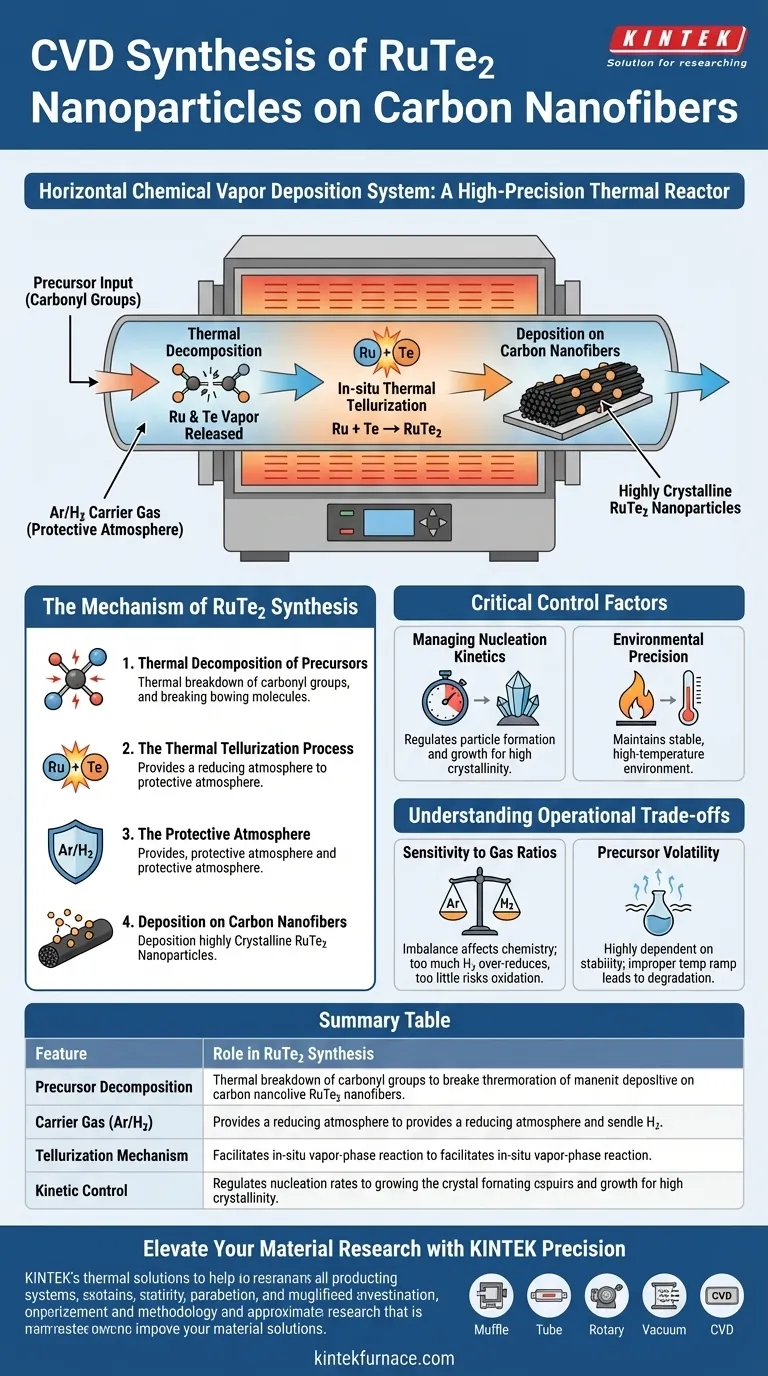
A horizontal Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system functions as a high-precision thermal reactor designed to synthesize RuTe2 nanoparticles through a specific sequence of decomposition and recombination. By maintaining a high-temperature environment protected by an argon/hydrogen gas mixture, the system facilitates the thermal decomposition of carbonyl precursors and creates the conditions necessary for ruthenium and tellurium vapors to react in-situ, depositing directly onto carbon nanofibers.
Core Takeaway The CVD system is not merely a furnace; it is a kinetic control environment that synchronizes the breakdown of precursors with a "thermal tellurization" process. This precise atmospheric management allows for the growth of highly crystalline RuTe2 nanoparticles directly on carbon supports, preventing oxidation or uncontrolled aggregation.

The Mechanism of RuTe2 Synthesis
Thermal Decomposition of Precursors
The process begins with the introduction of precursors containing carbonyl groups into the horizontal CVD system.
