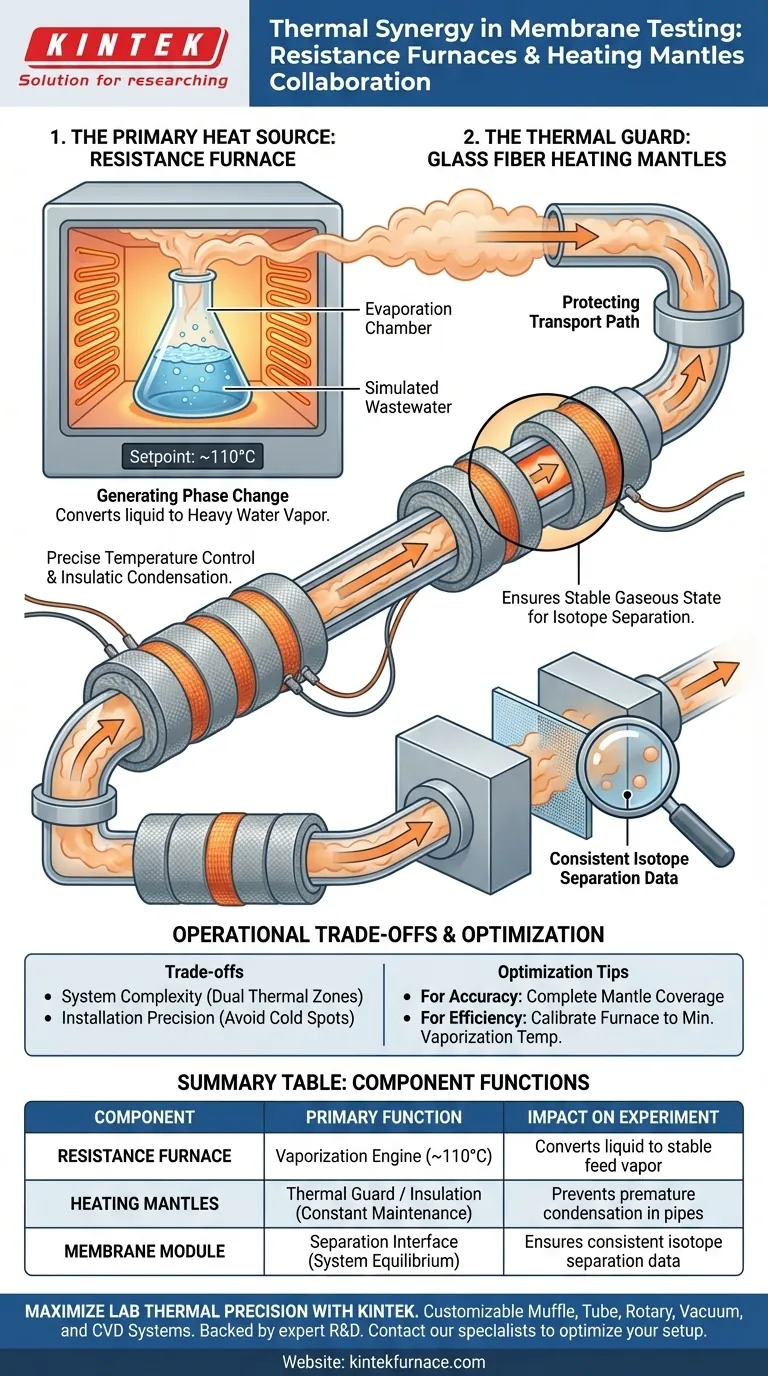
Resistance furnaces and glass fiber heating mantles function as a two-stage thermal management system to maintain the physical state of the feed solution. The resistance furnace provides the high-energy input required to vaporize liquid wastewater in the main chamber. The glass fiber heating mantles subsequently maintain this temperature through the transport lines, ensuring the material remains a gas until it interacts with the membrane.
