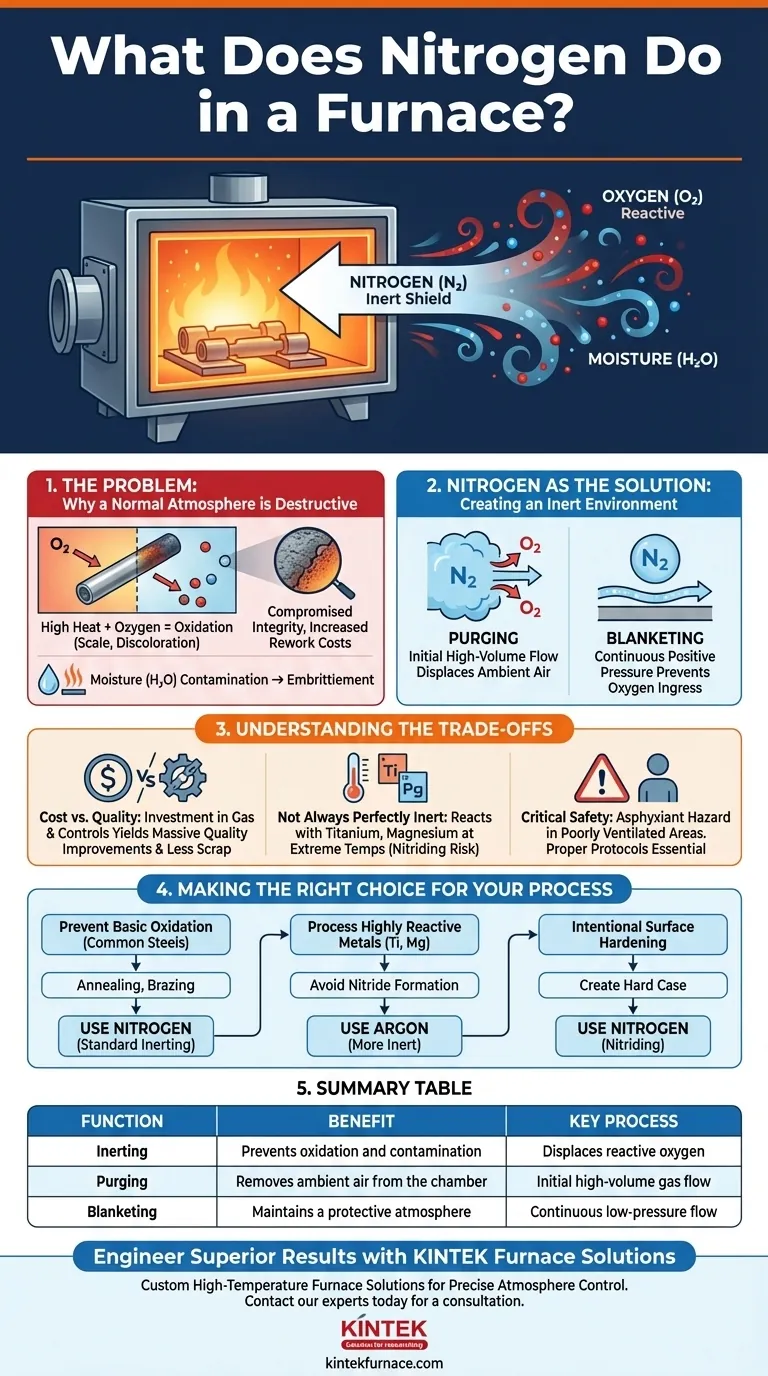
In a furnace, nitrogen's primary role is to create an inert, oxygen-free atmosphere. This controlled environment is critical for high-temperature processes because it displaces the reactive oxygen in the air, thereby preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and ensuring the quality, strength, and surface finish of the material being processed.
The air we breathe is a reactive mixture that causes oxidation and contamination at high temperatures. Nitrogen serves as a stable, inert "shield," displacing that reactive air to protect the material being heated and ensure the integrity of the final product.
