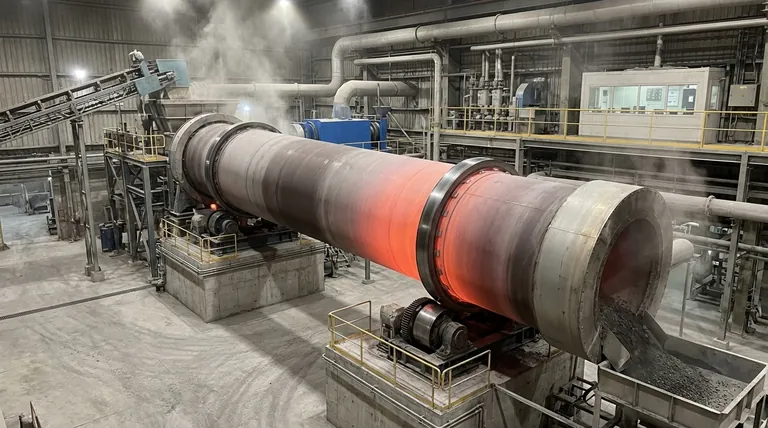
In the cement industry, a rotary kiln is the central piece of equipment responsible for the high-temperature chemical transformation of raw materials into clinker, the primary component of cement. Often called the "heart" of the cement plant, this massive, rotating cylinder subjects a mixture of limestone, clay, and shale to extreme heat, triggering the chemical reactions necessary to create cement's essential binding properties.
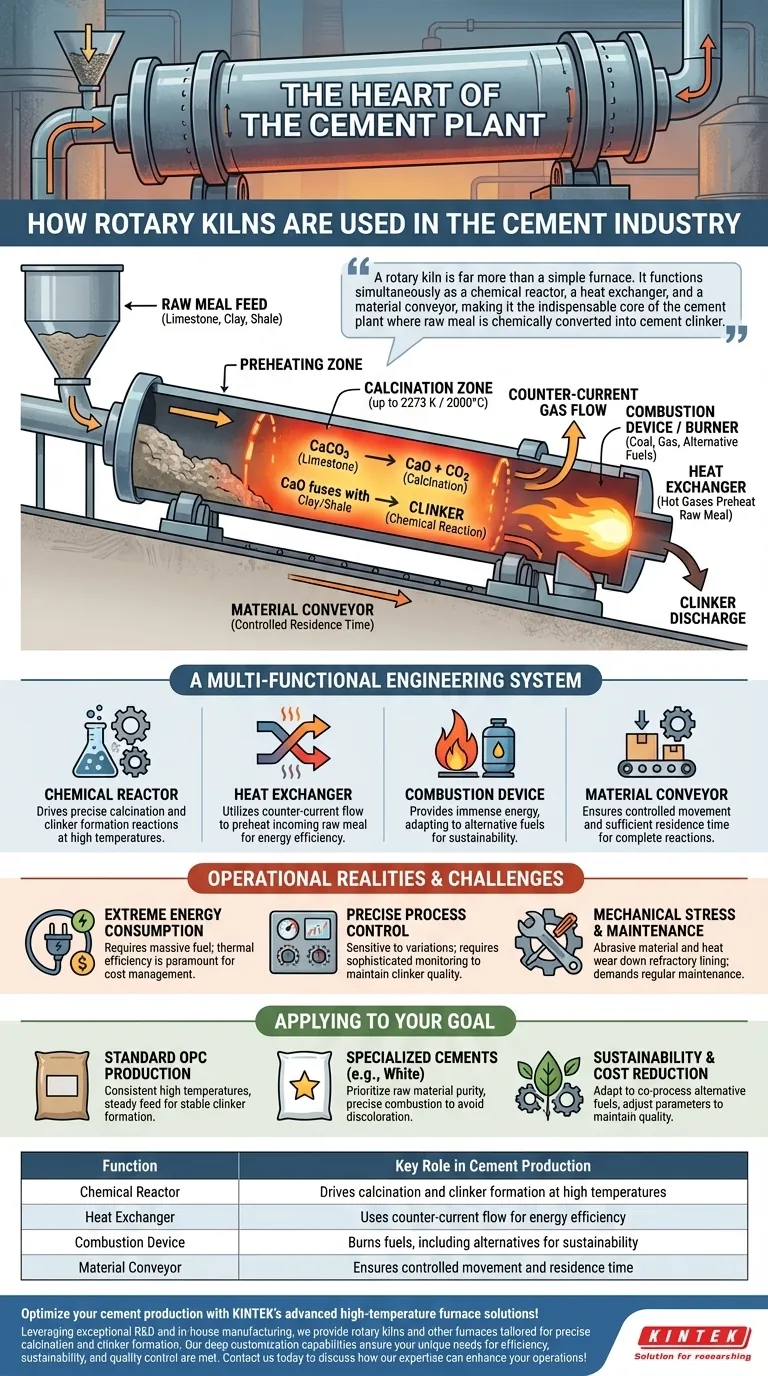
A rotary kiln is far more than a simple furnace. It functions simultaneously as a chemical reactor, a heat exchanger, and a material conveyor, making it the indispensable core of the cement plant where raw meal is chemically converted into cement clinker.