Accurate membrane performance testing relies on a seamless transition from liquid to stable vapor. The furnace creates the vapor, while the mantles protect it from environmental cooling, preventing premature condensation that would compromise isotope separation data.
The Primary Heat Source: The Resistance Furnace
Generating the Phase Change
The resistance furnace serves as the central energy engine for the experiment. Its specific role is to heat the simulated wastewater contained within the evaporation chamber.
Achieving Vaporization Temperatures
The furnace drives the liquid to a specific setpoint, typically around 110°C. This high temperature ensures the wastewater undergoes a complete phase change, converting from a liquid solution into the heavy water vapor required for the test.
The Thermal Guard: Glass Fiber Heating Mantles
Protecting the Transport Path
Once the vapor leaves the furnace, it travels through external infrastructure to reach the membrane modules. Glass fiber heating mantles are wrapped tightly around these external pipes and valves.
Preventing Condensation
The primary function of these mantles is to provide precise temperature control and insulation during transport. Without this secondary heating, the vapor would naturally cool upon contact with the metal piping, reverting to a liquid state.
Ensuring Isotope Separation Stability
By preventing condensation, the mantles ensure the feed enters the composite membrane modules in a stable gaseous state. This consistency is critical for isotope separation tests, which require steady-state vapor flow to generate valid performance data.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
System Complexity
Using two distinct heating methods increases the complexity of the experimental setup. Operators must manage two separate thermal zones—the evaporation chamber and the transport lines—ensuring they remain synchronized.
Installation Precision
The effectiveness of the heating mantles depends entirely on coverage. Gaps in the wrapping, particularly around complex valves or joints, can create "cold spots" that cause localized condensation, potentially disrupting the entire flow stream.
Optimizing Your Thermal Setup
If your primary focus is Isotope Separation Accuracy: Ensure the heating mantles completely cover all external valves and joints to eliminate any possibility of phase reversion before the membrane.
If your primary focus is Energy Efficiency: Calibrate the resistance furnace to the minimum temperature required for vaporization (e.g., 110°C) to avoid overheating the initial chamber while relying on mantles for maintenance.
By strictly segregating the roles of vaporization and temperature maintenance, you ensure a stable, controllable environment for high-precision membrane testing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Temperature Target | Impact on Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Furnace | Vaporization Engine | ~110°C | Converts liquid wastewater into stable feed vapor |
| Heating Mantles | Thermal Guard/Insulation | Constant Maintenance | Prevents premature condensation in transport pipes |
| Membrane Module | Separation Interface | System Equilibrium | Ensures consistent isotope separation data |
Maximize Your Lab’s Thermal Precision with KINTEK
Don't let condensation compromise your isotope separation data. KINTEK provides high-performance thermal solutions designed for the rigorous demands of membrane research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your unique distillation and vaporization needs.
Ready to optimize your experimental setup? Contact our technical specialists today to discover how our high-temperature lab furnaces can enhance your testing accuracy and operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Zhen Luo, Ruizhi Fan. Enhanced Separation Performance of Graphene Oxide Membrane through Modification with Graphitic Carbon Nitride. DOI: 10.3390/w16070967
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What does nitrogen do in a furnace? Create an Inert, Oxygen-Free Atmosphere for Superior Results
- What are the key advantages of a box type atmosphere furnace? Superior Control, Efficiency, and Versatility for Heat Treatment
- How does an endothermic atmosphere differ from exothermic, and what are its applications? Discover Key Differences and Uses
- What role does an atmosphere box furnace play in material synthesis and preparation? Unlock Precision in Advanced Material Creation
- What is the function of a controlled atmosphere furnace for Zn-SiC sintering? Ensure Superior Inert Metal Bonding
- Why is an inert atmosphere required for Mo6S8 annealing at 1000°C? Ensure High-Purity Cathode Synthesis
- Why are retort furnaces considered versatile tools? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing Control
- What materials are used for the furnace structure of the box type annealing atmosphere furnace? Discover Durable, High-Temp Solutions



















