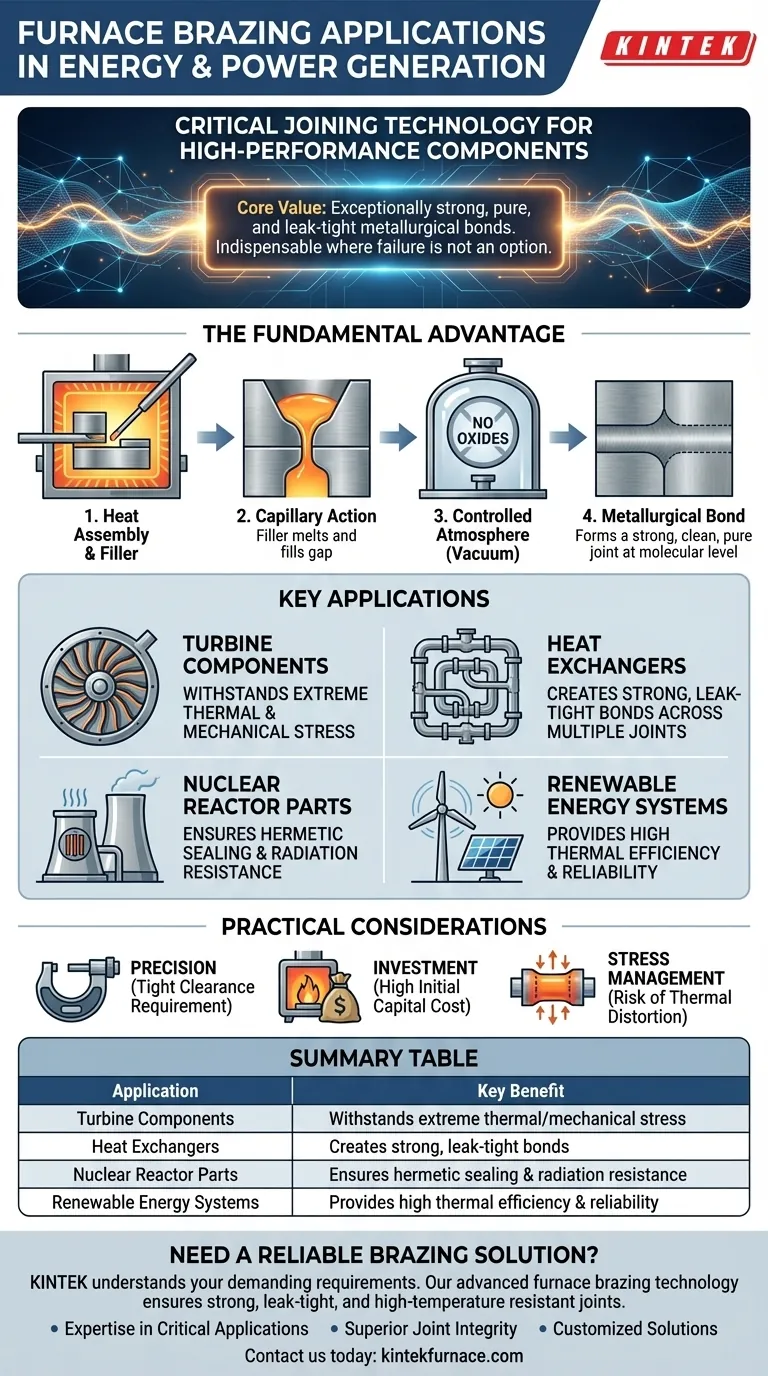
In the energy and power generation sector, furnace brazing is a critical joining technology used to manufacture high-performance components. Its applications range from creating turbine blades and heat exchangers in traditional power plants to assembling parts for nuclear reactors and renewable energy systems like solar panels and wind turbines.
The core value of furnace brazing lies in its ability to create exceptionally strong, pure, and leak-tight metallurgical bonds. This makes it indispensable for energy applications where component failure under extreme temperature, pressure, and corrosive conditions is not an option.

The Fundamental Advantage of Furnace Brazing
Furnace brazing is more than just a method for sticking metal parts together; it's a sophisticated process that creates a deep, reliable bond at the molecular level. Understanding how it works reveals why it's so trusted for critical applications.