The Kiln's Role as the Plant's Core
The rotary kiln is the "firing" stage in the industry's "two grinding, one firing" production model. Its purpose is to take finely ground raw material and chemically alter it through intense, uniform heat.
From Raw Meal to Clinker
Raw materials like limestone and clay are first ground into a fine powder known as raw meal. This meal is fed into the upper, elevated end of the slowly rotating kiln. As the kiln turns, the material gradually moves down toward the lower end where the heat source is located.
The Process of Calcination
The kiln's primary function is to facilitate calcination. As the raw meal travels through progressively hotter zones, reaching temperatures up to 2273 K (2000°C / 3632°F), the limestone (calcium carbonate) decomposes. This reaction releases carbon dioxide and leaves behind highly reactive calcium oxide.
Ensuring Uniform Quality
This superheated calcium oxide then fuses with the other elements from the clay and shale, forming new crystalline compounds. The final product that exits the kiln is clinker—small, hard nodules that are the immediate precursor to finished cement. The kiln's constant rotation ensures all material is evenly heated, which is critical for consistent clinker quality.
A Multi-Functional Engineering System
The rotary kiln's design allows it to perform several distinct functions simultaneously, making it a highly efficient, integrated system.
The Chemical Reactor
At its core, the kiln is a chemical reactor. The extreme heat environment it creates is precisely controlled to drive the specific endothermic and exothermic reactions that transform simple minerals into the complex compounds that give cement its strength.
The Heat Exchanger
Kilns are designed for exceptional thermal efficiency. Hot combustion gases from the burner at the lower end flow up the kiln, in the opposite direction of the raw material. This counter-current flow allows the hot gases to preheat the incoming raw meal, conserving energy.
The Combustion Device
A powerful burner at the kiln's lower end provides the immense energy required. While traditionally fired by coal or natural gas, modern kilns are increasingly adapted to use alternative fuels, including industrial byproducts and waste materials, as part of sustainability initiatives.
The Material Conveyor
The kiln is set at a slight angle to the horizontal. This incline, combined with the slow, steady rotation, acts as a conveyor system. It ensures the material moves through the kiln at a controlled rate, allowing sufficient residence time for all chemical reactions to complete.
Understanding the Operational Realities
While indispensable, operating a rotary kiln involves significant challenges and trade-offs that are critical to manage.
Extreme Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures over 2000°C requires a massive amount of fuel. Energy consumption is the single largest variable cost in cement production, making thermal efficiency a paramount concern for plant operators.
Precise Process Control
The quality of the final clinker is highly sensitive to operational parameters. Minor deviations in the feed rate of the raw meal, the kiln's rotational speed, or the temperature profile can lead to inconsistent or poor-quality product. This necessitates sophisticated process control systems and constant monitoring.
Mechanical Stress and Maintenance
The combination of extreme heat, continuous rotation, and abrasive material places immense mechanical stress on the kiln's components. The protective refractory brick lining inside the kiln wears down and requires regular replacement, representing a significant maintenance cost and production downtime.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The operational focus for a rotary kiln can be tuned to produce different outcomes based on market demands and strategic objectives.
- If your primary focus is producing standard Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC): The key is maintaining consistent high temperatures and a steady feed of traditional raw materials to ensure stable clinker formation.
- If your primary focus is producing specialized cements (e.g., white cement): You must prioritize raw material purity and precise combustion control to avoid mineral impurities that could discolor the final product.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and cost reduction: The system can be adapted to co-process alternative fuels and raw materials, which requires careful adjustments to the combustion and heat exchange parameters to maintain clinker quality.
Ultimately, mastering the rotary kiln is mastering the core chemistry and thermodynamics of cement production itself.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Role in Cement Production |
|---|---|
| Chemical Reactor | Drives calcination and clinker formation at high temperatures |
| Heat Exchanger | Uses counter-current flow for energy efficiency |
| Combustion Device | Burns fuels, including alternatives for sustainability |
| Material Conveyor | Ensures controlled movement and residence time |
Optimize your cement production with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide rotary kilns and other furnaces tailored for precise calcination and clinker formation. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique needs for efficiency, sustainability, and quality control are met. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















