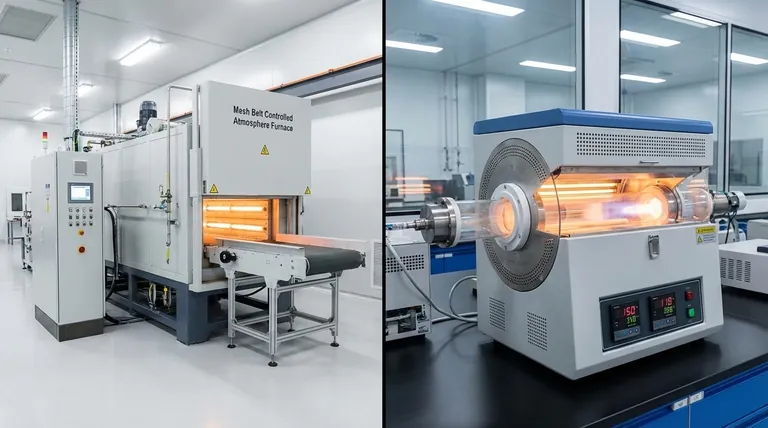
The two primary types of atmosphere furnaces are categorized by their operational method: Batch Furnaces for processing materials in distinct, separate loads, and Continuous Furnaces for processing a constant stream of material. These operational types are most commonly realized through two physical designs: the rectangular Box Furnace, which is ideal for batch work, and the cylindrical Tube Furnace, which can be used for both batch and continuous-flow applications.
The core decision between furnace types is a strategic choice between operational flexibility and production volume. Batch furnaces offer versatility for varied parts and processes, while continuous furnaces deliver maximum efficiency and consistency for high-volume manufacturing.

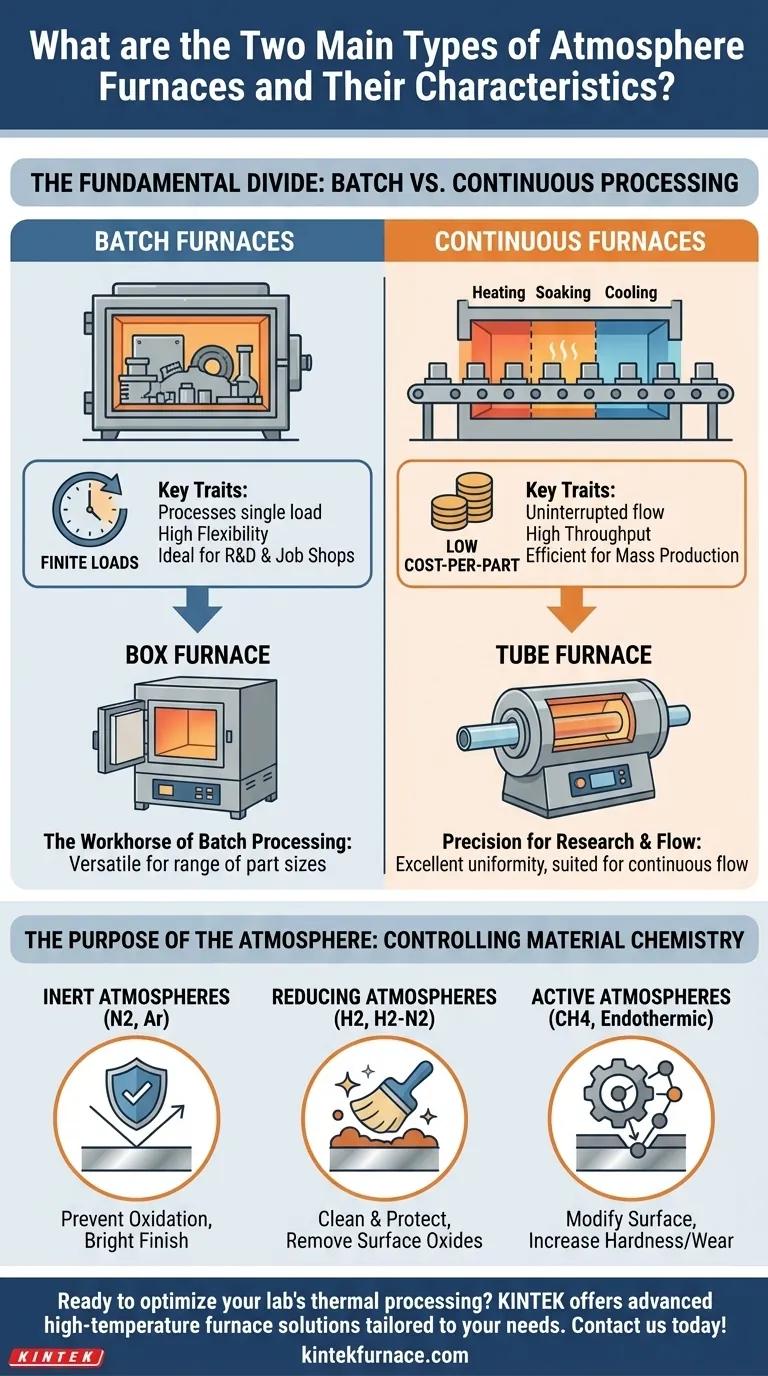
The Fundamental Divide: Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The most important distinction in atmosphere furnaces is not their shape, but how they process material. This choice between batch and continuous operation dictates workflow, throughput, and cost structure.
