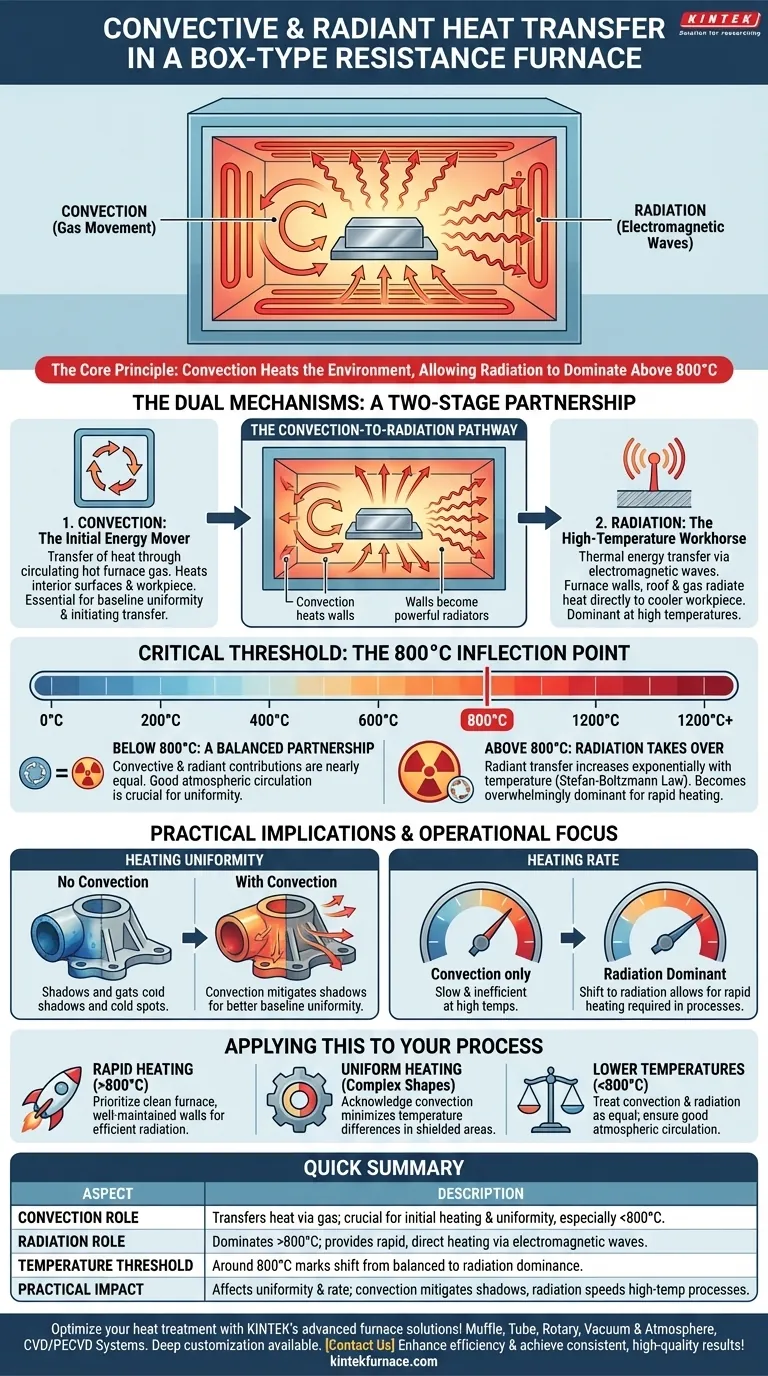
In a box-type resistance furnace, convective heat transfer is a fundamental mechanism that works in tandem with radiation to heat the workpiece. It involves the movement of hot furnace gas, which circulates and transfers thermal energy to both the furnace interior surfaces and the metal being treated. However, its significance relative to radiation changes dramatically with temperature.
While convection is essential for initiating heat transfer and ensuring baseline uniformity, its direct influence diminishes at high temperatures. The core principle to grasp is that convection heats the furnace environment, which then allows the far more powerful mechanism of radiant heat transfer to dominate the process above approximately 800°C.
