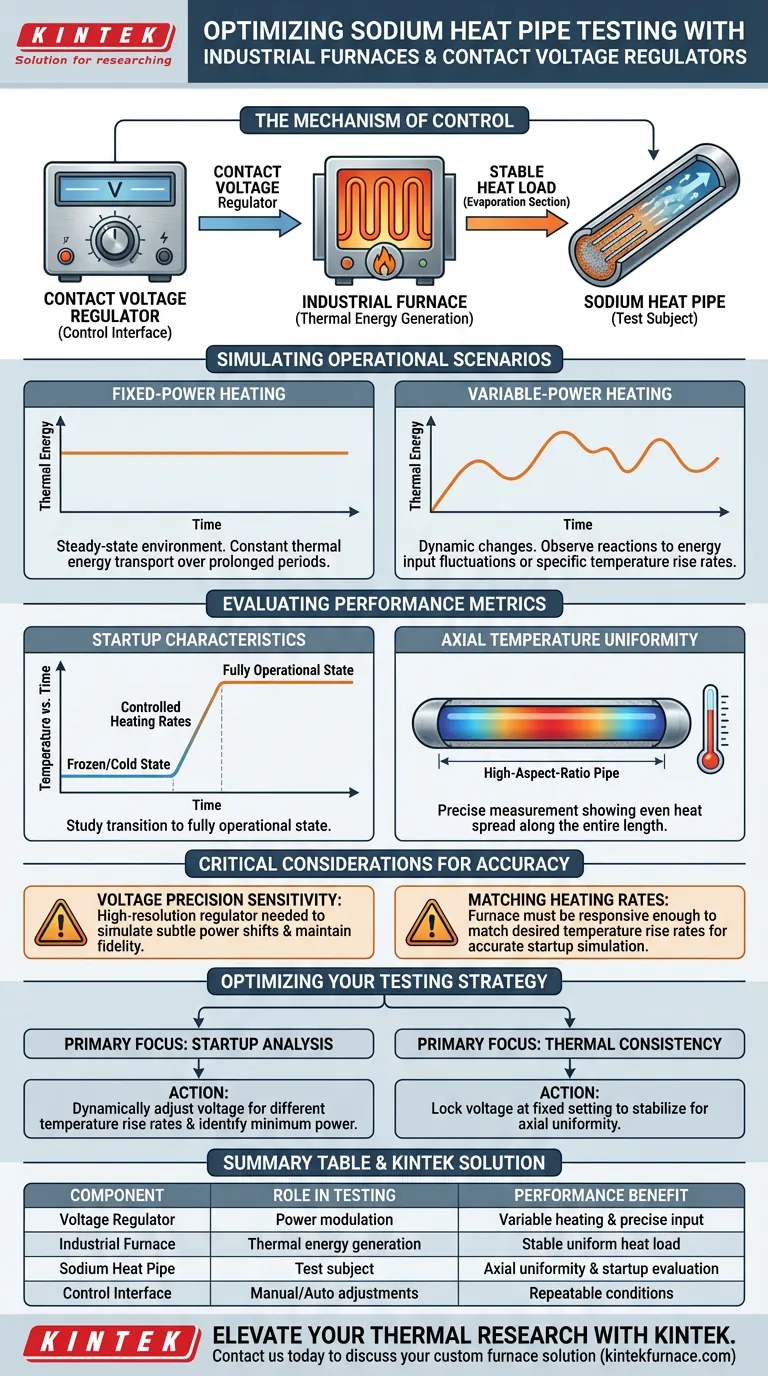
Industrial furnaces paired with contact voltage regulators function as the precise heat source system for testing sodium heat pipes. By converting adjustable electrical input into controlled thermal energy, this equipment combination applies a stable heat load to the pipe's evaporation section, enabling detailed performance analysis.
The core value of this setup lies in its ability to simulate diverse operating realities. By strictly modulating input voltage, researchers can replicate both fixed and fluctuating power conditions to evaluate how high-aspect-ratio pipes handle startup and thermal distribution.