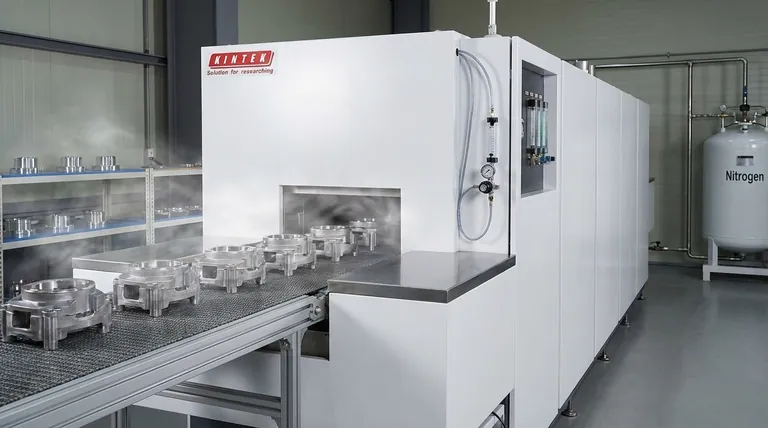

The Problem: Why a Normal Atmosphere is Destructive
The Impact of Oxygen and Heat
At room temperature, the oxygen in the air is relatively benign. However, heat acts as a powerful catalyst for chemical reactions.
When a material is heated in a furnace filled with normal air, this combination of high temperature and abundant oxygen becomes highly destructive, triggering rapid oxidation.
The Consequences of Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical reaction that degrades a material's surface. For metals, this often manifests as scale or discoloration.
This unwanted surface layer can ruin the part's dimensional accuracy, compromise its structural integrity, and create significant cleaning and rework costs.
Contamination from Moisture
Standard air also contains water vapor (moisture). At high temperatures, this moisture can also react with the workpiece, introducing hydrogen and causing embrittlement or further unwanted surface reactions.
Nitrogen as the Solution: Creating an Inert Environment
The Principle of Inerting
Nitrogen (N₂) is an inert gas, meaning it is chemically stable and non-reactive under most conditions. This stability comes from the powerful triple bond holding its two atoms together, which is difficult to break.
By filling a furnace with nitrogen, you replace the reactive oxygen and moisture with a neutral, predictable gas that will not interfere with the material.
Purging: Actively Removing Oxygen
The process begins with purging. This involves flowing a high volume of nitrogen gas into the sealed furnace chamber.
This flow physically pushes out, or displaces, the oxygen-rich ambient air until the oxygen concentration drops to a negligible level.
Blanketing: Maintaining Protection
After the initial purge, a continuous, low-pressure flow of nitrogen is often maintained. This is known as blanketing.
This positive pressure ensures that if any small leaks exist in the furnace seals, nitrogen will flow out rather than allowing destructive oxygen to leak in.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost vs. Quality
Using nitrogen is an operational cost. It requires a supply of the gas (from liquid dewars or an on-site generator) and the control systems to manage its flow.
However, this cost is almost always justified by the massive improvement in product quality, the reduction in scrap or rework, and the overall consistency of the manufacturing process.
Not Always Perfectly Inert
While highly stable, nitrogen is not perfectly inert under all conditions. At extremely high temperatures, it can react with certain highly reactive metals like titanium, magnesium, or some specialty stainless steels.
This reaction, known as nitriding, can sometimes be an unwanted form of contamination. For these specific applications, a more noble gas like argon may be required.
Critical Safety Considerations
Nitrogen is not toxic, but it is an asphyxiant. It displaces oxygen in the air.
A nitrogen leak in a poorly ventilated area can create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere that poses a severe, life-threatening hazard to personnel. Proper safety protocols and monitoring are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
By understanding nitrogen's function, you can better control your heat-treating outcomes. The key is to match the atmospheric control to the material and the desired result.
- If your primary focus is preventing basic oxidation on common steels: Nitrogen purging and blanketing is the industry-standard and most cost-effective solution for processes like annealing or brazing.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals: You must evaluate whether nitrogen could form unwanted nitrides at your process temperature and consider using a more inert gas like argon.
- If your primary focus is intentionally surface hardening a part: You may use nitrogen in a reactive process called nitriding, where the goal is to have nitrogen bond with the metal's surface to create a hard case.
By controlling the furnace atmosphere with nitrogen, you move from hoping for a good result to engineering one.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Inerting | Prevents oxidation and contamination | Displaces reactive oxygen |
| Purging | Removes ambient air from the chamber | Initial high-volume gas flow |
| Blanketing | Maintains a protective atmosphere | Continuous low-pressure flow |
Engineer Superior Results with KINTEK Furnace Solutions
Don't leave your heat-treating outcomes to chance. Controlling the furnace atmosphere is critical for achieving the material quality, strength, and surface finish you require.
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your precise needs. Whether your process requires a standard inert atmosphere or a highly customized environment for reactive materials, our product line—including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and more—is backed by deep customization capabilities.
Let's discuss how we can design a furnace system to perfectly control your process atmosphere. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance



















