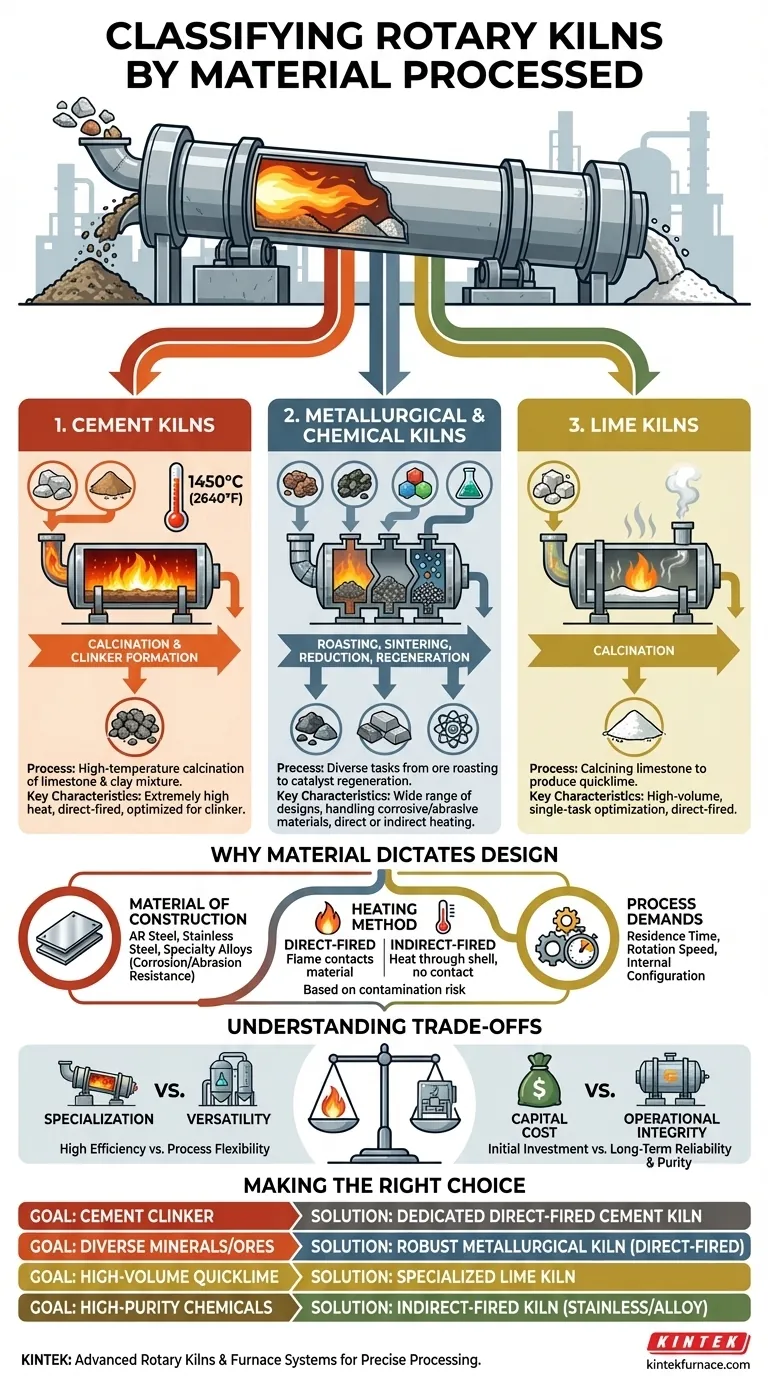
At its core, a rotary kiln’s classification is determined by the specific material it is designed to thermally process. The three primary categories are cement kilns, metallurgical chemical kilns, and lime kilns, each optimized for the unique physical and chemical reactions of its feedstock.
While the names seem simple, this classification goes beyond mere labels. It reflects fundamental differences in a kiln's construction, heating method, and operating temperature, all dictated by the specific transformation the material must undergo.

