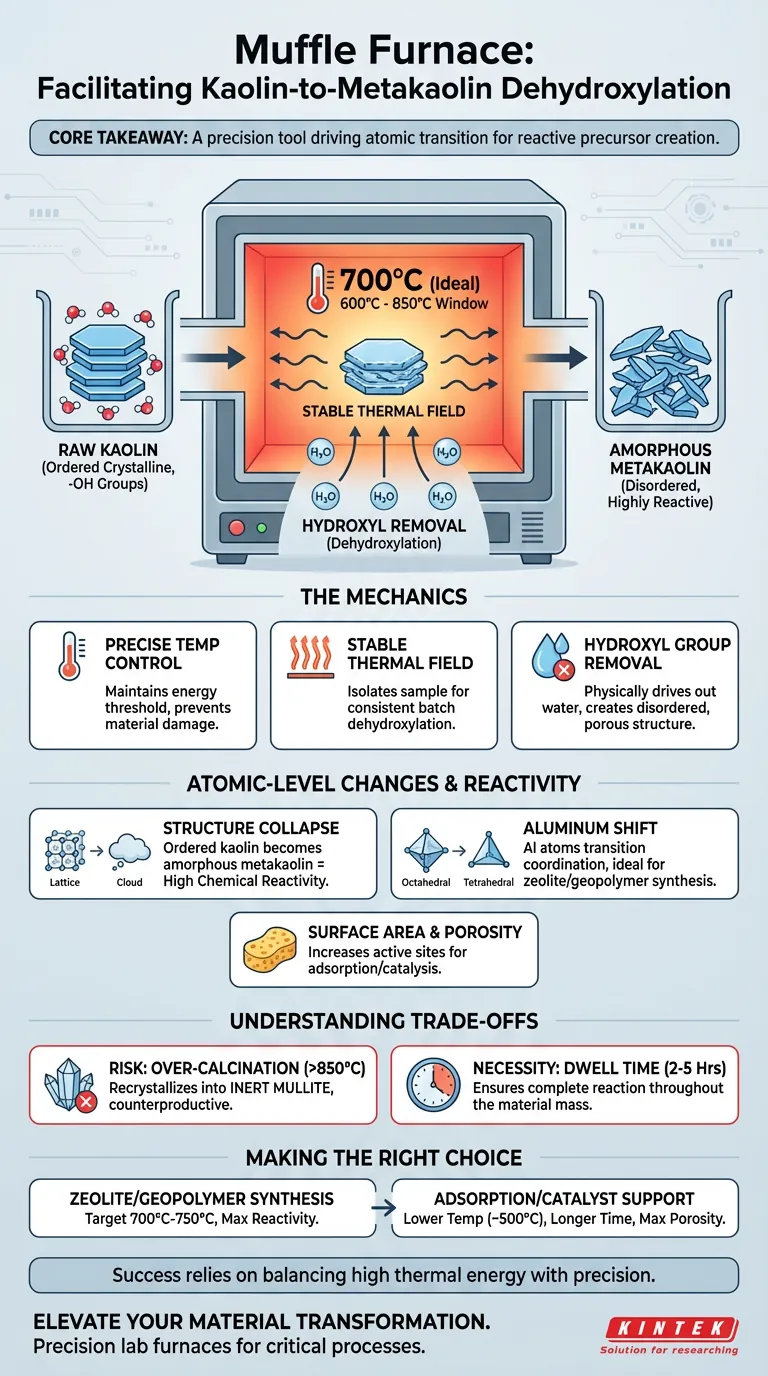
A muffle furnace facilitates dehydroxylation by creating a strictly controlled, high-temperature environment—typically at 700°C—that chemically alters the kaolin structure. By maintaining a stable thermal field, the furnace removes hydroxyl groups (water), causing the ordered crystalline layers of kaolin to collapse into an amorphous, highly reactive state known as metakaolin.
Core Takeaway: The muffle furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision tool that drives the atomic transition of aluminum from octahedral to tetrahedral or pentahedral coordination. This structural collapse is the critical prerequisite for converting inert kaolin into a reactive precursor for zeolites and geopolymers.

The Mechanics of Thermal Transformation
Precise Temperature Control
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this process is to maintain a specific temperature, ideally around 700°C.
While the dehydroxylation window can range from 600°C to 850°C, precise control is vital. The furnace ensures the material reaches the necessary energy threshold to break chemical bonds without fluctuating into temperature zones that could damage the material's reactivity.
Creating a Stable Thermal Field
A muffle furnace isolates the sample from the fuel and combustion byproducts, providing a stable thermal field.
