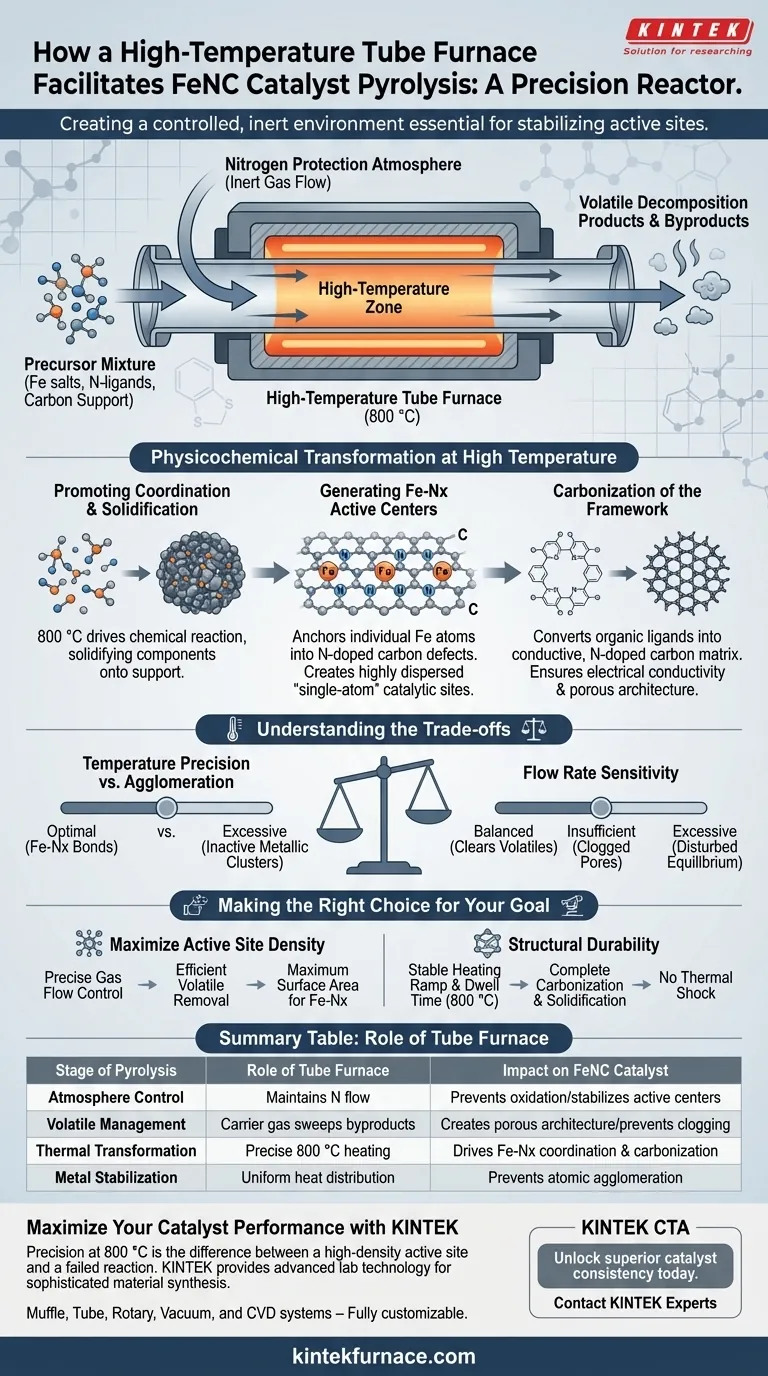
A high-temperature tube furnace acts as a precision reactor that facilitates the pyrolysis of FeNC catalysts by creating a controlled, inert environment essential for stabilizing active sites. Specifically, it utilizes a nitrogen protection atmosphere at temperatures around 800 °C to drive the physicochemical coordination of iron and nitrogen while simultaneously purging volatile byproducts.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace does not merely heat the material; it orchestrates a delicate balance between carbonization and chemical bonding. By maintaining a strict nitrogen flow, it forces iron salts to coordinate with nitrogen ligands on the carbon support, locking in the critical Fe-Nx active centers before the metal can agglomerate.

The Critical Role of Controlled Atmosphere
Establishing Nitrogen Protection
The fundamental function of the tube furnace during this stage is the maintenance of a nitrogen protection atmosphere.
