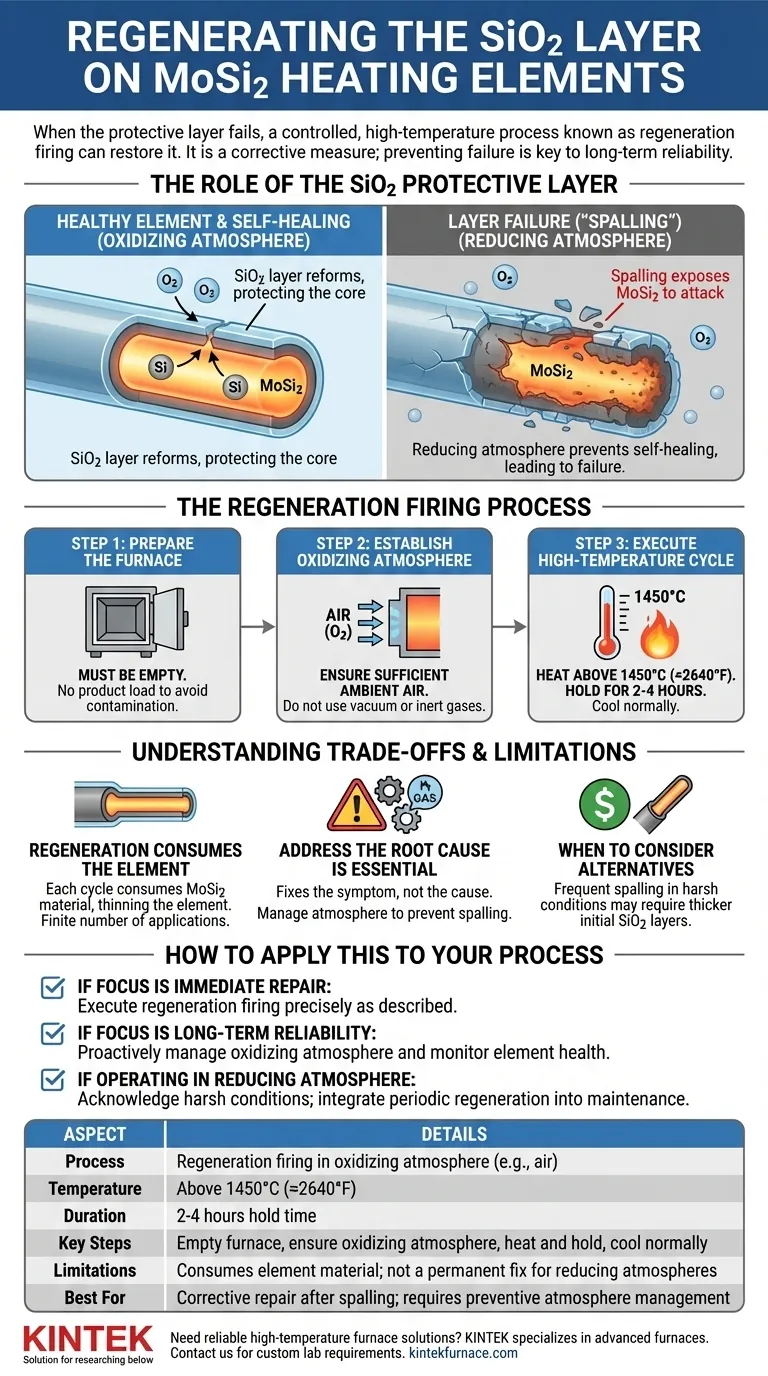
When the protective layer on your MoSi2 heating element fails, it is possible to restore it through a controlled, high-temperature process. This procedure, known as regeneration firing, involves heating the elements in an empty furnace to over 1450°C for several hours within an oxidizing atmosphere, such as air. This forces the underlying Molybdenum Disilicide to react with oxygen and form a new, stable layer of Silicon Dioxide (SiO2).
Regeneration is an effective repair for a damaged SiO2 layer, but it is a corrective measure. The true solution to long-term reliability lies in understanding the atmospheric conditions that cause the layer to fail and operating the furnace to prevent it.

The Role of the SiO2 Protective Layer
To properly manage your heating elements, you must first understand the function and vulnerability of their protective coating. This layer is not just an applied coating; it's a dynamic part of the element itself.
How the Layer Forms
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are designed to be self-healing. When heated in the presence of oxygen, the silicon in the element oxidizes to form a thin, non-porous, and self-healing layer of glassy Silicon Dioxide (SiO2). This passive layer protects the core element from further, destructive oxidation at extreme temperatures.
Why the Layer Fails ("Spalling")
The primary cause of failure, often called spalling or bursting, is operating the furnace in a reducing atmosphere. Without sufficient oxygen, the self-healing process cannot occur. Any existing cracks or defects in the SiO2 layer cannot be repaired, and the underlying MoSi2 becomes vulnerable to attack, leading to layer failure and eventual element burnout.
The Regeneration Firing Process
Regeneration is a straightforward but precise process. It forces the reformation of the protective SiO2 layer under ideal conditions.
Step 1: Prepare the Furnace
The furnace must be empty during this process. Running a regeneration cycle with a product load can lead to contamination and uneven heating, compromising both the product and the regeneration itself.
Step 2: Establish an Oxidizing Atmosphere
An oxidizing atmosphere is critical. For most applications, this simply means ensuring a sufficient supply of ambient air to the furnace chamber. Do not operate in a vacuum or with inert gases like nitrogen or argon during this cycle.
Step 3: Execute the High-Temperature Cycle
Heat the elements to a temperature above 1450°C (approximately 2640°F). Hold the furnace at this temperature for several hours (typically 2-4 hours is sufficient) to allow a new, dense, and uniform SiO2 layer to form across the entire surface of the elements. After the hold time, the furnace can be cooled down normally.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While effective, regeneration is not a perfect solution and has important implications for the element's lifespan.
Regeneration Consumes the Element
Each regeneration cycle consumes a small amount of the core MoSi2 material to create the new SiO2 layer. This means the element becomes slightly thinner with each cycle. It is a process with a finite number of applications before the element's performance is degraded.
Addressing the Root Cause is Essential
Regeneration fixes the symptom, not the cause. If your industrial process requires a reducing atmosphere, you must accept that periodic regeneration will be a necessary part of your maintenance schedule. Failure to do so will result in premature element failure.
When to Consider Alternatives
If spalling is a frequent issue due to harsh operating conditions, regeneration may only be a temporary fix. In such cases, investing in elements manufactured with an initially thicker protective SiO2 layer may be a more cost-effective long-term solution.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your maintenance strategy should be guided by your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is immediate repair: Execute the regeneration firing process precisely as described, ensuring the furnace is empty and has an air atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Proactively manage your furnace atmosphere to be oxidizing whenever possible and monitor element health to schedule regeneration before a catastrophic failure occurs.
- If you must operate in a reducing atmosphere: Acknowledge this as a harsh condition for the elements and integrate periodic regeneration cycles into your standard preventive maintenance plan.
By understanding both the cure and the cause, you can ensure the maximum lifespan and performance of your heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Regeneration firing in oxidizing atmosphere (e.g., air) |
| Temperature | Above 1450°C (≈2640°F) |
| Duration | 2-4 hours hold time |
| Key Steps | Empty furnace, ensure oxidizing atmosphere, heat and hold, cool normally |
| Limitations | Consumes element material over time; not a permanent fix for reducing atmospheres |
| Best For | Corrective repair after spalling; requires preventive atmosphere management for longevity |
Need reliable high-temperature furnace solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique lab requirements, ensuring optimal performance and durability. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's efficiency and protect your investments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















