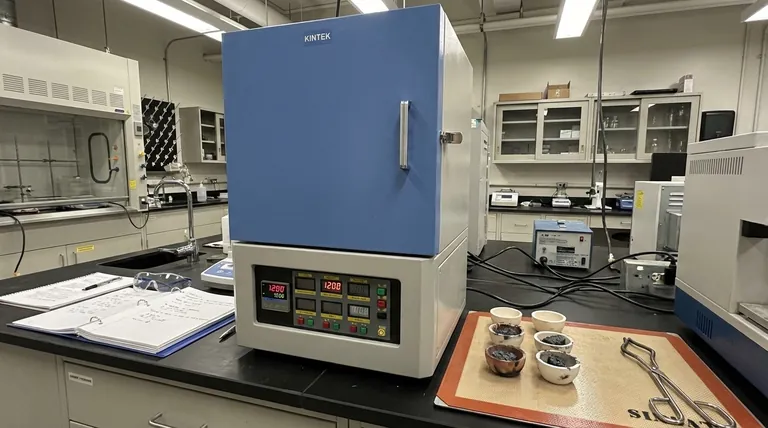
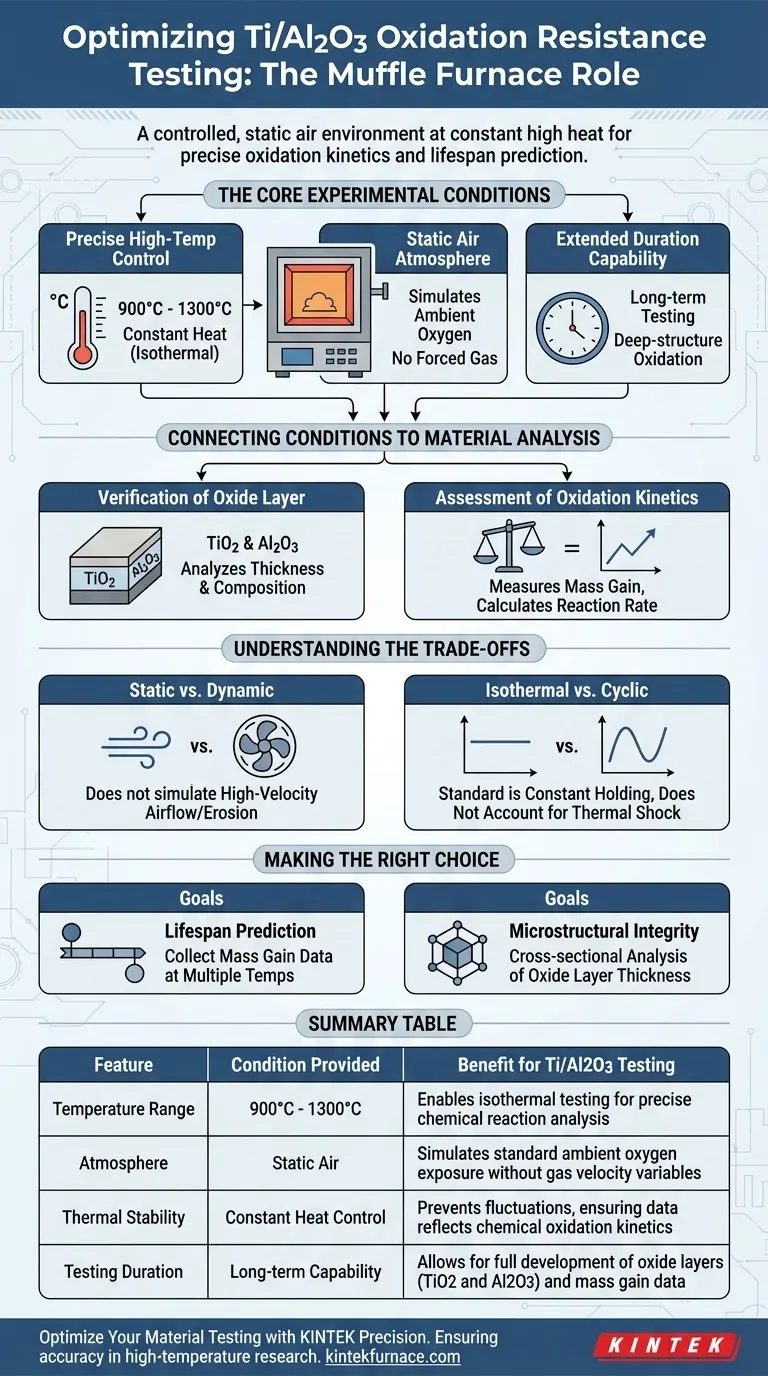
A muffle furnace provides a controlled, static air environment maintained at constant high temperatures—typically between 900°C and 1300°C—to strictly simulate oxidation conditions. This equipment ensures precise thermal stability over extended periods, allowing researchers to induce surface reactions on Ti/Al2O3 composites and measure the resulting oxide layer formation without atmospheric interference.