This uniformity is essential for consistent dehydroxylation throughout the sample batch. Without this stability, uneven heating could result in a mixture of unreacted kaolin and over-calcined material, compromising the quality of the final product.
Removal of Hydroxyl Groups
Under this sustained heat, hydroxyl groups (-OH) and adsorbed water are physically driven out of the kaolin structure.
This chemical loss of water is the definition of dehydroxylation. It leaves behind a disordered, anhydrous structure that is significantly more porous and chemically active than the original raw material.
Atomic-Level Changes and Reactivity
Collapse of Crystalline Structure
Native kaolin possesses a layered, ordered crystal structure that is generally chemically inert.
The heat from the muffle furnace destroys this order. As the structure collapses, the material transforms into amorphous metakaolin. This lack of order (amorphicity) is directly correlated with high chemical reactivity.
Aluminum Coordination Shift
The most critical atomic change facilitated by the furnace is the alteration of aluminum atoms.
In raw kaolin, aluminum exists in octahedral coordination. The thermal treatment forces these atoms to transition into tetrahedral or pentahedral coordination. This specific atomic arrangement makes the material an ideal source of silicon and aluminum for synthesizing zeolites and geopolymers.
Surface Area and Porosity
Beyond structural collapse, the process significantly modifies the physical surface of the material.
By removing impurities and water, the furnace treatment increases specific surface area and porosity. This creates more active adsorption sites, which is beneficial if the metakaolin is intended for use as a catalyst carrier or an adsorbent for antibacterial agents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Over-Calcination
While high heat is necessary, exceeding the optimal temperature range can be detrimental.
If the furnace temperature drifts too high (often above 850°C), the amorphous metakaolin can recrystallize into mullite, an inert phase. Mullite lacks the reactivity required for geopolymer or zeolite synthesis, rendering the process counterproductive.
The Necessity of Dwell Time
Temperature alone is insufficient; the duration of exposure (dwell time) is equally critical.
The material typically requires 2 to 5 hours of continuous heating to ensure complete dehydroxylation. A muffle furnace allows for this extended insulation, ensuring the reaction permeates the entire mass of the material rather than just the surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters you set on your muffle furnace should depend on the intended application of the metakaolin.
- If your primary focus is Zeolite or Geopolymer Synthesis: Target 700°C to 750°C, prioritizing the atomic transition to tetrahedral/pentahedral aluminum for maximum chemical reactivity.
- If your primary focus is Adsorption or Catalyst Support: A lower range (near 500°C) for a longer duration (e.g., 5 hours) may be sufficient to maximize porosity and surface area without requiring total structural collapse.
Success in dehydroxylation relies on balancing high thermal energy with the precision required to stop the reaction before the material becomes inert.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Dehydroxylation Requirement | Role of Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Precise window (600°C - 850°C) | Prevents recrystallization into inert mullite |
| Thermal Field | Uniform heat distribution | Ensures consistent amorphicity across the batch |
| Structural Shift | Octahedral to Tetrahedral/Pentahedral | Forces atomic-level aluminum coordination changes |
| Environment | Clean, isolated heating | Protects sample from combustion byproducts |
| Dwell Time | 2 to 5 hours sustained heat | Provides stable insulation for complete reaction |
Elevate Your Material Transformation with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between reactive metakaolin and inert waste. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically designed for critical thermal processes like dehydroxylation and calcination.
Whether you are synthesizing zeolites or developing geopolymers, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the stable thermal fields and customizable controls your research demands.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature workflows?
→ Contact Our Specialists for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Antúsia dos Santos Barbosa, Meiry Gláucia Freire Rodrigues. Synthesis of NaA Zeolite: Conventional Route and Green Route. DOI: 10.21926/cr.2401002
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in LLZO crystal phase regulation? Optimize Li-Ion Electrolytes
- What is the role of convective heat transfer in a box type resistance furnace? Unlock Efficient Heating Dynamics
- What are the standard features included with Box Furnaces? A Guide to Core Capabilities & Performance
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in Ba1-xCaxTiO3 calcination? Ensure Purity & Precision in Ceramic Synthesis
- What experimental conditions does a muffle furnace provide for oxidation resistance testing of Ti/Al2O3 composites?
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in LFP regeneration? Restore Battery Life with Precision
- What is a muffle furnace and its primary use? Discover High-Temp, Contamination-Free Heating Solutions
- What role does the Muffle Furnace play in the pretreatment of K-Mo catalyst precursors? Key for Thermal Oxidation



















