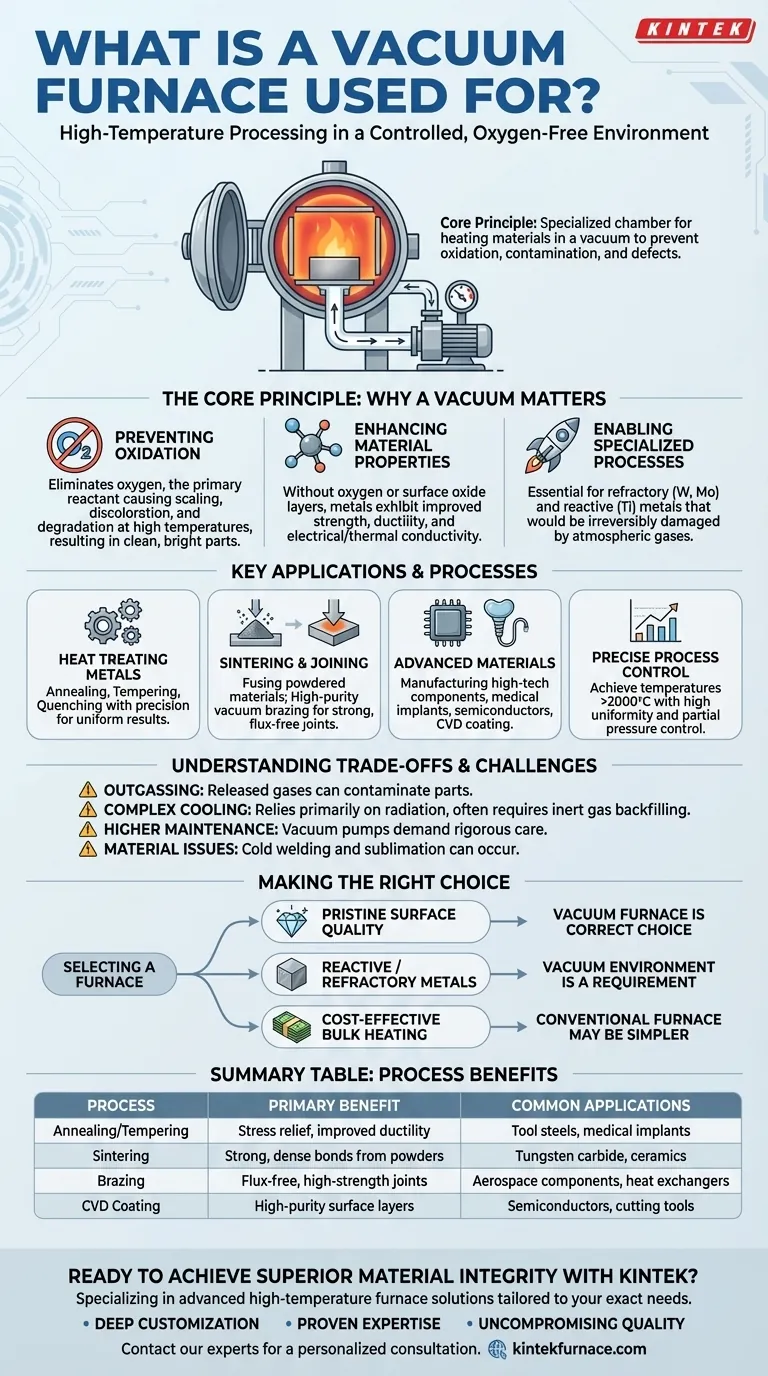
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized chamber used to heat materials to very high temperatures in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. By removing air and other gases, it enables critical industrial processes like annealing, sintering, and heat treating without causing the oxidation, contamination, or surface defects that would occur in a conventional furnace.
The essential purpose of a vacuum furnace is not simply to heat materials, but to do so in a chemically pure environment. This prevention of unwanted reactions is the key to achieving superior material properties, pristine surface finishes, and high-performance components that are impossible to create otherwise.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum Matters
At the high temperatures required for metallurgy and materials science, most elements become highly reactive. The oxygen that makes up 21% of our atmosphere will aggressively bond with hot metal surfaces, forming oxides that degrade the material's integrity and finish.
Preventing Oxidation
The primary function of the vacuum is to remove oxygen. By pumping the chamber down to a low pressure, we eliminate the primary reactant responsible for scaling, discoloration, and contamination, resulting in a clean, bright part.
