In modern industrial applications, box-type high-temperature resistance furnaces address environmental and energy concerns through a dual approach. First, their design prioritizes energy efficiency by incorporating advanced insulation and precise control systems to minimize heat loss and power consumption. Second, they are instrumental in a range of direct environmental applications, from creating materials for new energy technologies to neutralizing hazardous waste.
The true value of these furnaces lies not just in their inherent efficiency, but in their role as an enabling technology for critical sustainable processes, including battery material synthesis and waste remediation.

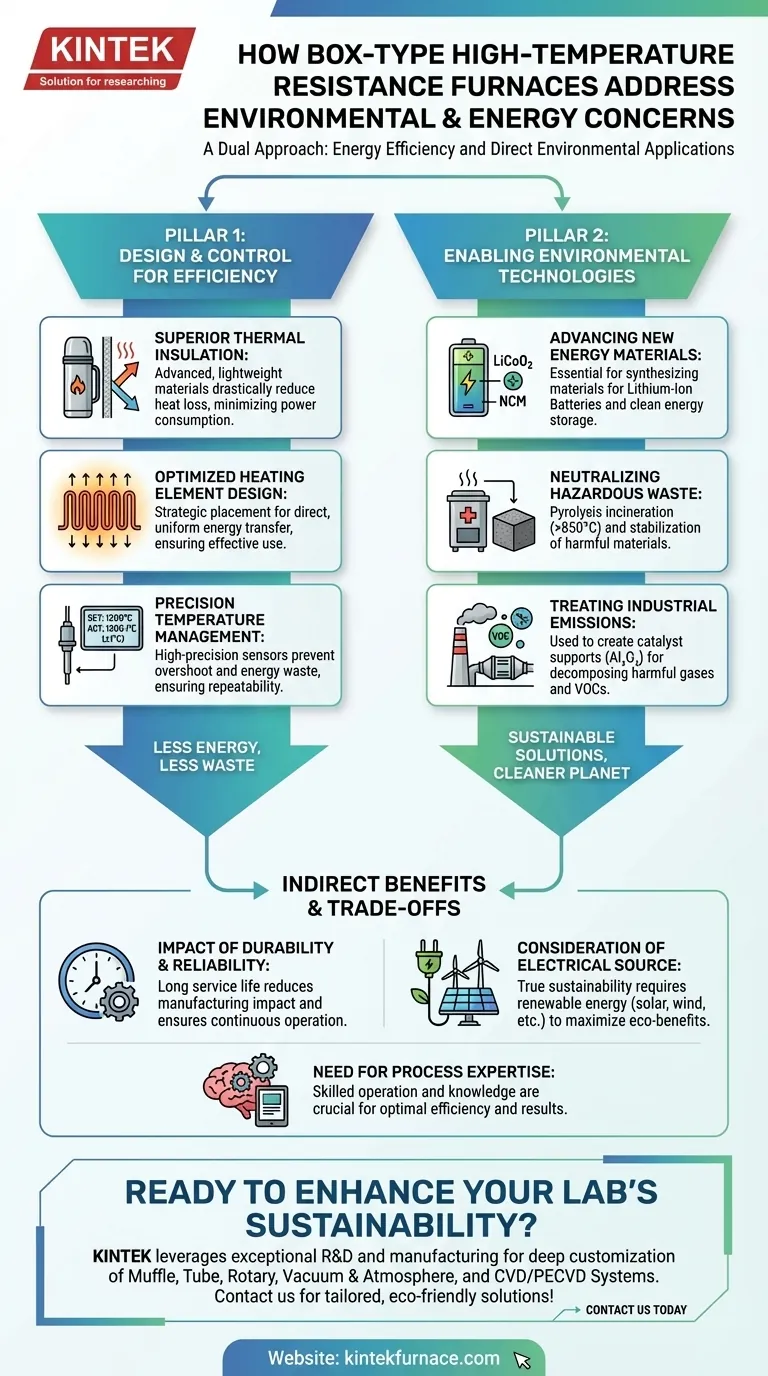
The Two Pillars of Efficiency: Design and Control
The primary method for reducing a furnace's environmental footprint is to minimize the energy it consumes. Modern designs achieve this through sophisticated engineering of the furnace body and its control systems.