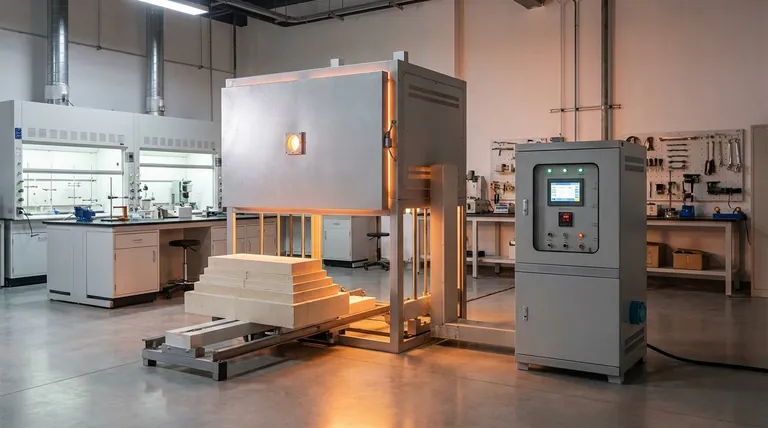

The Dual Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
To understand the furnace's operation, you must see convection and radiation not as competitors, but as partners in a two-stage process.
Convection: The Initial Energy Mover
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid—in this case, the gas or atmosphere inside the furnace. The furnace's resistance heating elements heat this gas.
This hot gas then circulates throughout the chamber, transferring its thermal energy to every surface it touches, including the furnace walls and the metal workpiece itself.
Radiation: The High-Temperature Workhorse
All objects with a temperature above absolute zero emit thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. This is radiant heat.
Inside a hot furnace, the internal walls, roof, and even the hot gases themselves radiate immense amounts of energy directly to the cooler metal workpiece.
The Convection-to-Radiation Pathway
A critical role of convection is indirect. Convection from the hot furnace gas heats the refractory lining of the furnace walls and roof.
These superheated walls then become powerful radiators, transmitting the heat they absorbed via convection to the metal in the form of intense thermal radiation.
The Critical Temperature Threshold: 800°C
The balance between convection and radiation is not static; it is dictated by the furnace's operating temperature. The 800°C (approx. 1475°F) mark is a key inflection point.
Below 800°C: A Balanced Partnership
At lower operating temperatures, the contributions of convective and radiant heat transfer are nearly equal.
In this range, ensuring good circulation of the furnace atmosphere is just as important as the radiant properties of the chamber for achieving uniform and efficient heating.
Above 800°C: Radiation Takes Over
The energy transferred by radiation increases with the fourth power of the absolute temperature (the Stefan-Boltzmann law). This means its effect grows exponentially as the furnace gets hotter.
Once temperatures exceed 800°C, this exponential increase causes radiant heat transfer to become the overwhelmingly dominant mechanism, rapidly overshadowing the more linear effect of convection.
Understanding the Practical Implications
This dynamic relationship between heat transfer modes has direct consequences for furnace operation and design.
Impact on Heating Uniformity
Radiation travels in straight lines. This can create "shadows" on complex-shaped parts, where some surfaces receive less direct radiant energy.
Convection helps mitigate this by allowing hot gas to flow into and around these shielded areas, providing a more uniform baseline temperature across the entire workpiece.
Impact on Heating Rate
Relying solely on convection at high temperatures would be slow and inefficient. The shift to radiation dominance is what allows for the rapid heating rates required in many heat treatment processes.
The initial convective heating phase creates the hot environment necessary for the much faster radiant heating to take over and bring the metal to its final temperature quickly.
Applying This to Your Process
Your operational focus should adapt based on the temperature range and desired outcome for your workpiece.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating to high temperatures (above 800°C): Prioritize a clean furnace environment with well-maintained walls that can act as efficient radiators.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of complex shapes: Acknowledge that convection is your key tool for minimizing temperature differences in areas shielded from direct radiation.
- If your primary focus is processing at lower temperatures (below 800°C): Treat convection and radiation as equal partners and ensure your furnace allows for good atmospheric circulation.
By understanding this interplay between convection and radiation, you gain precise control over your heating process and ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Convection Role | Transfers heat via gas movement, crucial for initial heating and uniformity, especially below 800°C. |
| Radiation Role | Dominates above 800°C, providing rapid, direct heating via electromagnetic waves. |
| Temperature Threshold | Around 800°C marks the shift from balanced convection-radiation to radiation dominance. |
| Practical Impact | Affects heating uniformity and rate; convection mitigates shadows, radiation speeds high-temp processes. |
Optimize your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and achieve consistent, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