Enhancing Material Properties
This clean processing environment directly enhances a material's final characteristics. Without interstitial oxygen atoms or surface oxide layers, metals and alloys exhibit improved mechanical strength, ductility, and electrical and thermal conductivity.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain advanced materials, like refractory metals (tungsten, molybdenum) or reactive metals (titanium), can only be processed in a vacuum. Any presence of atmospheric gases at high temperatures would irreversibly damage them.
Key Applications and Processes
Vacuum furnaces are not a single-use tool but a versatile platform for a range of thermal processes, each benefiting from the controlled atmosphere.
Heat Treating Metals and Alloys
This is the most common use. Processes like annealing (softening), tempering (toughening), and quenching (hardening) can be performed with exceptional precision, ensuring uniform results throughout the workpiece.
Sintering and Joining
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials (like tungsten carbide) into a solid mass using heat. A vacuum prevents oxidation of the fine powders, ensuring strong, dense bonds. Similarly, high-purity vacuum brazing creates strong joints without the need for flux, which can leave corrosive residues.
Advanced Materials Processing
The vacuum furnace is critical in manufacturing high-tech components. It is used for producing medical implants, treating semiconductor materials, and in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where gases react on a heated surface to form a solid coating.
Precise Process Control
Modern vacuum furnace systems offer exceptional control over the entire thermal cycle. They can achieve temperatures exceeding 2000°C (3632°F) with uniformity of just a few degrees, and allow for partial pressure control—the intentional introduction of a specific gas to achieve a desired effect, such as in vacuum carburizing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, the vacuum environment introduces unique complexities that are not present in conventional atmosphere furnaces.
Outgassing and Contamination
Ironically, the vacuum itself can cause contamination. Outgassing occurs when gases trapped within the workpiece or on the chamber walls are released as the pressure drops, potentially contaminating the very part you are trying to keep clean.
Complex Cooling Control
In a normal furnace, gas is a medium for heat transfer. In a vacuum, there are very few gas particles, so cooling relies primarily on radiation. This makes rapid cooling (quenching) more difficult and often requires backfilling the chamber with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to increase the cooling rate.
Higher Maintenance Requirements
Vacuum systems, particularly the pumps that create the low-pressure environment, demand more rigorous and specialized maintenance than their atmospheric counterparts. Leaks or pump failures can compromise an entire production run.
Material-Specific Issues
Certain materials can exhibit strange behaviors in a vacuum. For example, cold welding can occur where two perfectly clean metal surfaces spontaneously fuse together on contact, and some elements may sublimate (turn directly from a solid to a gas) at high temperatures and low pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision based on the required outcome. Consider the following guidelines to determine if it is the appropriate tool for your application.
- If your primary focus is pristine surface quality and material purity: A vacuum furnace is the correct and often only choice for a bright, uncontaminated finish.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or refractory metals like titanium or molybdenum: A vacuum environment is a strict requirement to prevent catastrophic material degradation.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk heating where surface oxidation can be removed in a later step: A conventional atmosphere furnace may be a more economical and simpler solution.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize final material integrity over operational simplicity.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing/Tempering | Stress relief, improved ductility | Tool steels, medical implants |
| Sintering | Strong, dense bonds from powders | Tungsten carbide, ceramics |
| Brazing | Flux-free, high-strength joints | Aerospace components, heat exchangers |
| CVD Coating | High-purity surface layers | Semiconductors, cutting tools |
Ready to achieve superior material integrity with a vacuum furnace?
Your application demands precision, purity, and performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in designing and manufacturing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your exact needs.
Why choose KINTEK for your vacuum furnace needs?
- Deep Customization: We understand that every lab and process is unique. Leveraging our exceptional in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities, we go beyond standard models to deliver vacuum furnaces that precisely match your thermal profile, chamber size, and process control requirements.
- Proven Expertise: Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is trusted by leading manufacturers in aerospace, medical, and semiconductor industries for critical thermal processing.
- Uncompromising Quality: From preventing oxidation for a bright finish to enabling the sintering of advanced alloys, our furnaces are engineered for reliability and superior results.
Let's discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can solve your high-temperature processing challenges.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and see how our deep customization capability can work for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















