At their core, rotary kilns are industrial workhorses designed to induce precise chemical reactions and physical phase changes in solid materials through controlled heating. They are essential for a wide range of processes, from roasting ores like bauxite to extract metals, to producing high-value chemicals like titanium dioxide, and even to volatilizing and recovering valuable metals from industrial waste streams.
Beyond simple heating, the true value of a rotary kiln lies in its ability to create a highly controlled, dynamic processing environment. This allows industries to uniformly process diverse materials, extract valuable resources, and transform waste into new products, making them indispensable for both process efficiency and modern sustainability goals.
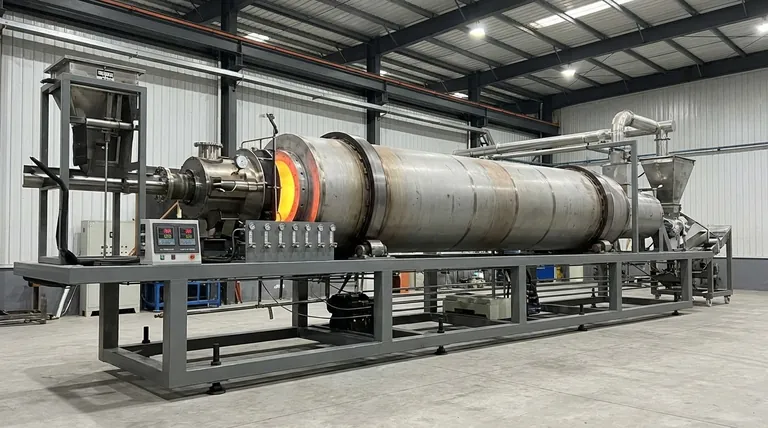

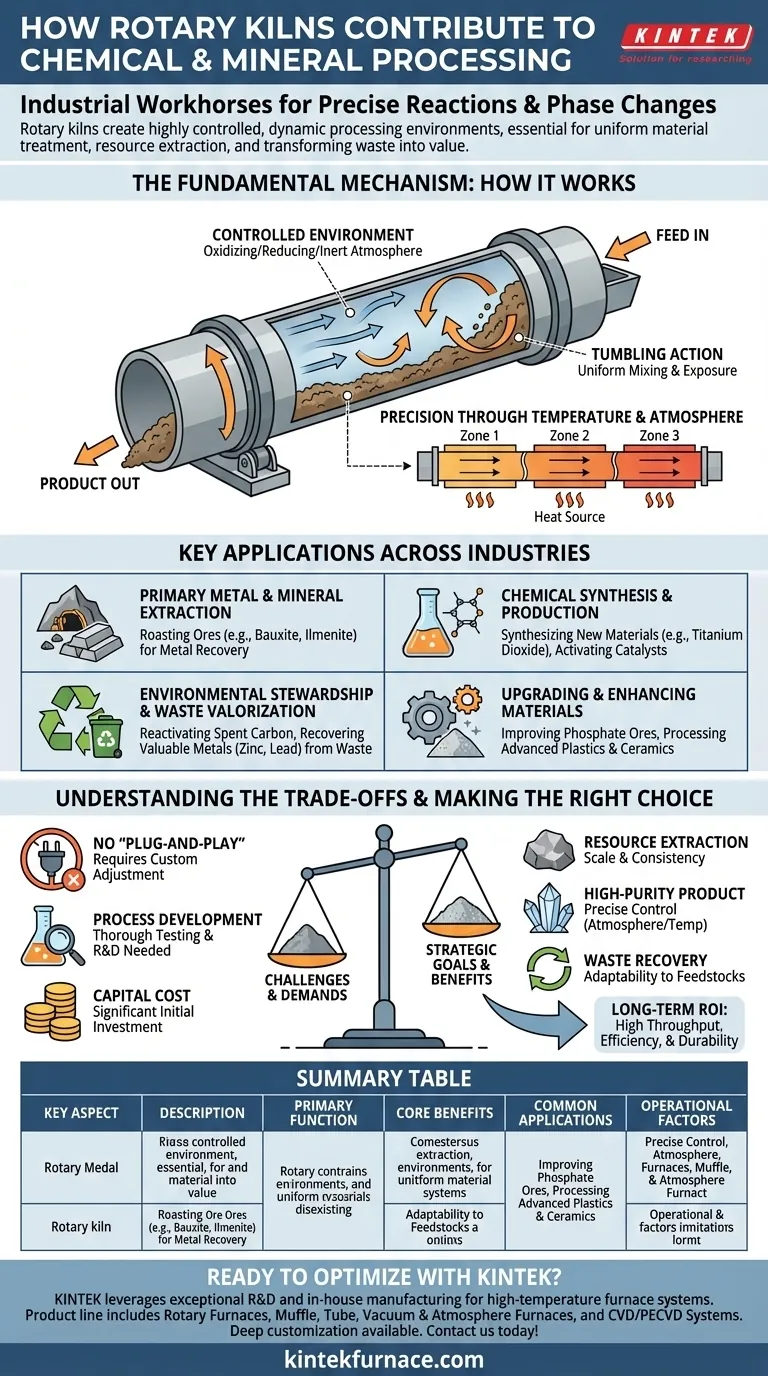
The Fundamental Mechanism: How a Rotary Kiln Works
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from its simple yet powerful design, which combines heat, motion, and atmospheric control to transform materials.
