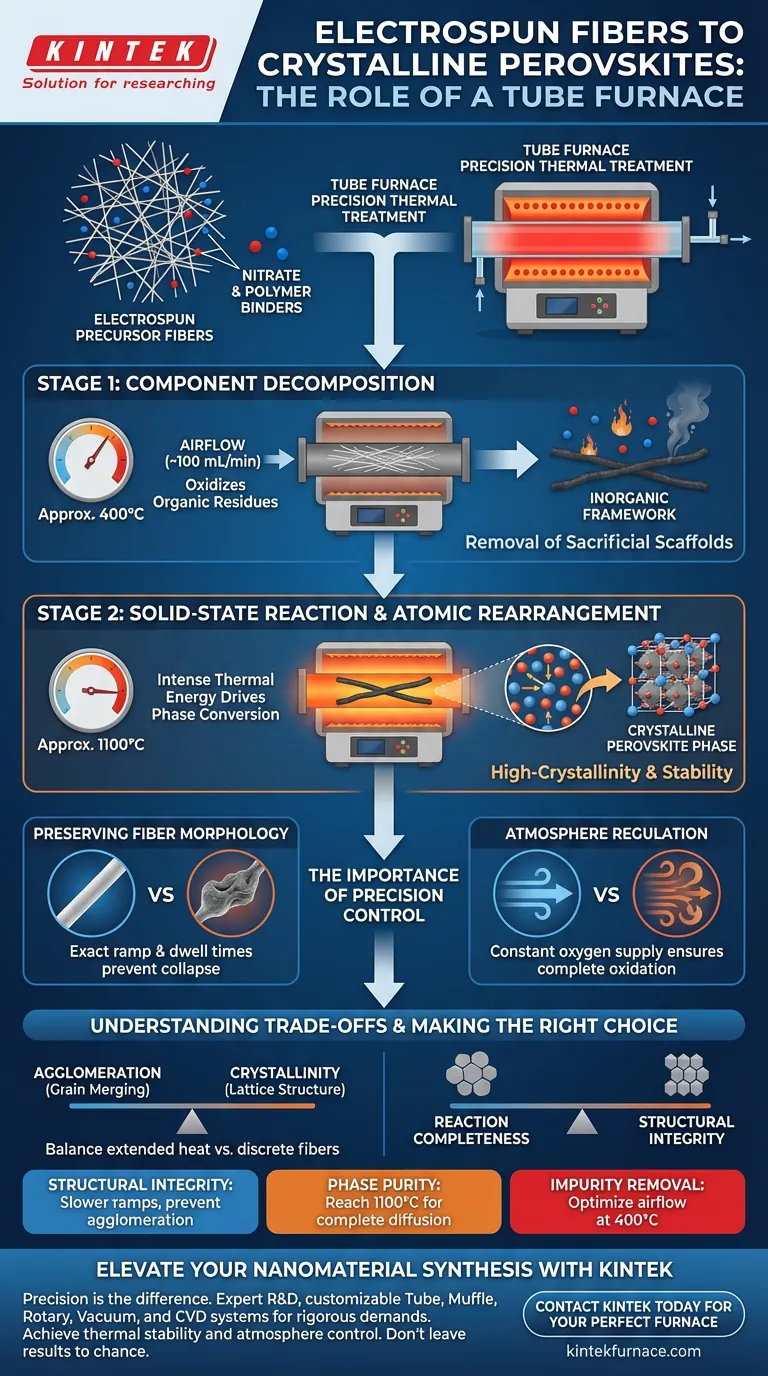
A laboratory high-temperature tube furnace serves as the critical reaction vessel for transforming electrospun precursor fibers into functional crystalline perovskites. By providing a precisely controlled thermal environment, it executes a two-stage process that removes organic scaffolds and drives atomic rearrangement without destroying the delicate fiber structure.
The tube furnace enables a sequential thermal treatment: decomposing nitrate and polymer binders at moderate temperatures (approx. 400°C) before ramping to high temperatures (around 1100°C) to crystallize the perovskite phase.

The Mechanism of Transformation
The conversion from a raw electrospun fiber to a crystalline perovskite is not a single-step heating event. It requires a distinct, multi-phase thermal profile that a tube furnace is uniquely designed to manage.
Stage 1: Component Decomposition
The first critical function of the furnace is the removal of the "sacrificial" components.