The Three Primary Classifications
Rotary kilns are versatile thermal processing machines, but for maximum efficiency and product quality, they are typically specialized. This specialization gives rise to three main types based on their industrial application.
Cement Kilns
A cement kiln is the heart of a cement plant. Its sole purpose is to heat a precise mixture of raw materials, like limestone and clay, to extremely high temperatures (around 1450°C or 2640°F).
This intense heat triggers a process called calcination and ultimately forms a new substance known as cement clinker. The entire design is optimized for this specific, high-temperature reaction.
Metallurgical & Chemical Kilns
This is a broad and diverse category covering numerous applications in the metallurgical and chemical industries. These kilns perform tasks like roasting and sintering ores, reducing metal oxides, or regenerating catalysts.
Because the processes are so varied, these kilns see the widest range of designs. A kiln for roasting a corrosive ore will be built very differently from one used for activating carbon.
Lime Kilns
As the name implies, a lime kiln is built for one primary task: calcining limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce quicklime (calcium oxide).
While this is also a form of calcination, the process and temperature requirements are distinct from cement production. These kilns are highly optimized for this single, high-volume transformation.
Why Material Dictates Kiln Design
The material being processed is the single most important factor influencing a kiln's design. The need to handle specific temperatures, chemical reactions, and physical characteristics drives every engineering decision.
Material of Construction
The kiln's shell and internal components must withstand the process environment. Abrasive materials require abrasion-resistant (AR) steel, while corrosive chemicals or high-purity applications necessitate stainless steel or other specialty alloys.
Heating Method (Direct vs. Indirect)
The heating method is chosen based on whether the material can come into contact with combustion byproducts.
Direct-fired kilns are most common, where a flame and hot gas flow directly through the kiln with the material. This is efficient for robust materials like cement and lime.
Indirect-fired kilns heat the material from the outside of the rotating shell. This is critical when the material must not be contaminated by flue gas, a common requirement in specialty chemical and food-grade applications.
Process Demands
The physical and chemical changes the material undergoes dictate the kiln's internal configuration, length, diameter, and rotation speed. These factors control residence time—how long the material spends in the kiln—which is critical for ensuring a complete reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or designing a rotary kiln involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to a successful project.
Specialization vs. Versatility
A highly specialized kiln, such as a cement kiln, is incredibly efficient for its intended task. However, it lacks the flexibility to process other materials effectively.
A general-purpose chemical kiln offers more versatility but may not achieve the same peak efficiency for any single process as a dedicated unit would.
Capital Cost vs. Operational Integrity
Building a kiln with specialty alloys to handle a corrosive material significantly increases the initial capital cost.
However, this investment prevents premature failure, reduces costly downtime, and ensures product purity, leading to lower long-term operational costs and a more reliable process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your end product and process requirements are the definitive guide for kiln selection.
- If your primary focus is producing cement clinker: You need a dedicated, direct-fired cement kiln designed to handle extremely high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse minerals or ores: A robust metallurgical kiln, likely made of carbon or AR steel and direct-fired, is the standard choice.
- If your primary focus is producing high-volume quicklime: A specialized lime kiln is the most efficient and cost-effective solution for calcining limestone.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or sensitive chemicals: An indirect-fired kiln, often constructed from stainless steel or specialty alloys, is essential to prevent contamination.
Understanding that a kiln is a purpose-built reactor, not just a heater, is the first step toward mastering your thermal processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Primary Material Processed | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cement Kilns | Limestone, clay for cement clinker | High temperatures (~1450°C), direct-fired, optimized for calcination |
| Metallurgical & Chemical Kilns | Ores, chemicals for roasting, reduction | Diverse designs, abrasion/corrosion-resistant materials, wide temperature range |
| Lime Kilns | Limestone for quicklime production | Specialized for calcination, high-volume, direct-fired |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced rotary kilns and other furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise performance for cement, metallurgical, lime, and chemical processing. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processing efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained



















