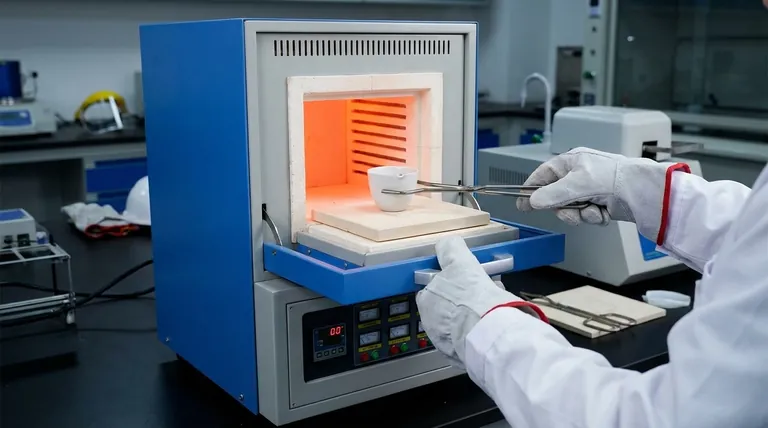
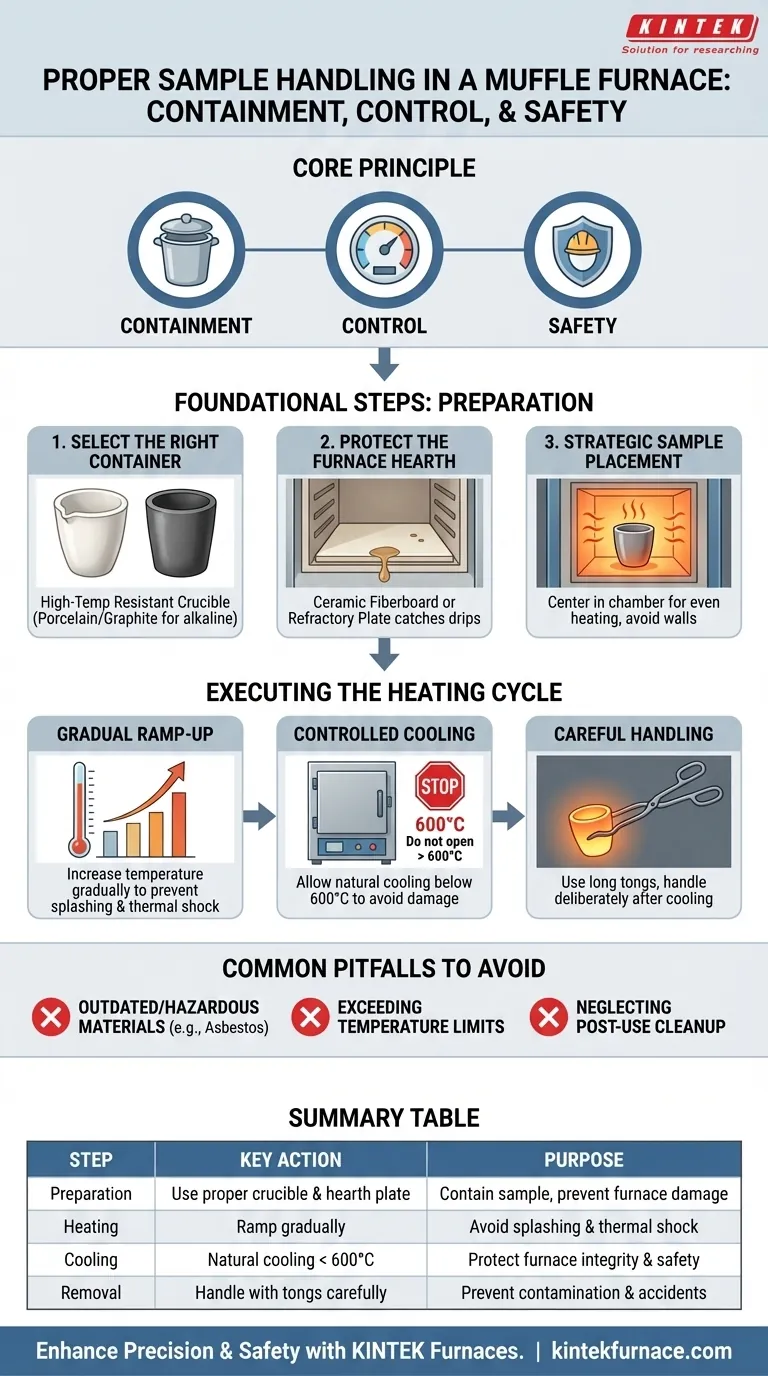
Proper sample handling in a muffle furnace is a systematic process focused on containment, control, and safety. To handle a sample correctly, you must place it in a high-temperature-resistant crucible, position it in the center of the furnace on a protective plate, and ramp up the temperature gradually to prevent splashing, which can damage the furnace and compromise your results.
