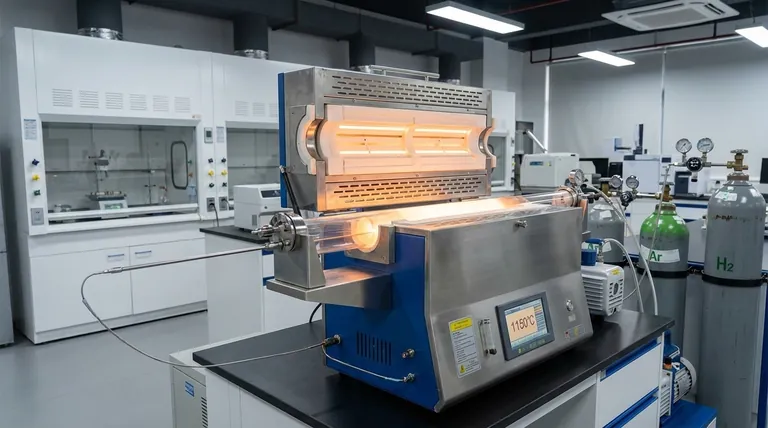
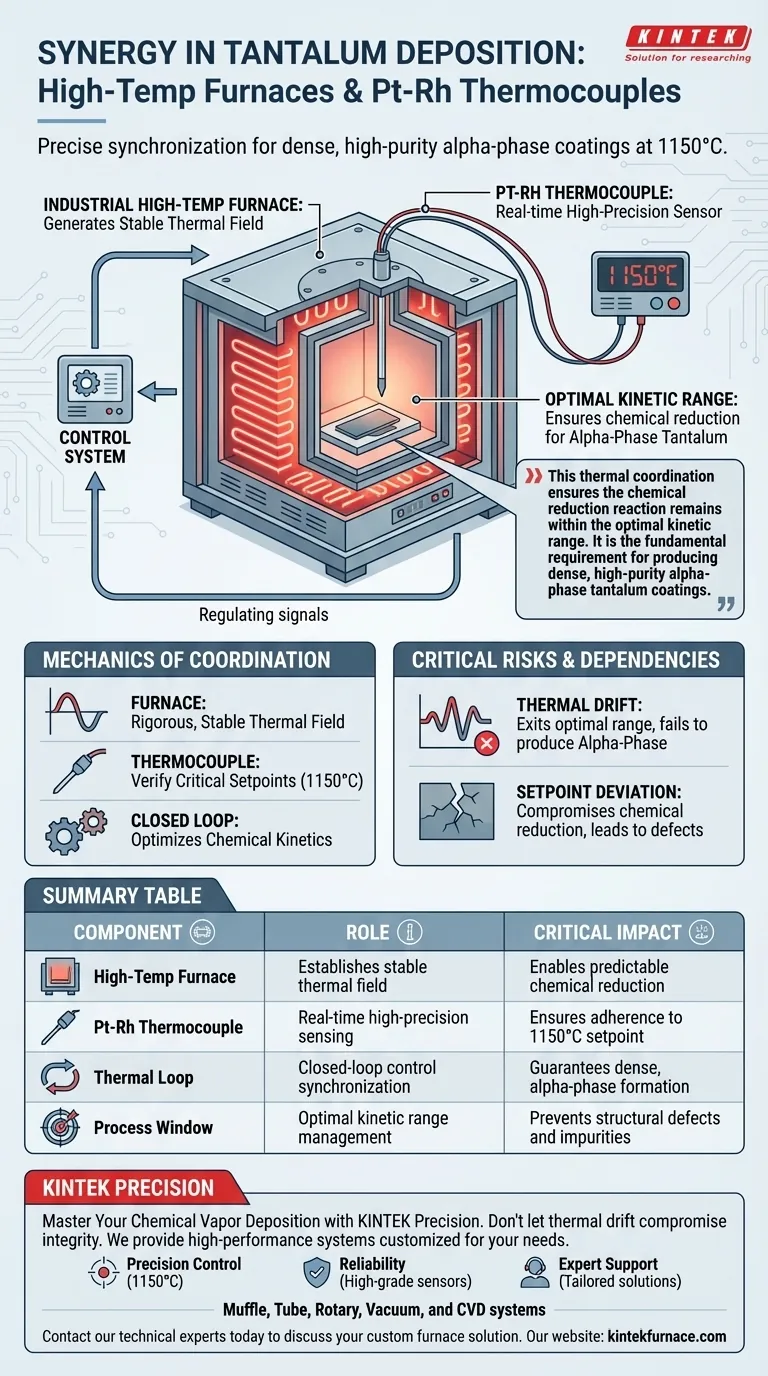
The precise synchronization of thermal energy and sensing technology is the engine behind successful tantalum coating deposition. Industrial high-temperature furnaces generate the stable thermal field required for chlorination and deposition chambers, while platinum-rhodium thermocouples provide real-time temperature data. Together, they maintain the specific 1150°C environment needed to control the chemical reduction process.