A Controlled Environment for Transformation
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical drum, slightly inclined to allow gravity to move material from one end to the other. The drum is sealed, which is critical for maintaining a specific internal atmosphere—whether it's oxidizing, reducing, or inert—to drive desired chemical reactions.
The Power of Tumbling Action
As the drum rotates, the material inside is continuously lifted and tumbled. This constant mixing is crucial, as it ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat and the controlled atmosphere, preventing hot spots and guaranteeing a consistent final product.
Precision Through Temperature and Atmosphere
The kiln is heated to precise temperatures, often in different zones along its length. By carefully managing the temperature profile and the composition of the gases inside, operators can meticulously control the physical and chemical changes taking place, from simply drying a material to fundamentally altering its chemical structure.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of the rotary kiln makes it a cornerstone technology in numerous sectors, solving a variety of processing challenges.
Primary Metal & Mineral Extraction
Kilns are foundational in metallurgy. They are used for roasting ores like ilmenite to prepare them for metal extraction and for reducing materials like barium sulfate to create other chemical compounds.
Chemical Synthesis & Production
In the chemical industry, rotary kilns are used to synthesize new materials. A primary example is the production of titanium dioxide, a brilliant white pigment used in everything from paint to sunscreen. They are also used to activate catalysts that are essential for large-scale chemical manufacturing.
Environmental Stewardship & Waste Valorization
Rotary kilns are increasingly vital for the circular economy. They can reactivate spent activated carbon used in water and air purification, and they excel at recovering valuable metals like zinc and lead from industrial byproducts and waste materials that would otherwise end up in a landfill.
Upgrading and Enhancing Materials
Kilns are also used to improve the quality of materials. For instance, they upgrade phosphate ores to enhance their suitability for agricultural fertilizers and are used in the advanced processing of high-performance plastics and ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, the flexibility of a rotary kiln is not automatic. Its successful implementation requires a clear understanding of its operational demands.
The "No-Free-Lunch" Principle
The kiln's ability to handle an immense variety of feedstocks and process conditions means it is not a "plug-and-play" solution. Each new material or process goal requires careful consideration and adjustment.
The Need for Process Development
The references correctly allude to the need for "thorough testing." To optimize a kiln for a specific material—be it a mineral ore or an industrial waste sludge—requires significant upfront investment in laboratory analysis and pilot-scale testing to determine the ideal temperature, rotation speed, and atmospheric conditions.
Balancing Capital Cost with Long-Term ROI
Rotary kilns are heavy-duty, robust machines built for long-term reliability in demanding environments. While this entails a significant capital investment, their high throughput, simple operation, and durability provide a strong return through process efficiency and low maintenance over decades of use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process Goal
To leverage a rotary kiln effectively, you must align its capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is resource extraction from raw ore: You will leverage the kiln's ability to drive specific, high-temperature reactions like roasting or reduction consistently and at scale.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-purity chemical or product: You must prioritize precise control over the kiln's internal atmosphere and multi-zone temperature profile to ensure the desired synthesis occurs without contamination.
- If your primary focus is waste recovery or circular economy initiatives: The kiln's adaptability to varied and often inconsistent feedstocks is its most critical feature, allowing you to turn a liability into a valuable resource.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is more than a piece of equipment; it is a strategic tool for unlocking material value, improving process efficiency, and building a more sustainable industrial future.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Induces chemical reactions and physical changes via controlled heating in a rotating drum. |
| Core Benefits | Uniform processing, resource extraction, waste valorization, and support for circular economy. |
| Common Applications | Roasting ores, synthesizing chemicals (e.g., titanium dioxide), recovering metals from waste. |
| Operational Factors | Temperature control, rotation speed, atmospheric conditions (oxidizing, reducing, inert). |
Ready to optimize your chemical or mineral processing with advanced rotary kiln solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and sustainability goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