The Mechanism of Control
Precise Power Regulation
The contact voltage regulator acts as the control interface for the experiment. By manually or automatically adjusting the input voltage, technical personnel can dictate the exact heating power the industrial furnace generates.
Stabilizing the Thermal Load
Consistency is critical for valid data. This setup ensures that the evaporation section of the sodium heat pipe receives a stable thermal load. This eliminates external variables, ensuring that any changes in temperature are due to the pipe's internal physics, not a fluctuating power source.
Simulating Operational Scenarios
Fixed-Power Heating
One of the primary testing modes enabled by this equipment is fixed-power heating. This simulates a steady-state environment where the heat pipe must transport a constant amount of thermal energy over a prolonged period.
Variable-Power Heating
Real-world applications often involve fluctuations. The voltage regulator allows for variable-power heating simulations. This lets engineers observe how the heat pipe reacts to dynamic changes in energy input or specific temperature rise rates.
Evaluating Performance Metrics
Analyzing Startup Characteristics
Sodium heat pipes operate at high temperatures and require a specific thermal threshold to function. The furnace and regulator setup allow researchers to study startup characteristics—specifically, how the pipe transitions from a frozen or cold state to a fully operational state under controlled heating rates.
Measuring Axial Temperature Uniformity
For high-aspect-ratio heat pipes (pipes that are long relative to their width), maintaining an even temperature is a challenge. This controlled heating environment permits the precise measurement of axial temperature uniformity, verifying that the pipe is spreading heat evenly along its entire length.
Critical Considerations for Testing Accuracy
Voltage Precision Sensitivity
The quality of the test data is directly tied to the resolution of the voltage regulator. If the regulator lacks fine-tuning capabilities, it may be impossible to simulate subtle power shifts, leading to a loss of fidelity in the performance data.
Matching Heating Rates
The furnace must be responsive enough to match the desired temperature rise rates. If the equipment lags behind the voltage adjustment, the simulation of rapid startup scenarios will be inaccurate, potentially masking issues with the heat pipe's response time.
Optimizing Your Testing Strategy
To maximize the value of your industrial furnace and regulator setup, align your control method with your specific data requirements.
- If your primary focus is Startup Analysis: Dynamically adjust the voltage to simulate different temperature rise rates, identifying the minimum power required to initiate heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Consistency: Lock the voltage at a fixed setting to maintain a constant thermal load, allowing the system to stabilize for accurate axial uniformity measurements.
Success in sodium heat pipe testing relies on using the voltage regulator not just as a switch, but as a precision instrument to model real-world thermal demands.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Testing | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Regulator | Power modulation & control | Enables variable heating rates and precise power input simulation. |
| Industrial Furnace | Thermal energy generation | Provides a stable, uniform heat load to the pipe's evaporation section. |
| Sodium Heat Pipe | Test subject | Evaluated for axial temperature uniformity and startup characteristics. |
| Control Interface | Manual/Auto adjustments | Ensures repeatable testing conditions for both fixed and dynamic power. |
Elevate Your Thermal Research with KINTEK
Precise heat pipe testing requires uncompromising thermal control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside a full range of lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Whether you are analyzing startup characteristics or axial uniformity, our precision-engineered systems provide the stability your data demands. Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace solution and see how KINTEK empowers your path to innovation.
Visual Guide
References
- Shuaijie Sha, Junjie Wang. Experimental and numerical simulation study of sodium heat pipe with large aspect ratio. DOI: 10.2298/tsci231030059s
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the main features and advantages of a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Achieve Superior Material Quality & Efficiency
- Why are vacuum furnaces important in aerospace? Essential for High-Strength, Pure Components
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between an atmosphere furnace and a vacuum furnace? Choose the Right Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- What are the applications of furnace brazing in the energy and power generation sector? Achieve Superior Joint Integrity for Critical Components
- What are the technical advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for electrocatalyst powders? Pt/HCCP Drying Guide
- Why is a vacuum furnace beneficial for applications requiring high purity? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the significance of the vacuum environment for sintering stainless steel? Unlock High-Density Purity



















