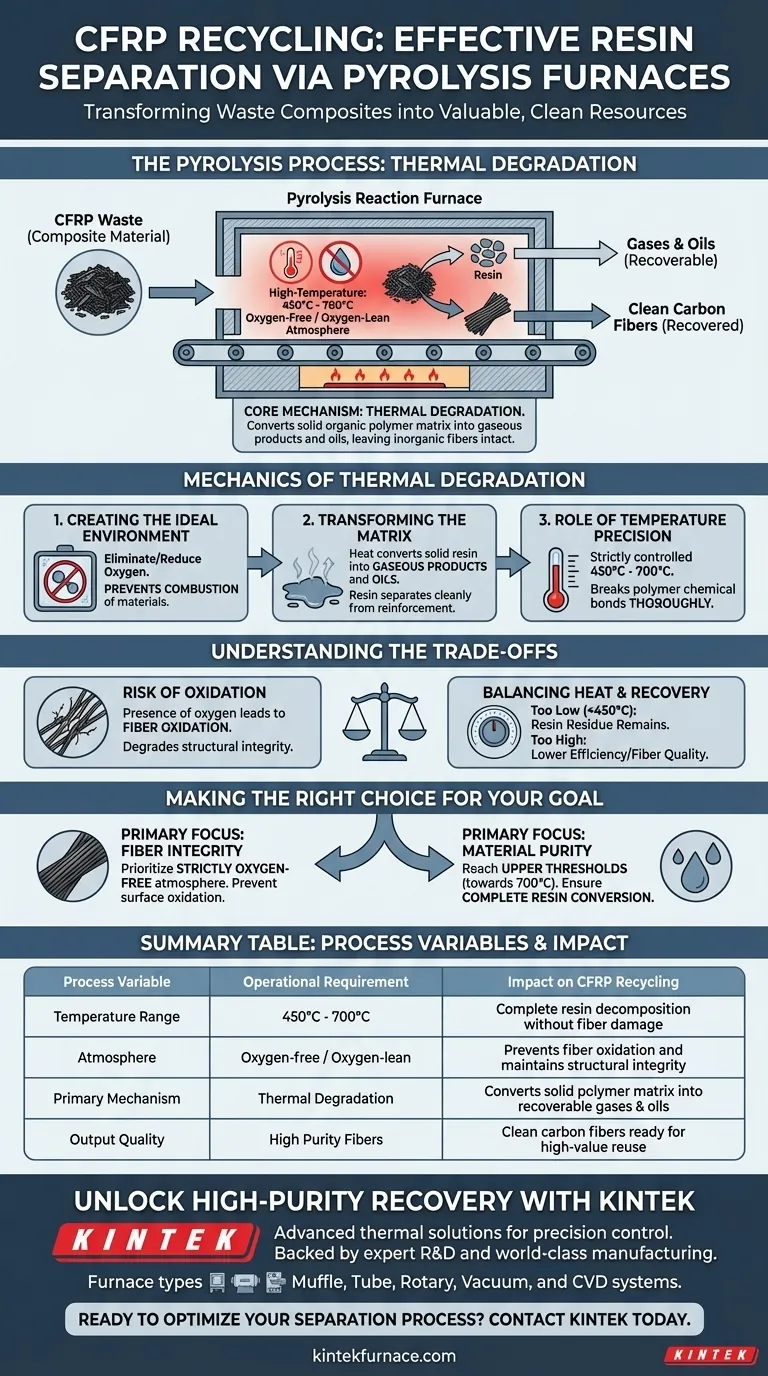
Pyrolysis reaction furnaces facilitate resin separation by subjecting Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) to a specialized thermal decomposition process. By maintaining a high-temperature environment between 450°C and 700°C within an oxygen-free or oxygen-lean atmosphere, these furnaces force the resin matrix to break down chemically without burning the valuable carbon fibers.
The core mechanism relies on thermal degradation, which converts the solid organic polymer matrix into recoverable gases and oils. By strictly limiting oxygen exposure, the furnace ensures the resin is stripped away while the inorganic carbon fibers remain intact and unoxidized.