Superior Thermal Insulation
The furnace chamber is constructed with high-efficiency, lightweight insulation materials.
These materials act like a high-performance thermos, drastically reducing heat loss to the surrounding environment. By keeping the thermal energy contained, the furnace requires significantly less power to maintain its target temperature.
Optimized Heating Element Design
The layout and quality of the heating elements are critical for energy utilization.
By optimizing their placement, energy is transferred to the workload more directly and uniformly. This ensures that every kilowatt of energy is used effectively, reducing overall consumption and preventing wasted power.
Precision Temperature Management
Modern furnaces utilize high-precision temperature control systems with advanced sensors.
Achieving accuracy within ±1°C prevents the system from overshooting the setpoint, a common source of wasted energy. This precision also ensures process repeatability, reducing the material and energy waste associated with failed or inconsistent production runs.
Enabling Environmental Technologies and Waste Remediation
Beyond simply using less energy, these furnaces are a key tool for developing and implementing solutions to pressing environmental challenges. They provide the controlled, high-temperature environment necessary for specific chemical and physical transformations.
Advancing New Energy Materials
These furnaces are essential for synthesizing materials used in lithium-ion batteries.
Applications include the high-temperature synthesis of cathode materials like LiCoO₂ and NCM, as well as modifying anode materials like graphite. By enabling the production of these components, the furnaces directly support the growth of clean energy storage.
Neutralizing Hazardous Waste
High-temperature processes can effectively and safely dispose of harmful materials.
Pyrolysis incineration of medical waste at temperatures above 850°C ensures its complete and harmless destruction. Similarly, these furnaces are used for the stabilization of fly ash, melting it to trap heavy metals within a stable, glassy matrix, preventing them from leaching into the environment.
Treating Industrial Emissions
The furnaces play a role in combating air pollution by helping create catalytic converters.
They are used to prepare catalyst supports, such as Al₂O₃, which are then used to create catalysts that decompose Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and other harmful gases in industrial waste streams.
Understanding the Indirect Benefits and Trade-offs
While the direct efficiency and application benefits are clear, a full assessment requires looking at the entire lifecycle and operational context.
The Impact of Durability and Reliability
The use of high-quality heating elements and oxidation-resistant insulation results in a long service life.
A durable furnace reduces the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and transporting replacement units. Furthermore, its stability allows for continuous operation, avoiding the energy-intensive process of shutting down and reheating a production line.
The Consideration of Electrical Source
A resistance furnace's primary energy input is electricity. Its "green" credentials are therefore directly tied to the source of that power.
If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, the furnace's environmental impact is merely shifted upstream. Its true potential for sustainability is only fully realized when powered by renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydroelectric power.
The Need for Process Expertise
While modern interfaces are user-friendly, achieving optimal efficiency and successful environmental applications requires deep process knowledge.
Incorrectly configured heating cycles or improper material loading can negate the furnace's inherent efficiency, leading to wasted energy and failed batches. Maximizing its environmental benefits depends on skilled operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage a box-type resistance furnace effectively, align your selection and operational strategy with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational energy costs: Prioritize models with the highest quality insulation, multi-zone temperature control, and a reputation for thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is developing green technologies: Select a furnace with high-precision temperature control (e.g., ±1°C or better) and a chamber atmosphere that is compatible with your material synthesis goals (e.g., battery cathodes, catalysts).
- If your primary focus is waste remediation: Ensure the furnace can reliably reach and sustain the required temperatures (e.g., >850°C for pyrolysis) and is constructed from materials that can withstand potentially corrosive byproducts.
Ultimately, a modern box-type resistance furnace is more than a heating device; it is a critical tool for advancing sustainable industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Advanced insulation, optimized heating elements, precision control | Reduces power consumption and heat loss, lowers operational costs |
| Environmental Applications | Supports battery material synthesis, waste incineration, emission control | Enables sustainable processes, neutralizes hazards, reduces pollution |
| Durability & Reliability | High-quality materials, long service life | Minimizes replacement needs, ensures continuous operation, cuts lifecycle impact |
| Operational Considerations | Tied to electricity source, requires process expertise | Maximizes benefits with renewable energy and skilled use for optimal results |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for energy efficiency, new material development, or waste remediation. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals and deliver tailored, eco-friendly solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?



