Under the influence of the system's high-temperature environment, these carbonyl groups undergo thermal decomposition. This step is critical for releasing the reactive chemical species required for the subsequent formation of the nanoparticles.
The Thermal Tellurization Process
Once the precursors have decomposed, the system facilitates a specific reaction known as thermal tellurization.
In this phase, an in-situ reaction occurs between the generated ruthenium vapor and tellurium vapor. This vapor-phase interaction allows the elements to combine chemically to form ruthenium ditelluride (RuTe2) before or during their deposition onto the substrate.
The Protective Atmosphere
To ensure the purity of the reaction, the entire process takes place under a flowing Ar/H2 (Argon/Hydrogen) mixed carrier gas.
This gas mixture serves a dual purpose: it acts as a carrier to transport vapors through the reaction zone, and it provides a reducing atmosphere that protects the developing nanoparticles from oxidation or other environmental contaminants.
Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers
The final physical result is the generation of nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers.
Because the reaction occurs in-situ within the CVD chamber, the RuTe2 forms as highly crystalline nanoparticles directly on the fiber structure, ensuring strong integration between the active material and the support.
Critical Control Factors
Managing Nucleation Kinetics
While the primary mechanism is chemical, the CVD system’s value lies in its ability to regulate the nucleation kinetics of the material.
By precisely controlling the furnace temperature and gas flow, the system dictates how fast the particles form and grow. This control is what allows for the high crystallinity observed in the final RuTe2 product.
Environmental Precision
The high-quality formation of these nanoparticles relies on the system's ability to maintain a stable, high-temperature reaction environment.
Fluctuations in the thermal profile or gas composition would disrupt the tellurization process, potentially leading to incomplete reactions or amorphous structures rather than crystalline nanoparticles.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gas Ratios
The Ar/H2 mixture is a critical variable; an imbalance in this ratio can alter the reaction chemistry.
Too much hydrogen might over-reduce the system or affect the carbon support, while too little may fail to prevent oxidation of the highly reactive metal vapors.
Precursor Volatility
Reliance on the thermal decomposition of carbonyl groups means the process is highly dependent on the stability and vaporization properties of the specific precursor used.
If the temperature ramp is not perfectly tuned to the precursor's decomposition threshold, the material may degrade prematurely or fail to react with the tellurium vapor efficiently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a CVD process for metal-telluride formation, your specific objectives should dictate your operational parameters.
- If your primary focus is High Crystallinity: Prioritize precise temperature stability and a consistent Ar/H2 flow rate to ensure the thermal tellurization process proceeds without interruption.
- If your primary focus is Substrate Coverage: Adjust the precursor flow rates to modulate the nucleation density on the carbon nanofibers, ensuring uniform distribution rather than isolated agglomerates.
Successful RuTe2 synthesis relies on balancing thermal energy with precise atmospheric protection to drive the tellurization reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in RuTe2 Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Precursor Decomposition | Thermal breakdown of carbonyl groups to release reactive species. |
| Carrier Gas (Ar/H2) | Provides a reducing atmosphere and protects against oxidation. |
| Tellurization Mechanism | Facilitates in-situ vapor-phase reaction between Ru and Te. |
| Kinetic Control | Regulates nucleation rates for high crystallinity and uniform distribution. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Maximize your synthesis success with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique nanoparticle and thin-film requirements.
Whether you are managing complex thermal tellurization or high-purity gas environments, our systems provide the stability and control your lab demands. Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs and see how our expertise can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- Mehtap Aygün. RuTe2 Decorated Carbon Nanofiber Electrocatalyst Synthesized via a Sustainable Method for Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution in Acidic and Alkaline Electrolytes. DOI: 10.21597/jist.1647816
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a CVD system for NH4I? Enhance Catalyst Performance with In-Situ Etching
- How are hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) films processed using CVD tube furnaces? Optimize Growth for High-Quality 2D Materials
- How does chemical vapor infiltration work? A Guide to High-Performance Composite Manufacturing
- What industries commonly use PVD and CVD? Discover Key Applications in Tech and Manufacturing
- What is the core function of a dual-zone tube CVD system? Precision Synthesis for MnS Nanosheets
- How might AI and machine learning enhance CVD tube furnace processes? Boost Quality, Speed, and Safety
- How do CVD coatings compare to spray-on PTFE coatings? Discover Superior Performance and Safety
- What are the four main stages of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process? Master Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