By sealing the reaction environment, the furnace prevents oxygen from entering, which would otherwise combust the carbon support and oxidize the iron precursors prematurely.
Expelling Volatile Decomposition Products
During pyrolysis, the organic components of the precursor materials decompose, releasing volatile gases.
The nitrogen flow within the tube acts as a carrier mechanism, actively sweeping these decomposition products away from the solid catalyst.
Removing these volatiles is critical to prevent them from re-adsorbing or interfering with the formation of the desired pore structure.
Physicochemical Transformation at High Temperature
Promoting Coordination and Solidification
At processing temperatures (typically around 800 °C), the thermal energy drives a specific chemical reaction between metal salts and nitrogen-containing organic ligands.
The furnace environment facilitates the solidification of these components onto the carbon support.
This thermal treatment transforms the loose precursor mixture into a robust, integrated material where iron atoms are chemically bonded to the structure rather than physically resting on top of it.
Generating Fe-Nx Active Centers
The ultimate goal of this pyrolysis stage is the creation of uniformly distributed Fe-Nx active centers.
The tube furnace provides the thermodynamic conditions necessary to anchor individual iron atoms into nitrogen-doped carbon defects.
This results in the "single-atom" or highly dispersed catalytic sites that define the performance of high-quality FeNC catalysts.
Carbonization of the Framework
Beyond the metal sites, the high heat induces the carbonization of the supporting framework (such as ZIF-8 or other polymers).
This process converts organic ligands into a conductive, nitrogen-doped carbon matrix.
This structural evolution ensures the catalyst has the necessary electrical conductivity and porous architecture to function in electrochemical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision vs. Agglomeration
While high temperatures are needed to graphitize carbon and form Fe-Nx bonds, excessive heat can be detrimental.
If the temperature control is imprecise and exceeds optimal limits, the metal atoms may migrate and aggregate into inactive metallic clusters (nanoparticles) rather than remaining as dispersed atomic sites.
Flow Rate Sensitivity
The rate of nitrogen flow is a critical variable that must be balanced.
Insufficient flow may fail to clear volatile debris, clogging the catalyst's pores. Conversely, turbulent or excessive flow could disturb the thermal equilibrium or physically displace lighter precursor powders before they solidify.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If your primary focus is maximizing active site density: Prioritize a furnace with precise gas flow control to ensure volatiles are removed efficiently, allowing maximum surface area for Fe-Nx coordination.
If your primary focus is structural durability: Focus on the stability of the heating ramp and dwell time at 800 °C to ensure complete carbonization and solidification of the support matrix without thermal shock.
The tube furnace is the instrument that transforms a chemical mixture into a functional catalyst by strictly enforcing the atmospheric and thermal laws required for atomic coordination.
Summary Table:
| Stage of Pyrolysis | Role of Tube Furnace | Impact on FeNC Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Maintains nitrogen flow (inert) | Prevents oxidation; stabilizes active centers. |
| Volatile Management | Carrier gas sweeps byproducts | Creates porous architecture; prevents pore clogging. |
| Thermal Transformation | Precise 800 °C heating | Drives Fe-Nx coordination and carbonization. |
| Metal Stabilization | Uniform heat distribution | Prevents atomic agglomeration into inactive clusters. |
Maximize Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Precision at 800 °C is the difference between a high-density active site and a failed reaction. KINTEK provides the advanced lab technology needed for sophisticated material synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or industrial needs.
Unlock superior catalyst consistency today.
Visual Guide
References
- Han Zheng, Weimeng Si. Decorating Ti3C2 MXene Nanosheets with Fe-Nx-C Nanoparticles for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction. DOI: 10.3390/inorganics13060188
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a Drop Tube Furnace? Master Single-Particle Solid Fuel Ignition Analysis
- How is a Pulse Ignition device used for coal cloud explosions? Master MAIT Testing with Godbert-Greenwald Furnaces
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in transforming photopolymerized parts into fully aromatic polyimide?
- What is a tubular furnace used for? A Guide to Precise High-Temperature Processing
- How does the use of a tube furnace enhance cellulose-amine materials? Unlock Superior Porosity & Surface Area
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the preparation of barium ferrite? Achieve Optimal Magnetism
- How does a tube furnace ensure uniform heating? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- Why is an inert gas delivery system critical for a tube furnace? Engineering High-Performance Biochar



















