Rotary furnaces are uniquely suited for aluminum melting and scrap recycling because their rotational design creates superior thermal efficiency and maximizes metal recovery. This constant tumbling motion ensures the entire aluminum charge is heated uniformly while continuously mixing it with salt flux, a process that efficiently strips away impurities and oxides common in scrap materials.
While other furnaces can melt aluminum, the rotary furnace's ability to constantly agitate the charge makes it exceptionally effective at maximizing the amount of usable metal recovered from diverse and often contaminated scrap sources.
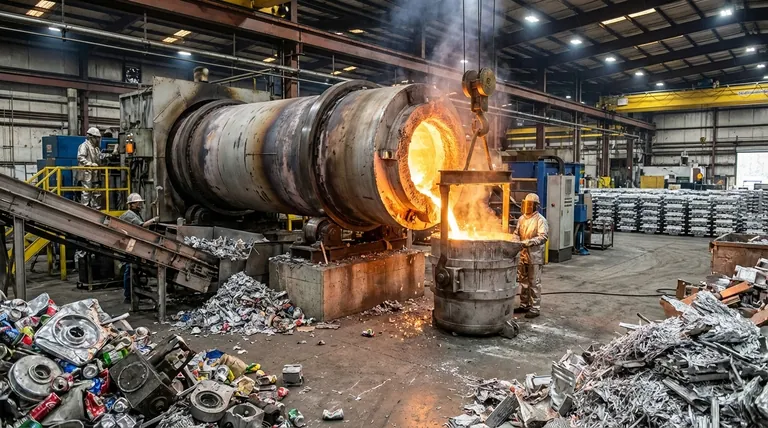

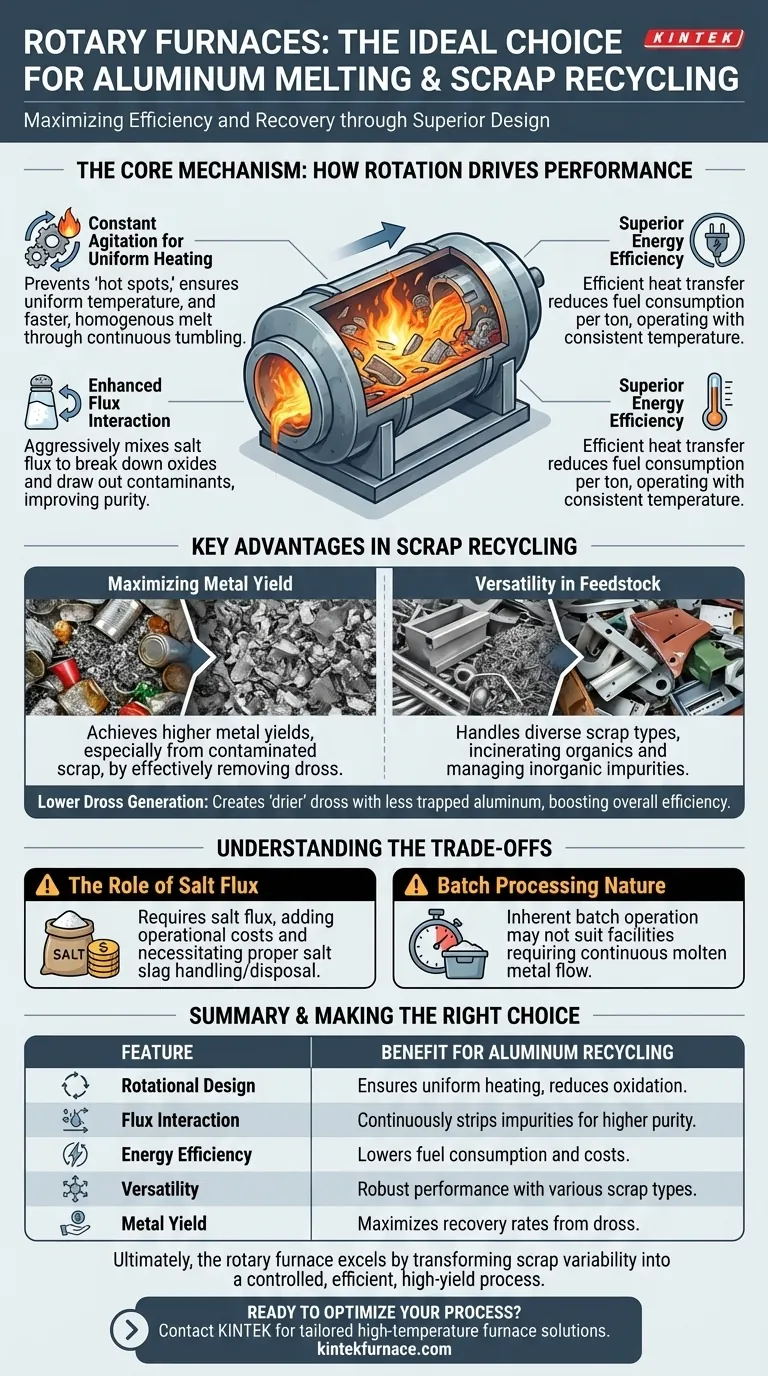
The Core Mechanism: How Rotation Drives Performance
The defining feature of a rotary furnace is its cylindrical drum that rotates or tilts along its horizontal axis. This simple mechanical action is the source of its primary advantages in aluminum recycling.