This thermal coordination ensures the chemical reduction reaction remains within the optimal kinetic range. It is the fundamental requirement for producing dense, high-purity alpha-phase tantalum coatings.

The Mechanics of Thermal Coordination
To understand the quality of a tantalum coating, you must look at how the equipment manages the chemical reaction's speed and environment.
The Role of the Industrial Furnace
The primary function of the high-temperature furnace is to establish a rigorous, stable thermal field.
This apparatus encloses both the chlorination and deposition chambers. Its job is not merely to reach high heat, but to maintain a consistent environment that allows the chemical processes to unfold predictably.
Precision Monitoring via Thermocouples
Platinum-rhodium thermocouples act as the system's nervous system, serving as high-precision sensors.
They monitor temperatures in real-time within the furnace. This allows operators to verify that the environment is holding steady at critical setpoints, specifically the deposition temperature of 1150°C.
Optimizing Chemical Kinetics
The interaction between the furnace's output and the thermocouple's feedback creates a closed control loop.
This coordination ensures that the chemical reduction reaction occurs strictly within the optimal kinetic range. By locking in these variables, the process avoids the irregularities that lead to poor coating adhesion or structural defects.
Critical Dependencies and Risks
While the equipment is robust, the process relies heavily on the exact calibration of these two components. Understanding the stakes of this relationship is key to process control.
The Cost of Thermal Drift
If the furnace fluctuates or the thermocouple provides inaccurate data, the system exits the optimal kinetic range.
This results in a failure to produce the desired alpha-phase tantalum. Without the correct phase formation, the coating will likely fail to meet industrial standards for density and purity.
Sensitivity to Setpoints
The process targets a specific deposition temperature of 1150°C for a reason.
Deviating from this precise thermal window compromises the chemical reduction. The system relies on the platinum-rhodium sensors to detect even minor variances that could alter the final material properties.
Ensuring Coating Integrity
To maximize the performance of your tantalum deposition process, focus on the interplay between heat generation and measurement.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure your thermocouples are calibrated to maintain the strict 1150°C setpoint required for high-purity results.
- If your primary focus is coating structure: Verify that the furnace can maintain a stable thermal field across the entire deposition chamber to guarantee dense, alpha-phase formation.
The reliability of your tantalum coating is a direct reflection of the stability and accuracy of your thermal control loop.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Tantalum Deposition | Critical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Furnace | Establishes stable thermal field | Enables predictable chemical reduction |
| Pt-Rh Thermocouple | Real-time high-precision sensing | Ensures adherence to 1150°C setpoint |
| Thermal Loop | Closed-loop control synchronization | Guarantees dense, alpha-phase formation |
| Process Window | Optimal kinetic range management | Prevents structural defects and impurities |
Master Your Chemical Vapor Deposition with KINTEK Precision
Don't let thermal drift compromise your material integrity. At KINTEK, we understand that high-purity tantalum coatings require uncompromising accuracy. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or industrial needs.
Our value to you:
- Precision Control: Optimized for critical setpoints like 1150°C.
- Reliability: Integrated with high-grade sensors for stable thermal fields.
- Expert Support: Solutions tailored to your specific chemical reduction processes.
Ready to elevate your deposition outcomes? Contact our technical experts today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Junyu Zhu, Haohong Jiang. Fabrication and mechanical properties of porous tantalum carbon composites by chemical vapor deposition. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86680-x
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are alloys used in electrical heating devices? Discover the Key to Durable, Efficient Heat Generation
- What safety measures are incorporated into heating elements? Ensure Reliable Protection for Your Applications
- How do high-precision thermocouples and closed-loop control systems influence nickel silicide film uniformity?
- What standard sizes are available for molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Find the Perfect Fit for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the advantages of using high-performance ceramic heaters for AgNP synthesis? Boost Efficiency and Precision
- What are the performance advantages of high-precision resistance heating systems? 100 K/s Heating for Hot Stamping
- What precautions should be taken when replacing SiC resistors? Ensure Safe, Long-Lasting Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