The muffle furnace functions as an isolation chamber that decouples thermal stress from mechanical stress, providing the stable baseline required to calculate oxidation kinetics and predict material lifespan.

The Core Experimental Conditions
To accurately evaluate oxidation resistance, the test environment must be rigorous and consistent. The muffle furnace achieves this through three specific mechanisms.
Precise High-Temperature Control
The primary function of the furnace is to reach and maintain extreme temperatures, ranging from 900°C to 1300°C.
This is not merely about reaching a peak temperature; the equipment provides constant heat (isothermal conditions). This stability is critical for ensuring that any changes in the material are due to chemical oxidation, not thermal fluctuations.
Static Air Atmosphere
Unlike equipment that pumps active gases over a sample, a muffle furnace typically utilizes a static air atmosphere.
This setup simulates a standard operating environment where the material is exposed to ambient oxygen under heat. It allows oxygen to react naturally with the Titanium (Ti) and Alumina (Al2O3) without the variable of forced gas velocity.
Extended Duration Capability
Oxidation is a time-dependent process. The furnace is designed to hold these high temperatures for long-duration testing.
This allows the reaction to progress fully, transitioning from initial surface changes to deep-structure oxidation.
Connecting Conditions to Material Analysis
The conditions provided by the muffle furnace are designed specifically to generate measurable data regarding the material's degradation.
Verification of Oxide Layer Composition
The high heat forces the formation of oxide scales, specifically titanium dioxide (TiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
By controlling the temperature, researchers can analyze the thickness and microstructure of these layers. This reveals how well the composite resists oxygen penetration.
Assessment of Oxidation Kinetics
Because the environment is stable, researchers can periodically remove samples to measure weight changes.
This leads to accurate oxidation mass gain data. By plotting this mass gain over time, you can generate kinetics curves that mathematically describe how fast the material is degrading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is the standard for oxidation testing, it is important to recognize the limitations of this specific experimental setup.
Static vs. Dynamic Limitations
The muffle furnace provides a static environment. It does not simulate high-velocity airflow or erosion, which might be present in aerospace applications like turbine engines.
If your material faces "hot corrosion" (high velocity + heat), muffle furnace data may underestimate the degradation rate.
Isothermal vs. Cyclic Constraints
Standard muffle furnace testing focuses on isothermal (constant) holding.
While useful for kinetics, this does not automatically account for thermal shock—the damage caused by rapid heating and cooling cycles. If thermal cycling is required, the experimental protocol must be manually adjusted to include heating and cooling intervals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The data you extract from a muffle furnace depends on how you align your testing protocols with your ultimate engineering objectives.
- If your primary focus is Lifespan Prediction: Prioritize collecting oxidation mass gain data at multiple temperature points (e.g., 900°C and 1300°C) to calculate the reaction rate constants.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Integrity: Focus on the cross-sectional analysis of the oxide layer thickness (TiO2 vs. Al2O3) to determine if the protective alumina layer remains intact.
By isolating the composite in this stable, high-heat environment, you transform theoretical material properties into verified performance data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Condition Provided | Benefit for Ti/Al2O3 Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 900°C to 1300°C | Enables isothermal testing for precise chemical reaction analysis |
| Atmosphere | Static Air | Simulates standard ambient oxygen exposure without gas velocity variables |
| Thermal Stability | Constant Heat Control | Prevents fluctuations, ensuring data reflects chemical oxidation kinetics |
| Testing Duration | Long-term Capability | Allows for full development of oxide layers (TiO2 and Al2O3) and mass gain data |
Optimize Your Material Testing with KINTEK Precision
Ensure your research yields accurate oxidation kinetics and reliable lifespan predictions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to your specific laboratory requirements.
Whether you are analyzing Ti/Al2O3 composites or developing next-generation alloys, our furnaces provide the thermal stability and atmospheric control you need.
Ready to elevate your high-temperature research? Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature box furnace in the annealing process of AA6061 aluminum alloy?
- Why is calcination in a muffle furnace necessary for cerium oxide catalysts? Optimize Your Rod-Shaped Catalyst Performance
- Why is a laboratory high-temperature box furnace essential for KNN ceramic powders? Mastering Solid-State Synthesis
- What process conditions must a muffle furnace satisfy for CoNiCrAlY oxidation? Ensure Precise High-Temp Stability
- How does a muffle furnace with precision temperature control contribute to the debinding of alumina ceramic green bodies?
- What key role does a laboratory electric resistance furnace play in sintering Ba1-xCaxTiO3? Drive Ceramic Performance
- How should samples be handled when burning or melting them in a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Accurate Results
- What are the advantages of the bottom-loading furnace configuration? Achieve High-Temp Control and Element Protection



