Handling samples in a muffle furnace is less about a single action and more about a systematic process. The core principle is containment—of the sample, the heat, and any potential reactions—to ensure accurate results while protecting the long-term integrity of the furnace.

Foundational Steps: Preparing for a Successful Burn
Before you even turn the furnace on, proper preparation is critical for both the accuracy of your results and the longevity of the equipment.
Selecting the Right Container
The container is your first line of defense. It must withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with your sample.
For most applications, a high-temperature-resistant porcelain crucible or dish is the standard choice. If you are melting highly alkaline substances, use a specialized refractory plate or graphite crucible to prevent corrosive reactions that can destroy a standard container.
Protecting the Furnace Hearth
Never place your crucible directly on the furnace floor. Spills or splashes can permanently corrode or bond to the hearth, causing irreversible damage.
Place a ceramic fiberboard or refractory hearth plate on the bottom of the furnace chamber. This board acts as a clean, sacrificial surface that catches any drips or slag. Any residue on this board should be cleaned promptly after the furnace has cooled.
Strategic Sample Placement
Where you place the sample inside the furnace directly impacts the outcome.
Position the crucible neatly in the center of the furnace chamber. This ensures the most even heating from all sides and prevents temperature gradients that could affect your results. Crucially, ensure the crucible does not touch the furnace walls, heating elements, or the thermocouple.
Executing the Heating Cycle with Control
The heating and cooling process must be deliberate and controlled. Rushing these steps is the most common cause of sample loss and equipment failure.
The Importance of a Gradual Ramp-Up
Rapidly increasing the temperature is a critical error. It can cause violent reactions, boil-overs, or splashing of the sample material.
Always increase the furnace temperature gradually according to a pre-defined heating profile. This controlled ramp rate prevents thermal shock to both the crucible and the furnace lining, and it ensures your sample doesn't escape the crucible.
The Cooling-Down Protocol
Opening a hot furnace is extremely dangerous and damaging. The drastic temperature change, known as thermal shock, can crack the furnace's ceramic lining or even shatter your crucible.
As a rule, do not open the furnace door at temperatures above 600°C. Turn off the power and allow the furnace to cool naturally for several hours or overnight. Patience at this stage is non-negotiable.
Careful Handling and Removal
Once the furnace has cooled to a safe temperature, use long, sturdy crucible tongs to handle the sample. Move deliberately and carefully to avoid bumping the tongs against the fragile furnace interior.
After removing the sample, close the furnace door to protect the chamber from ambient moisture, which can degrade the insulation over time.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding what not to do is as important as knowing the correct procedure. Avoiding these mistakes will save you from costly repairs and failed experiments.
Pitfall: Outdated and Hazardous Materials
Some older guides may mention using an asbestos board. Asbestos is a dangerous carcinogen and should never be used. Modern, safe alternatives like rigid ceramic fiberboards offer superior performance without the health risks.
Pitfall: Exceeding Temperature Limits
Every furnace has a maximum operating temperature. Pushing the equipment beyond this limit to speed up a process will drastically shorten the life of the heating elements and can lead to catastrophic failure.
Pitfall: Neglecting Post-Use Cleanup
After a run, residue like metal oxides or slag can be left on the hearth plate. Leaving this contamination in the furnace for the next run can cause cross-contamination and lead to cumulative damage to the hearth plate and furnace floor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific procedure should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (e.g., ashing): Your top priority is preventing sample loss, so a slow, controlled temperature ramp and careful handling are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is melting or material synthesis: Even heating is critical, so central placement on a clean hearth plate is paramount to ensure a uniform final product.
- If your primary focus is safety and equipment longevity: Always use a protective hearth plate and strictly adhere to the cooling protocol before opening the furnace door.
By treating the furnace as a precision instrument, you ensure every run is safe, repeatable, and accurate.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Use high-temperature crucible and protective hearth plate | Contain sample, prevent furnace damage |
| Heating | Ramp temperature gradually | Avoid splashing and thermal shock |
| Cooling | Allow natural cooling below 600°C | Protect furnace integrity and ensure safety |
| Removal | Handle with crucible tongs carefully | Prevent contamination and accidents |
Upgrade your laboratory's precision and safety with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for reliable, efficient results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