How the Process Works
The core principle involves heating an assembly of closely fitted metal components within a controlled-atmosphere furnace. A filler metal, which has a lower melting point than the base components, is placed at the joint. As the furnace reaches the brazing temperature, the filler melts and is drawn into the gap between the parts through capillary action.
Creating a Metallurgical Bond
As the molten filler metal cools and solidifies, it doesn't just act as a glue. It interacts with the base metals, forming a new, continuous metallurgical bond. This results in a joint that is incredibly strong and often as robust as the parent materials themselves.
The Role of the Controlled Environment
Performing this process inside a vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace is crucial. This environment prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces, which would otherwise interfere with the bonding process. The result is an exceptionally clean, strong, and pure joint, free from the contaminants that could cause it to fail in service.
Key Applications in Energy and Power Generation
The unique properties of furnace-brazed joints make them ideal for some of the most demanding environments in the energy sector.
High-Performance Turbine Components
Turbine blades in power plants operate under immense thermal and mechanical stress. Furnace brazing is used to join complex blade assemblies and internal cooling channels, ensuring they can withstand extreme temperatures and rotational forces without failing.
Efficient Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers rely on a vast network of joints to transfer thermal energy effectively. Furnace brazing creates strong, leak-tight bonds across hundreds or thousands of joints simultaneously, ensuring the integrity and efficiency required for power generation systems.
Nuclear Reactor Components
In the nuclear industry, reliability and safety are paramount. Furnace brazing is used to fabricate components that require absolute hermetic sealing and high resistance to corrosion and radiation, ensuring the long-term, safe operation of the reactor.
Renewable Energy Systems
The process is also vital for renewables. It is used in manufacturing components for the cooling systems of high-power wind turbines and in assembling parts for concentrating solar power systems, where high thermal efficiency is essential.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While powerful, furnace brazing is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on understanding its specific requirements and limitations.
The Requirement for Precision
For capillary action to work effectively, the components being joined must have a very tight and consistent clearance. This demands high-precision manufacturing of the individual parts before they enter the furnace.
High Initial Investment
Industrial brazing furnaces, especially vacuum furnaces, represent a significant capital investment. This makes the process best suited for high-value, critical components where the cost is justified by the required performance and reliability.
Thermal Stress Management
Because the entire assembly is heated to a uniform temperature, there is a risk of thermal distortion, especially with complex geometries or dissimilar materials. Proper design and fixturing are essential to manage these stresses and maintain dimensional accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting furnace brazing is a decision driven by the non-negotiable requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is ultimate joint integrity and reliability: Furnace brazing is the superior choice for mission-critical parts where failure could have catastrophic consequences.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: This process creates joints that maintain their strength and stability in extreme thermal environments found in turbines and reactors.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, leak-tight assemblies: Furnace brazing excels at bonding intricate, multi-joint components like heat exchangers in a single, controlled operation.
Ultimately, furnace brazing is a cornerstone technology that enables the construction of safe, efficient, and durable energy infrastructure.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit of Furnace Brazing |
|---|---|
| Turbine Components | Withstands extreme thermal and mechanical stress |
| Heat Exchangers | Creates strong, leak-tight bonds across multiple joints |
| Nuclear Reactor Parts | Ensures hermetic sealing and radiation resistance |
| Renewable Energy Systems | Provides high thermal efficiency and reliability |
Need a reliable brazing solution for your critical energy components?
At KINTEK, we understand the demanding requirements of the energy and power generation sector. Our advanced furnace brazing technology ensures the strong, leak-tight, and high-temperature resistant joints your applications demand.
Why choose KINTEK for your brazing needs?
- Expertise in Critical Applications: We specialize in brazing solutions for turbines, heat exchangers, nuclear components, and renewable energy systems.
- Superior Joint Integrity: Our controlled-atmosphere and vacuum furnaces create metallurgical bonds that withstand extreme conditions.
- Customized Solutions: Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for your unique brazing requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our furnace brazing expertise can enhance the reliability and performance of your energy components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