Batch Furnaces: Versatility for Varied Loads
A batch furnace processes a single, finite load of material at a time. The entire thermal cycle—heating, soaking, and cooling—is completed before the furnace is opened and the next load is introduced.
These furnaces are the workhorses of job shops, research and development labs, and facilities that handle a wide variety of part sizes and heat-treatment specifications. Their primary advantage is flexibility.
Common configurations, often called "atmosphere envelopes," include front-loading, top-loading, and bottom-loading (elevator) models to accommodate different part-handling requirements.
Continuous Furnaces: Efficiency for Mass Production
A continuous furnace processes material in an uninterrupted flow. Parts are constantly fed into one end of the furnace, move through various temperature zones, and exit the other end fully processed.
These systems are designed for high-volume, dedicated production where the same part or material is processed repeatedly. Their key advantage is high throughput and low cost-per-part at scale.
This method ensures exceptional process consistency, as every part experiences the exact same thermal profile.
Common Furnace Geometries and Their Roles
The operational methods above are enabled by specific physical designs. The box and tube geometries are the most prevalent.
The Box Furnace: The Workhorse of Batch Processing
As the name implies, a box furnace features a rectangular chamber. This design is exceptionally versatile for handling a wide range of part sizes and shapes, from small components in baskets to large, single workpieces.
They are almost exclusively used for batch processing and are fundamental in metallurgical applications like annealing, hardening, and brazing.
The Tube Furnace: Precision for Research and Flow
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical chamber, typically made of ceramic or alloy, through which the material passes. This design provides excellent temperature uniformity and atmosphere control within a confined space.
Tube furnaces come in two main variants:
- Split Tube: The furnace body is hinged and opens in half, allowing for easy placement and removal of the process tube. This is ideal for R&D and academic settings where frequent changes are common.
- Solid Tube: The heating chamber is fixed, and a process tube is inserted through it. This robust design is suited for established, repeatable processes.
While often used for batch work in labs, the tube geometry is naturally suited for creating continuous-flow systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires acknowledging the inherent compromises between different designs and operational methods.
Flexibility vs. Throughput
This is the central trade-off. Batch furnaces can be reconfigured for different processes and loads daily, offering maximum flexibility. Continuous furnaces offer immense throughput but are typically dedicated to a single process.
Cost: Initial Investment vs. Operational Efficiency
Continuous furnaces represent a significantly higher initial capital investment due to their size and complexity. However, for mass production, their automated nature and energy efficiency lead to a much lower operational cost per unit.
Atmosphere Purity and Consumption
Batch furnaces are sealed, purged of air, and then backfilled with the desired atmosphere. This can sometimes result in higher gas consumption per cycle compared to a well-balanced continuous furnace, which maintains a steady-state atmosphere.
The Purpose of the Atmosphere: Controlling Material Chemistry
The "atmosphere" itself is the reason for these furnaces. A controlled mixture of gases is introduced to achieve specific goals at high temperatures.
Inert Atmospheres: Preventing Oxidation
Gases like nitrogen and argon are used to displace oxygen. This prevents oxidation and scaling on the material's surface, resulting in a "bright" finish after processes like annealing or brazing.
Reducing Atmospheres: Cleaning and Protection
A hydrogen or hydrogen-nitrogen mix is a reducing atmosphere. It not only prevents oxidation but can also actively remove existing surface oxides, effectively cleaning the part at a chemical level.
Active Atmospheres: Modifying the Surface
Gases like methane or endothermic gas are used for carburizing or carbonitriding. These active atmospheres intentionally introduce elements like carbon into the surface of a steel part to increase its hardness and wear resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace begins with a clear understanding of your operational goals. The physical furnace is a tool to execute a specific thermal and chemical process.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or low-volume production with varied parts: A flexible batch furnace, such as a split-tube or a front-loading box furnace, is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable mass production of a consistent part: A continuous furnace will deliver the highest throughput and lowest long-term cost per unit.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific material property like surface hardness or a bright finish: Your choice of process gas atmosphere is just as critical as your choice between a batch or continuous furnace.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the right furnace not just by its shape, but by how it will best serve your process and business objectives.
Summary Table:
| Type | Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Furnace | Processes finite loads; flexible for varied parts; ideal for R&D and low-volume production | Annealing, hardening, brazing in labs and job shops |
| Continuous Furnace | Processes constant material flow; high throughput; efficient for mass production | High-volume manufacturing with consistent thermal profiles |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research, development, or high-volume production, we can help you achieve superior efficiency and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More



