Constant Agitation for Uniform Heating
The furnace's rotation continuously tumbles the solid aluminum scrap. This prevents the formation of "hot spots" on the metal's surface, which can cause excessive oxidation and metal loss.
By constantly moving the material, heat is transferred not just by radiation from the burner but also through direct conduction as the hot refractory lining contacts the charge. This results in a faster, more homogenous melt.
Enhanced Flux Interaction
In aluminum recycling, a layer of salt flux is used to protect the metal from oxidation and to absorb impurities. The tumbling action of a rotary furnace constantly mixes the molten aluminum with this flux.
This continuous washing action is critical. It aggressively breaks down the tough oxide layers on scrap pieces, allowing them to coalesce into the melt, and efficiently draws contaminants out of the molten bath.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Because heat is transferred so effectively throughout the charge, less energy is wasted. The consistent temperature profile means the burner can operate more efficiently, reducing overall fuel consumption per ton of aluminum produced compared to many static furnace designs.
Key Advantages in Scrap Recycling
While effective for melting primary aluminum, the rotary furnace truly excels when processing scrap, which is often varied, contaminated, and difficult to manage.
Maximizing Metal Yield
The primary goal of recycling is to recover as much metal as possible. The rotary furnace's efficient fluxing action is key to achieving high metal yields, often exceeding those of traditional stationary furnaces.
By effectively removing the non-metallic components and oxides (dross), more pure aluminum is left behind for tapping. This is especially valuable when processing materials with high surface area-to-volume ratios, like chips or used beverage cans (UBCs).
Versatility in Feedstock
Rotary furnaces are robust and can handle a wide variety of aluminum scrap types. This includes everything from clean industrial scrap to post-consumer scrap that may be contaminated with paint, plastics, oils, and other residues.
The controlled combustion environment helps to incinerate organic contaminants, while the fluxing process handles the inorganic impurities.
Lower Dross Generation
Dross is a mixture of aluminum oxide and trapped metallic aluminum that forms on the surface of the melt. Because the rotary furnace provides a more controlled melt with less direct exposure to open air, it limits the formation of excess oxides.
The resulting dross is also "drier," meaning it contains significantly less trapped, recoverable aluminum, further improving the overall efficiency of the recycling process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its compromises. Understanding the limitations of rotary furnaces is crucial for making an informed decision.
The Role of Salt Flux
The efficiency of a rotary furnace is heavily dependent on the use of salt flux. This adds to the operational cost.
Furthermore, the resulting byproduct, known as salt cake or salt slag, contains salt, oxides, and some residual metal. It must be properly handled and either sent for further processing or disposed of in a compliant manner, which has both economic and environmental implications.
Batch Processing Nature
Rotary furnaces are inherently batch-operation systems. The furnace is charged, melting occurs, the metal is tapped, and the dross is removed before the next cycle can begin.
This may be a disadvantage for facilities that require a continuous, uninterrupted flow of molten metal, where a large reverberatory furnace might be more suitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your specific feedstock and production goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield from low-quality, contaminated scrap: The rotary furnace is the superior choice due to its unparalleled ability to handle impurities and recover metal.
- If your primary focus is melting clean, uniform scrap or primary ingot: A simpler and potentially less expensive reverberatory or induction furnace may provide a more straightforward operation.
- If your operation requires a very large, continuous supply of molten metal: You may need to compare the batch output of multiple rotary furnaces against a large-scale continuous melting system.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace excels by transforming the challenge of aluminum scrap variability into a controlled, efficient, and high-yield recycling process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Aluminum Recycling |
|---|---|
| Rotational Design | Ensures uniform heating and constant agitation, reducing hot spots and oxidation. |
| Flux Interaction | Continuously mixes salt flux to strip impurities, improving metal purity and recovery. |
| Energy Efficiency | Lowers fuel consumption through effective heat transfer and consistent temperature control. |
| Versatility | Handles various scrap types, including contaminated materials, with robust performance. |
| Metal Yield | Maximizes recovery rates by efficiently removing dross and non-metallic components. |
Ready to optimize your aluminum recycling process? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're dealing with contaminated scrap or need high-yield melting, our rotary furnaces can boost your efficiency and metal recovery. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