At temperatures of approximately 400°C, the furnace facilitates the decomposition of nitrate salts and polymer components used to create the initial fiber solution.
This step must occur in an air environment to effectively oxidize and remove these organic residues, leaving behind the inorganic framework.
Stage 2: Solid-State Reaction
Once the organics are removed, the material requires intense thermal energy to achieve its final phase.
The furnace increases the temperature to roughly 1100°C to initiate a solid-state reaction.
At this ultra-high temperature, the precursors convert into the definitive crystalline perovskite phase.
Atomic Rearrangement
The sustained high heat promotes the necessary rearrangement of lattice atoms.
This diffusion allows the material to achieve a high-crystallinity structure, which is essential for the material's stability and oxygen release capabilities.
The Importance of Precision Control
The primary challenge in calcining nanofibers is preventing the structure from collapsing into a powder or a fused mass.
Preserving Fiber Morphology
The tube furnace’s high precision ensures that the thermal ramp and dwell times are exact.
This control is vital for maintaining the fiber morphology (the shape and structure) throughout the drastic phase change.
If the temperature fluctuates or ramps too aggressively, the fibers may melt or break; precise control preserves the high surface area generated by electrospinning.
Atmosphere Regulation
Tube furnaces offer superior control over the reaction atmosphere compared to standard box furnaces.
They can maintain a precise airflow (e.g., 100 mL per minute), which ensures sufficient oxygen is present for the initial decomposition and the subsequent formation of oxide phases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high-temperature tube furnaces are the standard for this synthesis, there are inherent risks in the thermal processing parameters.
Agglomeration vs. Crystallinity
There is a delicate balance between achieving high crystallinity and maintaining discrete fibers.
Extended thermal treatment at high temperatures (1000°C+) improves the lattice structure but increases the risk of grain agglomeration.
If the grains merge excessively, the unique benefits of the nanofiber structure—specifically its high surface-to-volume ratio—are diminished.
Reaction Completeness vs. Structural Integrity
Insufficient dwell times or temperatures below the optimal 1100°C range may preserve the fiber shape perfectly but result in an incomplete phase transformation.
This leaves the material with residual precursors or low crystallinity, which significantly hampers performance in redox cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your high-temperature tube furnace for perovskite fibers, you must align your heating protocol with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize slower ramp rates and precise temperature ceilings to prevent grain agglomeration and preserve fiber morphology.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the furnace reaches and holds the 1100°C threshold to drive complete atomic diffusion and lattice rearrangement.
- If your primary focus is Impurity Removal: Optimize the airflow rate during the 400°C dwell stage to fully oxidize and evacuate all nitrate and polymer residues.
Success relies on utilizing the furnace's precision to balance the destruction of organics with the construction of the crystal lattice.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature Range | Primary Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Component Decomposition | Approx. 400°C | Oxidation of nitrates and polymer binders | Removal of organic sacrificial scaffolds |
| Solid-State Reaction | Approx. 1100°C | Intense thermal energy application | Conversion to definitive crystalline phase |
| Atomic Rearrangement | Sustained High Heat | Lattice atom diffusion | High-crystallinity & structural stability |
| Atmosphere Control | Constant Airflow | Controlled oxygen supply | Complete oxidation of residues |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a collapsed structure and a high-performance crystalline perovskite. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory research.
Whether you are scaling up electrospun fiber production or refining complex phase transformations, our high-temperature furnaces provide the thermal stability and atmosphere control necessary for success. Don't leave your results to chance.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect furnace for your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Min Xu, John T. S. Irvine. Synergistic growth of nickel and platinum nanoparticles via exsolution and surface reaction. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48455-2
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the design of a dual-zone Tube Furnace facilitate precise metal phosphide conversion? Optimize Heterojunctions
- What is the function of an industrial tube furnace in NdFeB recycling? Unlock Efficient Rare Earth Recovery
- Why are high temperature tube furnaces important for industrial and scientific use? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What role does a programmable tube furnace play in the remelting of cast iron? Expert Insights on Thermal Precision
- Why are sealed quartz tubes required for Au-Seeded TiO2 nanowires? Ensure Vapor-Phase Stability and VLS Growth
- What precautions should be taken regarding liquids and metals in a tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Prevent Damage
- What are the main advantages of using a tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized for the calcination of nano-zinc oxide? Master Microstructure Control



