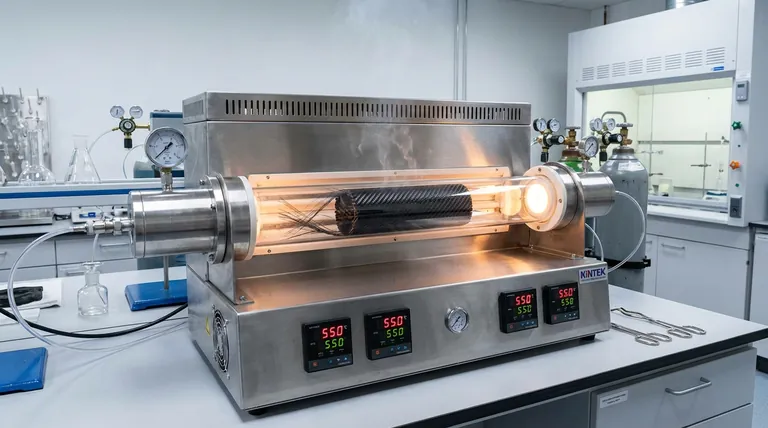

The Mechanics of Thermal Degradation
Creating the Ideal Environment
The effectiveness of a pyrolysis furnace hinges on its atmospheric control. The process must occur in an oxygen-free or oxygen-lean environment.
By eliminating or significantly reducing oxygen, the system prevents the combustion of the materials. This is the critical factor that allows the resin to decompose without fueling a fire that would destroy the carbon structure.
Transforming the Matrix
Inside the furnace, the organic polymer matrix—the "glue" holding the composite together—undergoes a physical and chemical transformation.
The heat causes the solid resin to transition into gaseous products and oils. As the resin vaporizes, it separates cleanly from the reinforcement material, leaving the carbon fibers behind.
The Role of Temperature Precision
The process operates within a specific thermal window, strictly between 450°C and 700°C.
This temperature range is sufficient to break the chemical bonds of the polymer matrix. However, it is controlled carefully to ensure the degradation is thorough enough to result in clean fibers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Oxidation
While the goal is to extract clean fibers, the presence of oxygen is the primary failure mode.
If the atmosphere is not strictly maintained as oxygen-lean or oxygen-free, the carbon fibers will oxidize. This degrades the structural integrity of the recycled fiber, rendering it less useful for future applications.
Balancing Heat and Recovery
The process requires a delicate balance of thermal energy.
The temperature must be high enough to fully convert the solid resin into gas and oil. If the temperature drops below the effective range (450°C), resin residue may remain on the fibers; if it exceeds the range excessively, it could impact energy efficiency or fiber quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of CFRP recycling using pyrolysis, focus on the control of environmental variables.
- If your primary focus is Fiber Integrity: Prioritize the maintenance of a strictly oxygen-free atmosphere to prevent any surface oxidation of the recovered carbon.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure the furnace consistently reaches the upper thresholds of the 450°C–700°C range to guarantee the complete conversion of resin into gaseous products.
By precisely managing temperature and atmosphere, you can transform waste composites into valuable, clean resources.
Summary Table:
| Process Variable | Operational Requirement | Impact on CFRP Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 450°C - 700°C | Ensures complete resin decomposition without fiber damage |
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-free / Oxygen-lean | Prevents fiber oxidation and maintains structural integrity |
| Primary Mechanism | Thermal Degradation | Converts solid polymer matrix into recoverable gases and oils |
| Output Quality | High Purity Fibers | Clean carbon fibers ready for high-value reuse |
Unlock High-Purity Carbon Fiber Recovery with KINTEK
Don't let valuable materials go to waste. KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions provide the precision control necessary for efficient CFRP recycling. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all of which can be customized to meet your specific pyrolysis and high-temperature lab requirements.
Ready to optimize your separation process? Contact our engineering team today to discover how our customizable furnaces can deliver the temperature accuracy and atmospheric control your project demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Charitidis J. Panagiotis. Recycling of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites-A Review. DOI: 10.48175/ijarsct-17474
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance for Your Materials
- How do direct-fired rotary kilns operate and what are their common applications? Achieve High-Volume Thermal Processing
- How do rotary kilns contribute to chemical and mineral processing? Unlock Efficiency and Sustainability
- Why are rotary furnaces particularly suitable for aluminum melting and scrap recycling? Boost Your Metal Recovery Efficiency
- How does a fluidized bed calcination system facilitate iron ore powder conversion? Boost Efficiency with Suspension.
- How are rotary kilns used in the cement industry? Master Clinker Production for Efficiency
- What are the main advantages of rotary kilns for industrial applications? Boost Efficiency and Quality in Your Processes
- What is the significance of rotation in a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion



















